SpringBoot学习笔记
一.简介
1.1优点
image-20200427162910483
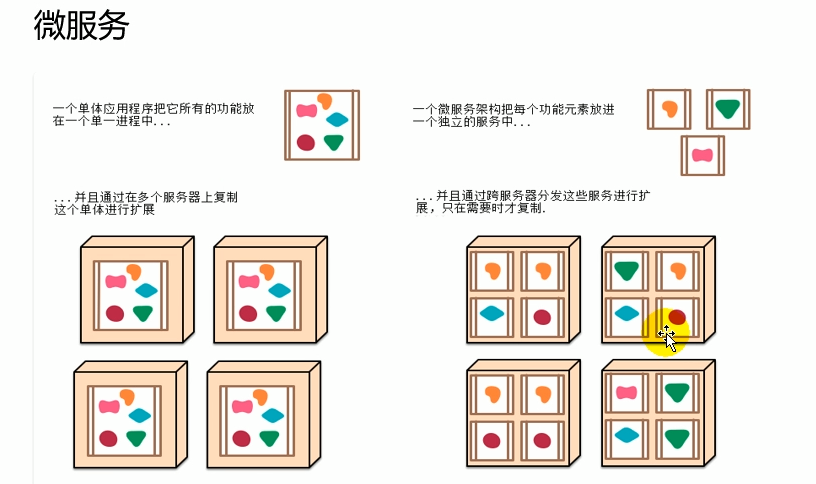
1.2微服务
微服务:架构风格
一个应用应该是一个小型服务,可以通过http的方式进行互通。
每一个功能元素最终都是一个可独立替换和独立升级的软件单元。
1.3HelloWorld
@SpringBootApplication !!!public class HelloWorld {public static void main (String[] args) {
@Controller public class HelloController {@ResponseBody @RequestMapping("/hello") public String Hello () {return "hello" ;
点击运行main方法即可。非常便捷
1.4HelloWorld分析
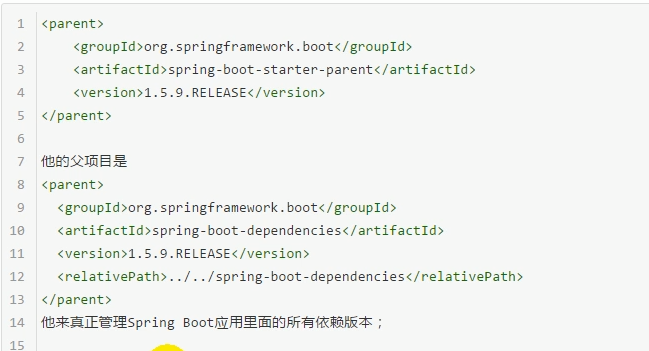
1.pom.xml
父项目
image-20200518111743445
SpringBoot的版本仲裁中心,以后导入依赖默认不需要写版本。(Springboot没有的版本号需要导入)
2.导入的依赖
<dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId > <version > 2.2.7.RELEASE</version > </dependency >
spring-boot-starter -web:场景启动器,
导入了web模块正常运行所依赖的组件
SpringBoot将所有功能场景都抽取出来,做成一个个的starters(启动器)
,只要在项目里引用这些starter场景
所有相关依赖都会被导入进来。
1.5@SpringBootApplication
@SpringBootApplication说明这个类是SpringBoot的zhu配置类 ,运行此类的main方法启动Springboot
@Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @SpringBootConfiguration @EnableAutoConfiguration @ComponentScan( excludeFilters = {@Filter( type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = {TypeExcludeFilter.class} ), @Filter( type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = {AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class} )} )
@SpringBootConfiguration
Spring中@Configuration配置类上标注注解
@RestController @Controller +@ResponseBody ,后面的所有方法都不需要写@ResponseBody
二、SpringBoot配置
2.1配置文件
Springboot使用全局配置文件,配置文件名是固定的
application.properties
application.yml
配置文件作用:修改Springboot自动配置的默认值。
image-20200518153028296
2.2yaml语法
2.2.1基本语法
2.2.2值的写法
字面量:普通的值(数字,字符串,布尔)
k: v:直接写
字符串不用加单引号或双引号
“”:不会转义字符串里的特殊字符 如”“会输出换行
‘’:会转义特殊字符,如”“会输出
对象、Map(属性和值)
k: v
Person: lastName:zhangsan age:20
注意缩进
数组(List、Set)
<dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId > <version > 2.1.6.RELEASE</version > <optional > true</optional > </dependency >
person: !!小写 Name: 张三 age: 18 Job: 程序员
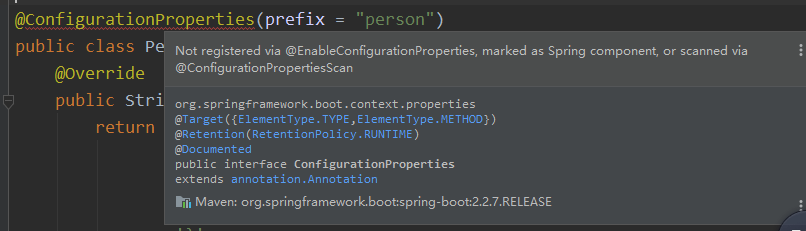
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person") public class Person {
出错:
image-20200518160306850
需要将其加入容器中才可以识别,添加@Component
2.2.3@Value和@ConfigurationProperties区别
功能
批量注入配置文件的属性
一个一个注入
松散绑定(松散语法)
支持(配置文件中last-name能映射到lastName)
不支持
SpEL
不支持
支持
JSR303数据校验
支持(@Validated校验属性的格式如 @Email )
不支持
复杂类型封装
支持(map,list)
不支持
如果说,我们只是在某个业务逻辑中需要获取一下配置文件中的某项值,使用@Value
;
如果说,我们专门编写了一个javaBean来和配置文件进行映射,我们就直接使用@ConfigurationProperties
; |
2.2.4@PropertySource,@ImportResource ,@Bean
@PropertySource
加载指定的配置文件
@PropertySource (value={classpath:person.properties}) @ImportResource 导入Spring
的配置文件让配置文件里的内容生效
image-20200702162938174
标注在主配置类上
SpringBoot中没有Spring 的配置文件,
如果导入容器配置文件内容不会自动识别,使用@ImportResource使配置文件生效
@Bean 添加组件
SpringBoot推荐使用全注解的方式
@Configuration public class MyAppConfig {@Bean public HelloService helloService () {"添加组件" );return new HelloService ();
2.2.5配置文件占位符
${random.value},${random.int},${random.long} ${random.int(10)},${random.int[1024,65536]}
person.last-name =张三${random.uuid} person.dog.name =${person.last-name:李四}_dog
2.2.6Profile多环境支持
编写配置文件时可以是application-{profile}.properties/yml
server: port: 8090 spring: profiles: active: dev --- server: port: 8091 spring: profiles: dev --- server: port: 8092 spring: profiles: prod
3.激活指定profile
1.使用多文件时在主配置文件指定spring-profiles-active=dev
2.命令行
program arguments:--spring-profiles-active=dev
3.虚拟机参数
VM options:-Dspring-profiles-active=dev
2.2.7配置文件加载位置
SpringBoot会扫面以下位置的application.properties或者application.yml作为默认配置文件
-file:.config
-file:./
-classpath:/config/
-classpath:/
优先级由高到低,高优先级的配置会覆盖低优先级的配置
互补配置:高优先级有的用高优先级,高优先级没有的用其他优先级的。
通过--Spring.config.location=G:/application.properties形成默认配置文件位置
项目打包好以后,我们可以使用命令行参数的形式,启动项目的时候来指定配置文件的新位置 ;指定配置文件和默
认加载的这些配置文件共同起作用形成互补配置。从而不需要重新打包
2.2.8外部配置加载顺序
Springboot也可以从以下位置加载配置,优先级从高到低
image-20200702174031306
6,7,8,9
由jar包外向jar包内寻找,优先加载带profile的,再加载不带profile的
2.2.9自动配置原理*
Springboot启动时加载主配置类,开启自动配置功能@EnableAutoConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
)利用AutoConfigurationImportSelector给容器中导入组件
可以查看selectImports()内容
List configurations =
getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata,atributes);获取候选
的配置
SpringFactoriesLoader . loadF actoryNames ()
总结:将类路径下META-INF/spring.factories
里面配置的所有EnableAutoConfiguration的值加入到了容器中;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer =\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.logging.ConditionEvaluationReportLoggingListener org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener =\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.BackgroundPreinitializer org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportListener =\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionEvaluationReportAutoConfigurationImportListener org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportFilter =\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnBeanCondition,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnWebApplicationCondition org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration =\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.BatchAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cassandra.CassandraAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.ConfigurationPropertiesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.LifecycleAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.MessageSourceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.couchbase.CouchbaseAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.dao.PersistenceExceptionTranslationAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ReactiveElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ReactiveElasticsearchRestClientAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jdbc.JdbcRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jpa.JpaRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.ldap.LdapRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.solr.SolrRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.r2dbc.R2dbcDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.r2dbc.R2dbcRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.r2dbc.R2dbcTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisReactiveAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.rest.RepositoryRestMvcAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.web.SpringDataWebAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRestClientAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.flyway.FlywayAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.gson.GsonAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.h2.H2ConsoleAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hateoas.HypermediaAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastJpaDependencyAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpMessageConvertersAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.codec.CodecsAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.influx.InfluxDbAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.info.ProjectInfoAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.integration.IntegrationAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JndiDataSourceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.XADataSourceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JmsAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jmx.JmxAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JndiConnectionFactoryAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.activemq.ActiveMQAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.artemis.ArtemisAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jersey.JerseyAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jooq.JooqAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jsonb.JsonbAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.kafka.KafkaAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.availability.ApplicationAvailabilityAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.embedded.EmbeddedLdapAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.LdapAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.liquibase.LiquibaseAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderValidatorAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.embedded.EmbeddedMongoAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoReactiveAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.quartz.QuartzAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.r2dbc.R2dbcAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketRequesterAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketServerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketStrategiesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.UserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityFilterAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveSecurityAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveUserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.rsocket.RSocketSecurityAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.saml2.Saml2RelyingPartyAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.sendgrid.SendGridAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.session.SessionAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.servlet.OAuth2ClientAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.reactive.ReactiveOAuth2ClientAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.resource.servlet.OAuth2ResourceServerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.resource.reactive.ReactiveOAuth2ResourceServerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.solr.SolrAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskSchedulingAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.jta.JtaAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.validation.ValidationAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.client.RestTemplateAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.embedded.EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.ReactiveWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.WebFluxAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.error.ErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.ClientHttpConnectorAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.WebClientAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.MultipartAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.reactive.WebSocketReactiveAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketServletAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.WebServicesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.client.WebServiceTemplateAutoConfiguration org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzer =\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.diagnostics.analyzer.NoSuchBeanDefinitionFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.flyway.FlywayMigrationScriptMissingFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceBeanCreationFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.HikariDriverConfigurationFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.r2dbc.ConnectionFactoryBeanCreationFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.session.NonUniqueSessionRepositoryFailureAnalyzer org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.template.TemplateAvailabilityProvider =\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerTemplateAvailabilityProvider,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheTemplateAvailabilityProvider,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAvailabilityProvider,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafTemplateAvailabilityProvider,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.JspTemplateAvailabilityProvider
每一个这样的xxxAutoConfiguration类都是容器中的一个组件,都加入到容器中;用他们来做自动配置;
每一个自动配置类进行自动配置
以HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration 为例解释自动配置原理
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) @EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class) @ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = ConditionalOnWebApplication.Type.SERVLET) @ConditionalOnClass(CharacterEncodingFilter.class) @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "server.servlet.encoding", value = "enabled", matchIfMissing = true) public class HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration {
所有配置文件中能配置的属性都是在xxxProperties类中封装着,配置文件能配置什么就可以参照某个功能对应的这个属性类
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "server", ignoreUnknownFields = true) public class ServerProperties {
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration {private final Encoding properties; public HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration (ServerProperties properties) {this .properties = properties.getServlet().getEncoding();@Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter () {CharacterEncodingFilter filter = new OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter ();this .properties.getCharset().name());this .properties.shouldForce(Encoding.Type.REQUEST));this .properties.shouldForce(Encoding.Type.RESPONSE));return filter;
精髓:
SpringBoot启动会加载大量的配置类 看我们需要的功能有没有SpringBoot默认写好的自动配置类 再看这个自动配置类中到底配置了哪些组件(如果有我们需要用的,我们就不需要再配置了) 给容器中自动配置类添加组件的时候会从Properties文件中获取某些属性,我们可以在配置文件中指定这些属性的值。
xxxAutoConfiguration:自动配置类
xxxProperties:封装配置文件中的
马士兵Springboot自动配置原理
image-20200710202024814
怎么看源码
1.8分靠猜测,2分去验证
2.不要一条路走到黑(不要一直点方法)
3.通过方法类的名字猜测具体的含义
4.多看方法类上的注释
5.记录对应的流程
6.遇到疑惑标记下来
Springboot启动流程
!!!load()
!!!@import解析工作 ,加载了哪些类,最重要的!
image-20200710203415702
image-20200710203520013
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 public ConfigurableApplicationContext run (String... args) {StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch ();ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null ;new ArrayList ();this .configureHeadlessProperty();SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = this .getRunListeners(args); try {ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments (args);ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this .prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments); this .configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);Banner printedBanner = this .printBanner(environment); this .createApplicationContext(); this .getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, new Class []{ConfigurableApplicationContext.class}, context); this .prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);this .refreshContext(context);this .afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);if (this .logStartupInfo) {new StartupInfoLogger (this .mainApplicationClass)).logStarted(this .getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);this .callRunners(context, applicationArguments);catch (Throwable var10) {this .handleRunFailure(context, var10, exceptionReporters, listeners);throw new IllegalStateException (var10);try {return context;catch (Throwable var9) {this .handleRunFailure(context, var9, exceptionReporters, (SpringApplicationRunListeners)null );throw new IllegalStateException (var9);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 private void prepareContext (ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {this .postProcessApplicationContext(context);this .applyInitializers(context);if (this .logStartupInfo) {this .logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null );this .logStartupProfileInfo(context);ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();"springApplicationArguments" , applicationArguments);if (printedBanner != null ) {"springBootBanner" , printedBanner);if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {this .allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);if (this .lazyInitialization) {new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor ());this .getAllSources(); "Sources must not be empty" );this .load(context, sources.toArray(new Object [0 ]));
private int load (Class<?> source) {if (this .isGroovyPresent() && BeanDefinitionLoader.GroovyBeanDefinitionSource.class.isAssignableFrom(source)) {GroovyBeanDefinitionSource loader = (BeanDefinitionLoader.GroovyBeanDefinitionSource)BeanUtils.instantiateClass(source, BeanDefinitionLoader.GroovyBeanDefinitionSource.class);this .load(loader);if (this .isComponent(source)) { this .annotatedReader.register(new Class []{source}); return 1 ;else {return 0 ;
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors (ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {this .getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean("loadTimeWeaver" )) {new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor (beanFactory));new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader (beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
public abstract class AnnotationConfigUtils {public static final String CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME = "org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor" ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 private void processImports (ConfigurationClass configClass, ConfigurationClassParser.SourceClass currentSourceClass, Collection<ConfigurationClassParser.SourceClass> importCandidates, Predicate<String> exclusionFilter, boolean checkForCircularImports) {if (!importCandidates.isEmpty()) {if (checkForCircularImports && this .isChainedImportOnStack(configClass)) {this .problemReporter.error(new ConfigurationClassParser .CircularImportProblem(configClass, this .importStack));else {this .importStack.push(configClass);try {Iterator var6 = importCandidates.iterator();while (var6.hasNext()) {SourceClass candidate = (ConfigurationClassParser.SourceClass)var6.next();if (candidate.isAssignable(ImportSelector.class)) {ImportSelector selector = (ImportSelector)ParserStrategyUtils.instantiateClass(candidateClass, ImportSelector.class, this .environment, this .resourceLoader, this .registry);if (selectorFilter != null ) {if (selector instanceof DeferredImportSelector) {this .deferredImportSelectorHandler.handle(configClass, (DeferredImportSelector)selector);else {this .asSourceClasses(importClassNames, exclusionFilter);this .processImports(configClass, currentSourceClass, importSourceClasses, exclusionFilter, false );else if (candidate.isAssignable(ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class)) {ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar registrar = (ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar)ParserStrategyUtils.instantiateClass(candidateClass, ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class, this .environment, this .resourceLoader, this .registry);else {this .importStack.registerImport(currentSourceClass.getMetadata(), candidate.getMetadata().getClassName());this .processConfigurationClass(candidate.asConfigClass(configClass), exclusionFilter);catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException var17) {throw var17;catch (Throwable var18) {throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException ("Failed to process import candidates for configuration class [" + configClass.getMetadata().getClassName() + "]" , var18);finally {this .importStack.pop();
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry (AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {return EMPTY_ENTRY;AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);return new AutoConfigurationEntry (configurations, exclusions);
tomcat启动
ServletWebConfigurationContext类中protected void onRefresh () {super .onRefresh();try {this .createWebServer(); catch (Throwable var2) {throw new ApplicationContextException ("Unable to start web server" , var2);
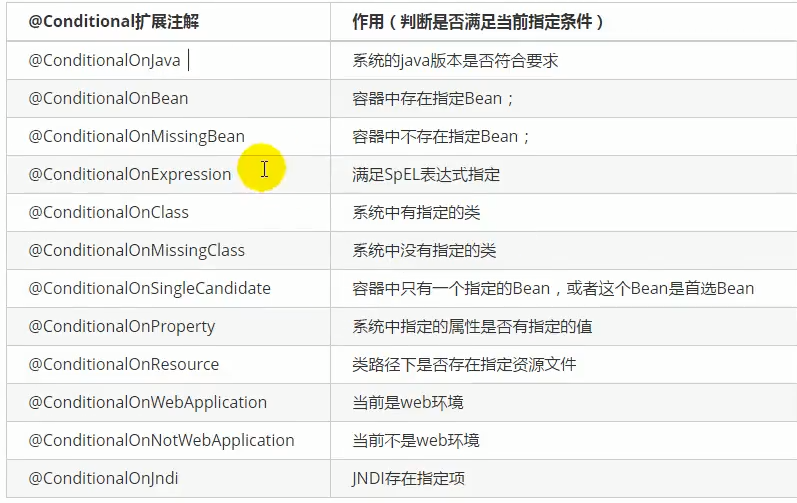
2.3.0 @Conditional与自动配置报告
@Conditional派生注解
作用:比如是@Conditional指定的条件成立,才会给容器中添加组件,配置类里面的内容才会生效。
image-20200703114148402
可以通过配置debug=true属性,来让控制台打印自动配置报告,可以知道配置了哪些类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 ============================EVALUATION REPORT = ===========================@ConditionalOnProperty (spring.aop.auto=true ) matched (OnPropertyCondition)@ConditionalOnMissingClass did not find unwanted class 'org.aspectj.weaver.Advice' (OnClassCondition)@ConditionalOnProperty (spring.aop.proxy-target-class=true ) matched (OnPropertyCondition)@ConditionalOnClass did not find required class 'javax.jms.ConnectionFactory' (OnClassCondition)
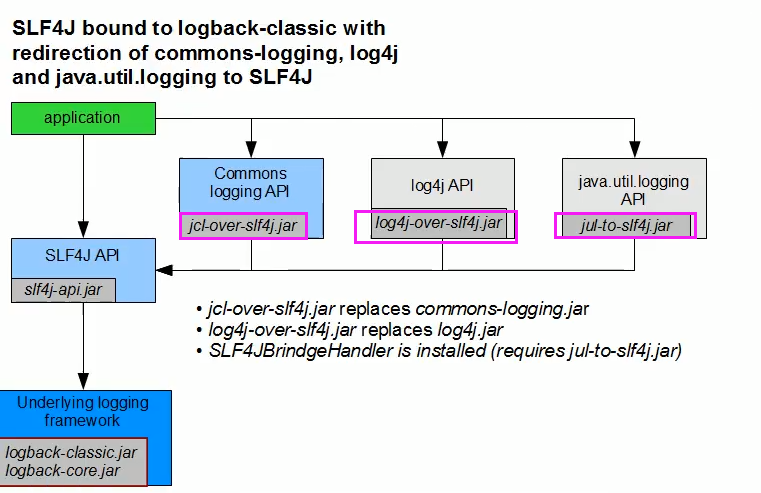
三、日志
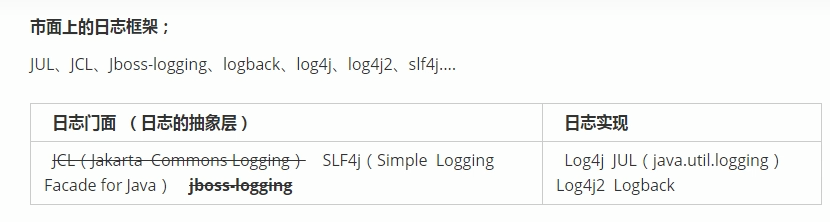
3.1日志框架
image-20200703161229074
左边选一个门面,右边选一个实现
日志门面:SLF4j;
日志实现:logback;(是log4j的升级,log4j2是apache推出的,比较复杂)
SpringBoot底层是Spring框架,Spring默认使用JCL;
SpringBoot选用SLF4j和logback;
3.2 SLF4j的使用
开发的时候,日志方法的调用,不应该直接调用日志的实现类,而应该调用日志抽象层的方法;
import org.slf4j.Logger;import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;public class HelloWorld {public static void main (String[] args) {Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloWorld.class);"Hello World" );
image-20200703162612914
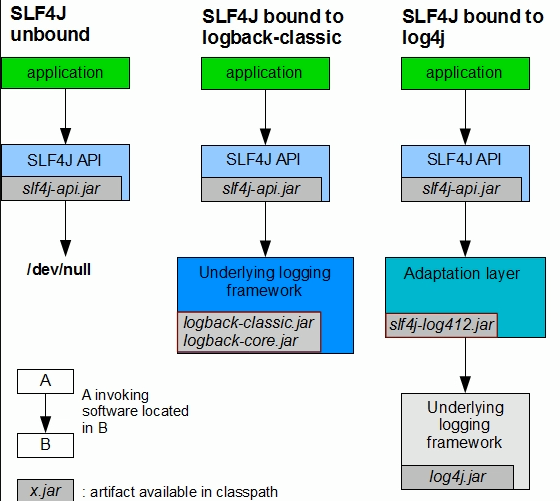
slf4j与logback和log4j配合使用
每一个日志的实现框架都有自己的配置文件。使用slf4j以后,配置文件还是做成日志实现框架的配置文件 ;
3.2.1遗留问题
不同框架使用的日志记录不同,需要统一日志框架。
image-20200703163643619
如何让系统中所有日志统一到slf4j?
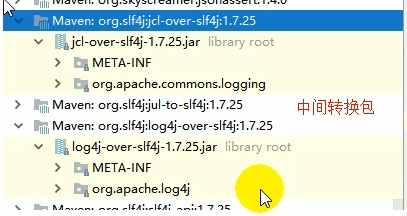
将系统中其他日志框架排除出去
用中间包替换原有的日志框架
导入slf4j其他的实现
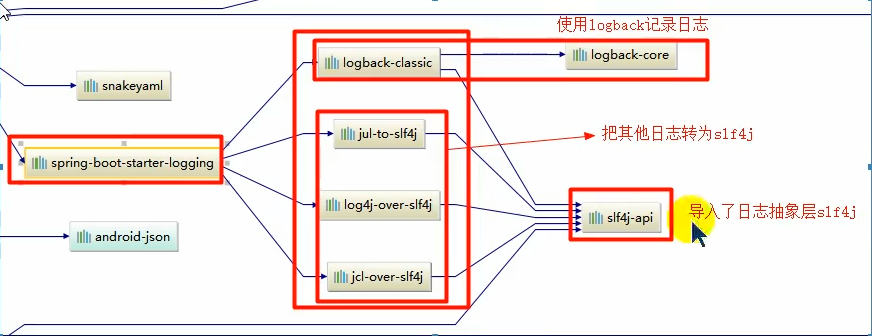
3.3Springboot日志关系
SpringBoot使用Spring-boot-starter-logging用作日志功能
image-20200703201856394
image-20200703202300674
如果引用其他框架,一定要把框架的默认日志依赖移除掉.
Spring框架使用的是commons-logging,在依赖界面使用<exclusions></exclusions>将其移除掉
<dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId > <scope > test</scope > <exclusions > <exclusion > <groupId > org.junit.vintage</groupId > <artifactId > junit-vintage-engine</artifactId > </exclusion > </exclusions > </dependency >
Logger logger= LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());@Autowired @Test void contextLoads () {"degug信息" );"warn信息" );"trace信息" );
日志的级别:trace<debug<info<warn<error
默认使用info级别(root级别 ),可以调整日志级别,日志就只会输出比该级别高的日志。
logging.level.com.fyw =trace #将com.fyw包下的日志调为trace级别 logging.file.path =springboot.log #设置输出日志文件名,默认在类路径下 //控制台输出格式 logging.pattern.console =%d{yyyy-MM-dd} [%thread] %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n //文件中输出格式 logging.pattern.file =%d{yyyy-MM-dd}=== [%thread] ===%-5level %logger{50} ===- %msg%n
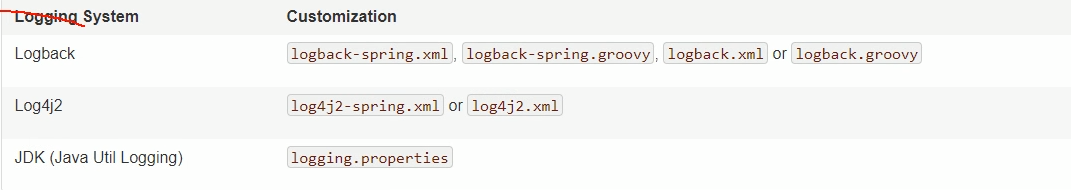
给类路径下放上每个日志框架自己的配置文件即可;SpringBoot就不使用他默认配置的了
image-20200703211607704
logback.xml:直接被日志框架识别了
logback-spring.xml:日志框架不直接加载日志的配置项,由SpringBoot解析日志配置,可以使用SpringBoot的高级profile功能
<springProfile name ="staging" > </springProfile >
否则会出现 no applicable action for [springProfile]
3.4切换日志框架
四、web开发
流程:
创建SpringBoot应用,选中需要的模块
SpringBoot已经将这些配置配置好了,只需要修改少量配置即可运行起来
编写业务逻辑代码
明白自动配置原理 ,可以弄明白SpringBoot帮我们配置了什么?能不能修改?哪些配置能修改?能不能扩展等。
4.1Springboot对静态资源的映射
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 WebMvcAutoConfiguration下的addResourceHandlers方法。@Override public void addResourceHandlers (ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {if (!this .resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {"Default resource handling disabled" );return ;Duration cachePeriod = this .resourceProperties.getCache().getPeriod();CacheControl cacheControl = this .resourceProperties.getCache().getCachecontrol().toHttpCacheControl();if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern("/webjars/**" )) {"/webjars/**" )"classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/" )String staticPathPattern = this .mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern();if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern(staticPathPattern)) {this .resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()))@Bean public WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping (ApplicationContext applicationContext, FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService, ResourceUrlProvider mvcResourceUrlProvider) {WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping = new WelcomePageHandlerMapping (new TemplateAvailabilityProviders (applicationContext), applicationContext, getWelcomePage(),this .mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern());return welcomePageHandlerMapping;
<dependency > <groupId > org.webjars.npm</groupId > <artifactId > jquery</artifactId > <version > 3.5.0</version > </dependency >
2./**访问当前项目任何资源(静态资源文件夹)
"/" :当前项目根路径", " classpath:/resources/", " classpath:/static/", " classpath:/public/
3.欢迎页映射:静态资源下的index.html被/**映射
localhost:8091 找index页面
4.2引入thymeleaf
修改版本thymeleaf3需要thymeleaf-layout-dialect.version2.0以上<properties > <java.version > 1.8</java.version > <thymeleaf.version > 3.0.11.RELEASE</thymeleaf.version > <thymeleaf-layout-dialect.version > 2.1.1</thymeleaf-layout-dialect.version > </properties >
添加依赖
<dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId > </dependency >
只要我们把HTML 页面放在classpath:/templates/ ,
thymeleaf就能自动渲染;
4.2.1使用thymeleaf
导入名称空间
```html
成功!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 20200704173410101 ](http://cdn.retainblog.top/blog/image-20200704173410101 .png)Simple expressions:Variable Expressions : ${...} OGNL 表达式,1 )、获取对象属性,调用方法2 )、使用内置的基本对象3 )、内置的一些工具对象Selection Variable Expressions : *{...} 和${}在功能上是一样的 配合th:Object ="${session.user}" Message Expressions : Link URL Expressions : @{...} :定义url连接 @{/order/process(execId=${execId},execType='FAST ')} 不需要"?变量名" 进行拼接Fragment Expressions : ~{...} :片段引用表达式Literals :字面量Text literals: 'one text' , 'Another one!' ,…Number literals: 0 , 34 , 3 .0 , 12 .3 ,…Boolean literals: true , false Null literal: nullLiteral tokens: one , sometext , main ,…Text operations: :文本操作String concatenation: +Literal substitutions: |The name is ${name}|Arithmetic operations: :数学运算Binary operators: + , - , * , / , %Minus sign (unary operator): -Boolean operations:Binary operators: and , or Boolean negation (unary operator): ! , not Comparisons and equality:Comparators : > , < , >= , <= ( gt , lt , ge , le )Equality operators: == , != ( eq , ne )Conditional operators:If -then: (if ) ? (then)If -then-else : (if ) ? (then) : (else )Default : (value) ?: (defaultvalue)Special tokens:Page 17 of 106 No -Operation : _
<body > <h1 > 成功!</h1 > <div th:text ="${hello}" > </div > <hr /> <div th:text ="${user}" th:each ="user:${users}" > </div > </body >
4.3 SpringMVC自动配置原理*
Spring Boot provides auto-configuration for Spring MVC that works
well with most applications.
The auto-configuration adds the following features on top of Spring’s
defaults:
Inclusion of ContentNegotiatingViewResolver and
BeanNameViewResolver beans.
自动配置了视图解析器ViewResolver,根据方法的返回值得到视图对象View,View觉得如何渲染(转发?重定向?)
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver组合所有视图解析器。
如何定制:可以自己给容器中添加一个视图解析器;自动将其组合进来。
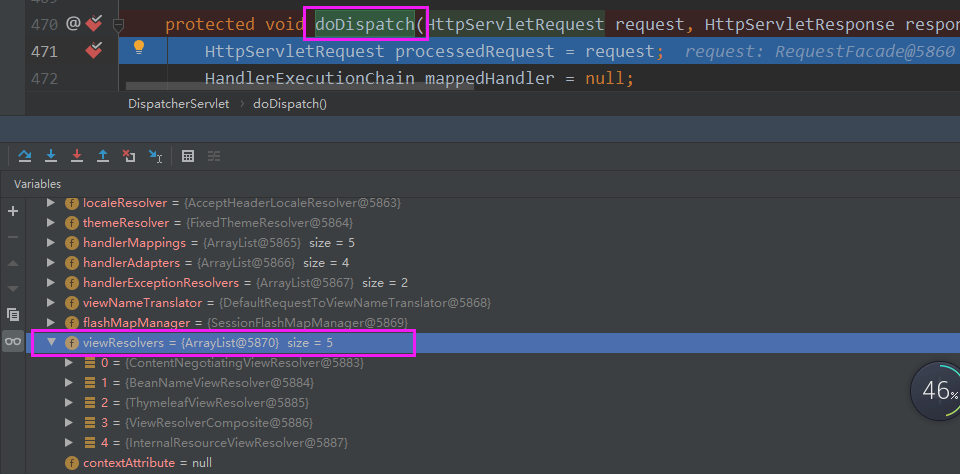
image-20200705114055844
DispatcherServlet中
Support for serving static resources, including support for
WebJars (see below).
Automatic registration of Converter,
GenericConverter, Formatter beans.
自动注册了转换器:public String hello(User user);
传入文本数据转User对象
Formatter(格式化器):2020/07/05=====Date
protected void addFormatters (FormatterRegistry registry) {this .configurers.addFormatters(registry);
Support for HttpMessageConverters (see below).
HttpMessageConverters
:SpringMVC用来转换Http请求和响应的lUser--json是从容器中确定;获取所有的HttpMessageConverters ;
自己添加的HttpMessageConverters
,只需要添加到容器中就可以
Automatic registration of MessageCodesResolver (see
below). //定义错误代码生成规则
Static index.html support. 静态首页访问
Custom Favicon support.
Automatic use of a ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer
bean (see below).
If you want to keep Spring Boot MVC features, and you just want to
add additional MVC
configuration (interceptors, formatters, view controllers etc.) you
can add your own @Configuration class of type
WebMvcConfigurerAdapter, but without
@EnableWebMvc. If you wish to provide custom instances of
RequestMappingHandlerMapping,
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter or
ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver you can declare a
WebMvcRegistrationsAdapter instance providing such
components.
If you want to take complete control of Spring MVC, you can add your
own @Configuration annotated with
@EnableWebMvc.
4.4全面接管SpringMVC
4.4.1扩展SpringMVC
添加拦截器,格式化器,视图控制器等
you can add your own @Configuration class of type
WebMvcConfigurerAdapter, but without
@EnableWebMvc
编写一个配置类,2.0以上实现implements
WebMvcConfigurer,不标注@EnableWebMvc。丢弃extendsWebMvcConfigurerAdapter``
@Configuration public class MyMVCConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {@Override public void addViewControllers (ViewControllerRegistry registry) {"/demo" ).setViewName("/success" );
原理
WebMvcConfiguration是SpringMVC的自动配置类
在做其他自动配置时会导入:@Import (EnableWebMvcConfiguration .class)
4.4.2 全面接管SpringMvc
使用@EnableWebMvc
优点:如果项目比较小时用不到这么多功能可以节省空间。
但不推荐全面接管Mvc
原理:
@Import({DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration.class}) public @interface EnableWebMvc {
public class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {private final WebMvcConfigurerComposite configurers = new WebMvcConfigurerComposite ();
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) @ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET) @ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class }) @ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class) @AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10) @AutoConfigureAfter({ DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class, TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration.class, ValidationAutoConfiguration.class }) public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {
@EnableWebMvc导入的WebMvcConfigurationSupport只是Mvc最基本的功能
4.4.3如何修改SpringBoot的默认配置
模式:
1
)、SpringBoot在自动配置很多组件的时候,先看容器中有没有用户自己配置的(
@Bean 、 @Component
)如果有就用用户配置的,如果没有,才自动配置;如果有些组件可以有多个(
ViewResolver )将 用户配置的和自己默认的组合起来;
2)、在SpringBoot中会有非常 多的XxxConfigurer帮助我们进行扩展配置
4.5案例 RestfulCRUD
@Override public void addViewControllers (ViewControllerRegistry registry) {"/" ).setViewName("index" );
@RequestMapping({"","/index.html"}) public String index () {return "index" ;
@Override public void addResourceHandlers (ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {"/**" ).addResourceLocations("classpath:/static/" );
4.5.1国际化
编写国家化配置文件,抽取需要显示的国际化消息
image-20200705181426319
springboot自动配置了国际化的组件
@ConfigurationProperties (prefix
= "spring.messages") public class MessageSourceAutoConfiguration {
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 private String basename = "messages" ; @Bean public MessageSource messageSource () {ResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource = new ResourceBundleMessageSource ();if (StringUtils.hasText(this .basename)) {this .basename)));if (this .encoding != null ) {this .encoding.name());this .fallbackToSystemLocale);this .cacheSeconds);this .alwaysUseMessageFormat);return messageSource;
3、获取国际化值
原理:
国际化Locale(区域信息对象);LocaleResolver(获取区域信息对象);
@Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.mvc", name = "locale") public LocaleResolver localeResolver () {if (this .mvcPropertiesreturn new FixedLocaleResolver (this .mvcProperties.getLocale());AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver localeResolver = new AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver ();this .mvcProperties.getLocale());return localeResolver;
默认的就是根据请求头带来的区域信息获取Locale进行国际化
4.点击链接切换国际化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public class MyLocaleResolver implements LocaleResolver {@Override public Locale resolveLocale (HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest) {String l = httpServletRequest.getParameter("l" ); Locale locale = Locale.getDefault();if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(l)){"_" );new Locale (split[0 ],split[1 ]);return locale;@Override public void setLocale (HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Locale locale) {@Bean public LocaleResolver localeResolver () { return new MyLocaleResolver ();
<a class ="btn btn-sm" th:href ="@{/(l='zh_CN')}" > 中文</a > <a class ="btn btn-sm" th:href ="@{/(l='en_US')}" > English</a >
4.5.2登录与拦截器
开发期间模板引擎页面修改以后,要实时生效
1)、禁用模板引擎的缓存
spring.thymeleaf.cache =false
2)、页面修改完成以后ctrl+f9:重新编译;
登陆错误消息的显示
<p style ="color: red" th:text ="${msg}" th:if ="${not #strings.isEmpty(msg)}" > </p >
跳转主页面
registry.addViewController("/main" ).setViewName("dashboard" );
@PostMapping("/user/login") public String login (@RequestParam("username") String username, @RequestParam("password") String password, Map<String,Object> map) {if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(username) && "123456" .equals(password)){return "redirect:/main" ; else {"msg" ,"用户名密码错误" );return "login" ;
拦截器实现登录检查
public class LoginHandlerInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {@Override public boolean preHandle (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {Object user = request.getSession().getAttribute("loginUser" );if (user==null ){"msg" ,"请先登录!" );"/" ).forward(request,response);return false ;else {return true ;
mvcconfig注册拦截器
@Override public void addInterceptors (InterceptorRegistry registry) {new LoginHandlerInterceptor ()).addPathPatterns("/**" ).excludePathPatterns("/" ,"/index.html" ,"/user/login" );
4.5.3CRUD-员工列表
实验要求:
1)、RestfulCRUD:CRUD满足Rest风格;
URI: /资源名称/资源标识 HTTP请求方式区分对资源CRUD操作
查询
getEmp
emp---GET
添加
addEmp?xxx
emp---POST
修改
updateEmp?id=xxx&xxx=xx
emp/{id}---PUT
删除
deleteEmp?id=1
emp/{id}---DELETE
2)、实验的请求架构;
查询所有员工
emps
GET
查询某个员工(来到修改页面)
emp/1
GET
来到添加页面
emp
GET
添加员工
emp
POST
来到修改页面(查出员工进行信息回显)
emp/1
GET
修改员工
emp
PUT
删除员工
emp/1
DELETE
@Controller public class EmployeeController {@Autowired @GetMapping("/emps") public String list (Model model) {"emps" ,all);return "../emp/list" ;
<link href ="/static/asserts/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel ="stylesheet" > <link href ="/static/asserts/css/dashboard.css" rel ="stylesheet" >
1、抽取公共片段<div th:fragment ="copy" > © 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery</div > <div th:insert ="~{footer :: copy}" > </div >
<nav class ="navbar navbar-dark sticky-top bg-dark flex-md-nowrap p-0" th:fragment ="topbar" >
三种引入公共片段的th属性:
th:insert :将公共片段整个插入到声明引入的元素中
th:replace :将声明引入的元素替换为公共片段
th:include :将被引入的片段的内容包含进这个标签中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 <footer th:fragment ="copy" > © 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery</footer > <div th:insert ="footer :: copy" > </div > <div th:replace ="footer :: copy" > </div > <div th:include ="footer :: copy" > </div > <div > <footer > © 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery</footer > </div > <footer > © 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery</footer > <div > © 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery</div >
4.6错误处理页面
其他客户端,响应json数据
{ "timestamp" : 1594366266983 , "status" : 404 , "error" : "Not Found" , "message" : "No message available" , "path" : "/m" }
原理:
参照ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration自动配置类
给容器添加了以下组件:
@Override public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes (RequestAttributes requestAttributes, boolean includeStackTrace) {new LinkedHashMap <String, Object>();"timestamp" , new Date ());return errorAttributes;
BasicErrorController 处理默认/error请求
@Controller
@RequestMapping ("\({server.error.path:\) {error.path:/error}}")
public class BasicErrorController extends AbstractErrorController {
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 @RequestMapping(produces = "text/html") public ModelAndView errorHtml (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);return (modelAndView == null ? new ModelAndView ("error" , model) : modelAndView);@RequestMapping @ResponseBody public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error (HttpServletRequest request) {HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);return new ResponseEntity <Map<String, Object>>(body, status);
ErrorPageCustomizer
@Value("${error.path:/error}") private String path = "/error" ;
DefaultErrorViewResolver
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 @Override public ModelAndView resolveErrorView (HttpServletRequest request, HttpStatus status, Map<String, Object> model) {ModelAndView modelAndView = resolve(String.valueOf(status), model);if (modelAndView == null && SERIES_VIEWS.containsKey(status.series())) {return modelAndView;private ModelAndView resolve (String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) {String errorViewName = "error/" + viewName;TemplateAvailabilityProvider provider = this .templateAvailabilityProvidersthis .applicationContext);if (provider != null ) {return new ModelAndView (errorViewName, model);return resolveResource(errorViewName, model);
步骤:
一但系统出现4xx或者5xx之类的错误;ErrorPageCustomizer就会生效(定制错误的响应规则);就会来到/error请求;就会被BasicErrorController 处理;
1)响应页面;去哪个页面是由DefaultErrorViewResolver 解析得到的;
protected ModelAndView resolveErrorView (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HttpStatus status, Map<String, Object> model) {for (ErrorViewResolver resolver : this .errorViewResolvers) {ModelAndView modelAndView = resolver.resolveErrorView(request, status, model);if (modelAndView != null ) {return modelAndView;return null ;
1)、如何定制错误的页面; 1)、有模板引擎的情况下;error/状态码;
【将错误页面命名为 错误状态码.html 放在模板引擎文件夹里面的
error文件夹下】,发生此状态码的错误就会来到 对应的页面;
我们可以使用4xx和5xx作为错误页面的文件名来匹配这种类型的所有错误,精确优先(优先寻找精确的状态码.html);
页面能获取的信息;
timestamp:时间戳
status:状态码
error:错误提示
exception:异常对象
message:异常消息
errors:JSR303数据校验的错误都在这里
2)、没有模板引擎(模板引擎找不到这个错误页面),静态资源文件夹下找;
3)、以上都没有错误页面,就是默认来到SpringBoot默认的错误提示页面;
2)、如何定制错误的json数据;
1)、自定义异常处理&返回定制json数据;
@ControllerAdvice public class MyExceptionHandler {@ResponseBody @ExceptionHandler(UserNotExistException.class) public Map<String,Object> handleException (Exception e) {new HashMap <>();"code" ,"user.notexist" );"message" ,e.getMessage());return map;
2)、转发到/error进行自适应响应效果处理
@ExceptionHandler(UserNotExistException.class) public String handleException (Exception e, HttpServletRequest request) {new HashMap <>();"javax.servlet.error.status_code" ,500 );"code" ,"user.notexist" );"message" ,e.getMessage());return "forward:/error" ;
3)、将我们的定制数据携带出去;
出现错误以后,会来到/error请求,会被BasicErrorController处理,响应出去可以获取的数据是由getErrorAttributes得到的(是AbstractErrorController(ErrorController)规定的方法);
1、完全来编写一个ErrorController的实现类【或者是编写AbstractErrorController的子类】,放在容器中;
2、页面上能用的数据,或者是json返回能用的数据都是通过errorAttributes.getErrorAttributes得到;
容器中DefaultErrorAttributes.getErrorAttributes();默认进行数据处理的;
自定义ErrorAttributes
@Component public class MyErrorAttributes extends DefaultErrorAttributes {@Override public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes (RequestAttributes requestAttributes, boolean includeStackTrace) {super .getErrorAttributes(requestAttributes, includeStackTrace);"company" ,"atguigu" );return map;
最终的效果:响应是自适应的,可以通过定制ErrorAttributes改变需要返回的内容,
4.7嵌入式Servlet
Springboot默认使用tomcat作为嵌入式Servlet容器
2、编写一个EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer :嵌入式的Servlet容器的定制器;来修改Servlet容器的配置
@Bean public EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer embeddedServletContainerCustomizer () {return new EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer () {@Override public void customize (ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer container) {8083 );
4.8注册Servlet三大组件(Servlet,Filter,Listener)
public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet {@Override protected void doPost (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {"Hello MyServlet" );@Override protected void doGet (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
@Configuration public class MyServerConfig {@Bean public ServletRegistrationBean myServlet () {ServletRegistrationBean servletRegistrationBean = new ServletRegistrationBean (new MyServlet (),"/myServlet" );return servletRegistrationBean;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class MyFilter implements Filter {@Override public void init (FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {@Override public void doFilter (ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {"MyFilter process" );@Override public void destroy () {
@Bean public FilterRegistrationBean myFilter () {new FilterRegistrationBean <>();new MyFilter ());"/hello" ,"/myServlet" ));return registrationBean;
ServletListenerRegistrationBean
public class MyListener implements ServletContextListener {@Override public void contextInitialized (ServletContextEvent sce) {"ServletContextEvent 启动" );@Override public void contextDestroyed (ServletContextEvent sce) {"ServletContextEvent 关闭" );
@Bean public ServletListenerRegistrationBean myListener () {new ServletListenerRegistrationBean <MyListener>(new MyListener ());return registrationBean;
SpringBoot帮我们自动SpringMVC的时候,自动的注册SpringMVC的前端控制器;DIspatcherServlet;
DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration中:
@Bean(name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_REGISTRATION_BEAN_NAME) @ConditionalOnBean(value = DispatcherServlet.class, name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME) public DispatcherServletRegistrationBean dispatcherServletRegistration (DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet, WebMvcProperties webMvcProperties, ObjectProvider<MultipartConfigElement> multipartConfig) {DispatcherServletRegistrationBean registration = new DispatcherServletRegistrationBean (dispatcherServlet,return registration;
4.9替换其他嵌入式servlet容器
Jetty(长连接)
Undertow(不支持jsp)
<dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId > </dependency >
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId > <exclusions > <exclusion > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > </exclusion > </exclusions > </dependency > <dependency > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactId > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > </dependency >
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId > <exclusions > <exclusion > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > </exclusion > </exclusions > </dependency > <dependency > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-undertow</artifactId > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > </dependency >
4)、嵌入式Servlet容器自动配置原理;
EmbeddedServletContainerAutoConfiguration:嵌入式的Servlet容器自动配置?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 @AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE) @Configuration @ConditionalOnWebApplication @Import(BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar.class) public class EmbeddedServletContainerAutoConfiguration {@Configuration @ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, Tomcat.class }) @ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = EmbeddedServletContainerFactory.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT) public static class EmbeddedTomcat {@Bean public TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory tomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory () {return new TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory ();@Configuration @ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, Server.class, Loader.class, WebAppContext.class }) @ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = EmbeddedServletContainerFactory.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT) public static class EmbeddedJetty {@Bean public JettyEmbeddedServletContainerFactory jettyEmbeddedServletContainerFactory () {return new JettyEmbeddedServletContainerFactory ();@Configuration @ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, Undertow.class, SslClientAuthMode.class }) @ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = EmbeddedServletContainerFactory.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT) public static class EmbeddedUndertow {@Bean public UndertowEmbeddedServletContainerFactory undertowEmbeddedServletContainerFactory () {return new UndertowEmbeddedServletContainerFactory ();
1)、EmbeddedServletContainerFactory(嵌入式Servlet容器工厂)
public interface EmbeddedServletContainerFactory {getEmbeddedServletContainer ( ServletContextInitializer... initializers) ;
2)、EmbeddedServletContainer:(嵌入式的Servlet容器)
3)、以TomcatServletWebServerFactory 为例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public WebServer getWebServer (ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {if (this .disableMBeanRegistry) {Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat (); File baseDir = this .baseDirectory != null ? this .baseDirectory : this .createTempDir("tomcat" );Connector connector = new Connector (this .protocol);true );this .customizeConnector(connector);false );this .configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());Iterator var5 = this .additionalTomcatConnectors.iterator();while (var5.hasNext()) {Connector additionalConnector = (Connector)var5.next();this .prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);return this .getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
4)、我们对嵌入式容器的配置修改是怎么生效?
ServerProperties、EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer
EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer :定制器帮我们修改了Servlet容器的配置?
怎么修改的原理?
5)、容器中导入了EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizerBeanPostProcessor
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization (Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {if (bean instanceof ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer) {return bean;private void postProcessBeforeInitialization ( ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer bean) {for (EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer customizer : getCustomizers()) {private Collection<EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer> getCustomizers () {if (this .customizers == null ) {this .customizers = new ArrayList <EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer>(this .beanFactoryfalse , false )this .customizers, AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE);this .customizers = Collections.unmodifiableList(this .customizers);return this .customizers;
步骤:
1)、SpringBoot根据导入的依赖情况,给容器中添加相应的EmbeddedServletContainerFactory【TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory】
2)、容器中某个组件要创建对象就会惊动后置处理器;EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizerBeanPostProcessor;
只要是嵌入式的Servlet容器工厂,后置处理器就工作;
3)、后置处理器,从容器中获取所有的EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer ,调用定制器的定制方法
###5)、嵌入式Servlet容器启动原理;
什么时候创建嵌入式的Servlet容器工厂?什么时候获取嵌入式的Servlet容器并启动Tomcat;
获取嵌入式的Servlet容器工厂:
1)、SpringBoot应用启动运行run方法
2)、refreshContext(context);SpringBoot刷新IOC容器【创建IOC容器对象,并初始化容器,创建容器中的每一个组件】;如果是web应用创建AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext ,否则:AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
3)、refresh(context);刷新刚才创建好的ioc容器;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 public void refresh () throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {synchronized (this .startupShutdownMonitor) {ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();try {catch (BeansException ex) {if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {"Exception encountered during context initialization - " +"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);throw ex;finally {
4)、 onRefresh(); web的ioc容器重写了onRefresh方法
5)、webioc容器会创建嵌入式的Servlet容器;createEmbeddedServletContainer ();
6)、获取嵌入式的Servlet容器工厂:
EmbeddedServletContainerFactory containerFactory =
getEmbeddedServletContainerFactory();
从ioc容器中获取EmbeddedServletContainerFactory
组件;TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory 创建对象,后置处理器一看是这个对象,就获取所有的定制器来先定制Servlet容器的相关配置;
7)、使用容器工厂获取嵌入式的Servlet容器 :this.embeddedServletContainer
= containerFactory
.getEmbeddedServletContainer(getSelfInitializer());
8)、嵌入式的Servlet容器创建对象并启动Servlet容器;
先启动嵌入式的Servlet容器,再将ioc容器中剩下没有创建出的对象获取出来;
==IOC容器启动创建嵌入式的Servlet容器==
数据操作
JDBC连接
<dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > mysql</groupId > <artifactId > mysql-connector-java</artifactId > <scope > runtime</scope > </dependency >
spring: datasource: username: root password: qwer url: jdbc:mysql://39.99.187.18:3306/Test driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
使用的数据源:
class com .zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource1454499111 wrapping com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@68c34db2
数据源的相关配置都在DataSourceProperties类中
数据源的自动配置原理:
2.x使用HikariCP-3.4.5.jar作为数据源
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) @ConditionalOnMissingBean(DataSource.class) @ConditionalOnProperty(name = "spring.datasource.type") static class Generic {@Bean dataSource (DataSourceProperties properties) {return properties.initializeDataSourceBuilder().build();
4、DataSourceInitializer:ApplicationListener ;
作用:
1)、runSchemaScripts();运行建表语句;
2)、runDataScripts();运行插入数据的sql语句;
默认只需要将文件命名为:
schema-*.sql、data-*.sql 默认规则:schema.sql,schema-all.sql; 可以使用 schema :- classpath:department.sql 指定位置
5、操作数据库:自动配置了JdbcTemplate操作数据库
spring: datasource: username: root password: qwer url: jdbc:mysql://39.99.187.18:3306/Test driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver schema: - classpath*:department.sql
整合Druid数据源
<dependency > <groupId > com.alibaba</groupId > <artifactId > druid</artifactId > <version > 1.1.22</version > </dependency >
spring: datasource: username: root password: 'qwer' url: jdbc:mysql://39.99.187.18:3306/Test driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
配置类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 package com.fyw.demo.config;import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;import com.alibaba.druid.support.http.StatViewServlet;import com.alibaba.druid.support.http.WebStatFilter;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.FilterRegistrationBean;import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletListenerRegistrationBean;import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletRegistrationBean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import javax.sql.DataSource;import java.util.Arrays;import java.util.EventListener;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;@Configuration public class DruidConfig {@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource") @Bean public DataSource druid () {return new DruidDataSource ();@Bean public ServletRegistrationBean statViewServlet () {ServletRegistrationBean bean = new ServletRegistrationBean (new StatViewServlet (),"/druid/*" );new HashMap <>();"loginUsername" ,"admin" );"loginPassword" ,"123456" );"deny" ,"127.0.0.1" );return bean;@Bean public FilterRegistrationBean webStatFilter () {FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean ();new WebStatFilter ());new HashMap <>();"exclusions" ,"*.js,*.css,/druid/*" );"/*" ));return bean;
image-20200718110718195
整合Mybatis
<dependency>2.1 .3 </version>
image-20200719103912341
spring: datasource: username: root password: 'qwer' url: jdbc:mysql://39.99.187.18:3306/mybatis driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource filters: stat,wall,log4j maxPoolpreparedStatementPerConnectionSize: 20 useGlobalDataSourceStat: true connectionProperties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=500 schema: - classpath:department.sql initialization-mode: always
导入lombok自动生成实体
<dependency > <groupId > org.projectlombok</groupId > <artifactId > lombok</artifactId > <version > 1.18.12</version > <scope > provided</scope > </dependency >
@Getter @Setter @ToString public class Employee {private Integer id;private String lastName;private String email;private Integer gender;private Integer dId;
Mybatis注解版
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 @Mapper @Component public interface DepartmentMapper {@Select("Select * from department where id=#{id}") getDeptById (Integer id) ;@Delete("Delete from department where id=#{id}") int deleteDeptById (Integer id) ;@Update("Update department set departmentName=#{departmentName} where id=#{id}") int updateDept (Department department) ;@Options(useGeneratedKeys = true,keyProperty = "id") @Insert("Insert into department(departmentName) values(#{departmentName})") int insertIntoDept (Department department) ;
开启自定义配置,开启驼峰命名
@org .springframework.context.annotation.Configurationpublic class MyBatisConfig {@Bean public ConfigurationCustomizer configurationCustomizer () {return new ConfigurationCustomizer (){@Override public void customize (Configuration configuration) {true );
当Mapper比较多的时候,在主类上添加@MapperScan("com.fyw.demo.mapper"),自动将包内文件扫描为Mapper而不需要使用@Mapper注解。
Myabtis配置文件版
public interface EmployeeMapper {getEmpById (Integer id) ;int insertIntoEmp (Employee employee) ;
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd" > <mapper namespace ="com.fyw.demo.mapper.EmployeeMapper" > <select id ="getEmpById" resultType ="com.fyw.demo.entities.Employee" > </select > <insert id ="insertIntoEmp" > </insert > </mapper >
@GetMapping("/emp/{id}") public Employee getEmpById (@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {return employeeMapper.getEmpById(id);@GetMapping("/emp") public Employee insertIntoEmp (Employee employee) {return employee;
mybatis: typeAliasesPackage: com.example.springboot.mybatisxml.entity mapperLocations: classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml config-location: classpath:mybatis/mybatis-config.xml
整合JPA
//使用JPA注解配置映射关系 @Entity
//告诉JPA这是一个实体类(和数据表映射的类) @Table (name = "tbl_user") //@Table来指定和哪个数据表对应 ;如果省略默认表名就是user;
public class User {
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 @Entity @Table(name = "tbl_user") public class User {@Entity @Table(name = "tbl_user") public class User {@Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private Integer id;@Column(name = "last_name",length = 50) private String lastName;@Column private String email;
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository <User,Integer> {
spring: jpa: hibernate: ddl-auto: update show-sql: true
原理解析
启动流程
1.创建SpringApplication对象
自定义Starters*
@Configuration @ConditionalOnXXX @AutoConfigureAfter @Bean @ConfigurationPropertie 结合相关xxxProperties类来绑定相关的配置@EnableConfigurationProperties
模式
<groupId > org.mystarter</groupId > <artifactId > my-spring-boot-starter</artifactId > <version > 1.0-SNAPSHOT</version > <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > com.mystarter</groupId > <artifactId > my-spring-boot-starter-autoconfigurer</artifactId > <version > 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version > </dependency > </dependencies >
image-20200722125703544
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 HelloProperties@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mystarter.hello") public class HelloProperties {private String prefix;private String suffix;public String getPrefix () {return prefix;public void setPrefix (String prefix) {this .prefix = prefix;public String getSuffix () {return suffix;public void setSuffix (String suffix) {this .suffix = suffix;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 HelloServicepublic class HelloService {public HelloProperties getHelloProperties () {return helloProperties;public String sayHelloMyStarter (String name) {return helloProperties.getPrefix() +"-" +name+helloProperties.getSuffix();public void setHelloProperties (HelloProperties helloProperties) {this .helloProperties = helloProperties;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 HelloServiceAutoConfiguration@Configuration @ConditionalOnWebApplication @EnableConfigurationProperties(HelloProperties.class) public class HelloServiceAutoConfiguration {@Autowired @Bean public HelloService helloService () {HelloService helloService = new HelloService ();return helloService;
AutoConfigurer的pom
<dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter</artifactId > </dependency > </dependencies >
Starter
<dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > com.mystarter</groupId > <artifactId > my-spring-boot-starter-autoconfigurer</artifactId > <version > 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version > </dependency > </dependencies >
然后依次将AutoConfigurer、starter install进maven仓库
在其他项目导入starter依赖
<dependency > <groupId > org.mystarter</groupId > <artifactId > my-spring-boot-starter</artifactId > <version > 1.0-SNAPSHOT</version > </dependency >
HelloController
@RestController public class HelloControllerStarter {@Autowired @GetMapping("/hello2") public String hello () {return helloService.sayHelloMyStarter("张三" );
编写配置
mystarter.hello.prefix =mystarter mystarter.hello.suffix =hello world
缓存抽象
重要接口
image-20200723153814201
mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case =true 设置驼峰命名规则,dId对应数据库d_id 但是设置后启动报错,UnsatisfiedDependencyException : Error creating bean with name 'employeeController': Unsatisfied dependency expressed through field 'employeeService'; neste
开启缓存
开启基于注解的缓存@EnableCaching
标注缓存注解
@Cacheable() public Employee getEmp (Integer id) {
image-20200723164033929
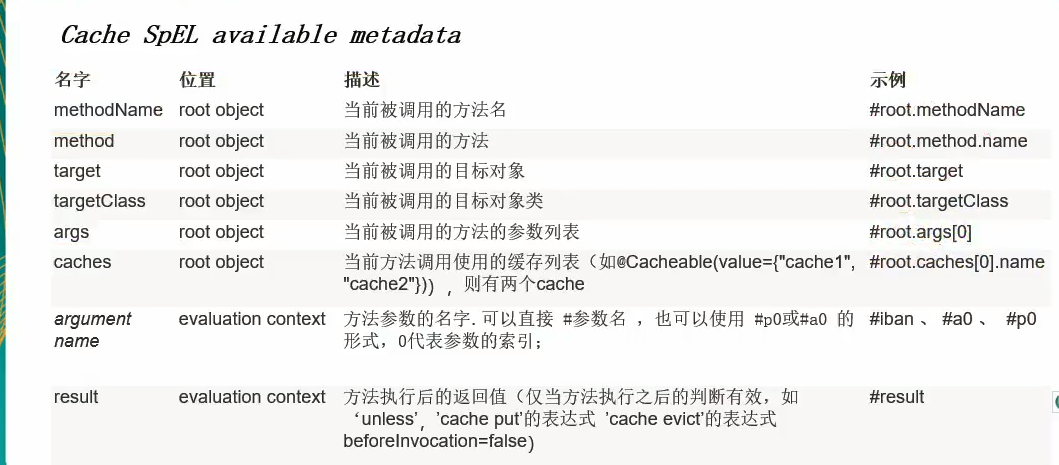
SpEL表达式
缓存工作原理
自动配置类:org/springframework/boot/autoconfigure/cache/CacheAutoConfiguration.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 @Import({ CacheConfigurationImportSelector.class, CacheManagerEntityManagerFactoryDependsOnPostProcessor.class }) static class CacheConfigurationImportSelector implements ImportSelector {@Override public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {new String [types.length];for (int i = 0 ; i < types.length; i++) {return imports; 0 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.GenericCacheConfiguration" 1 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.JCacheCacheConfiguration" 2 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.EhCacheCacheConfiguration" 3 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.HazelcastCacheConfiguration" 4 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.InfinispanCacheConfiguration" 5 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CouchbaseCacheConfiguration" 6 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration" 7 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CaffeineCacheConfiguration" 8 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.SimpleCacheConfiguration" 9 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.NoOpCacheConfiguration" true 查看 发现只有SimpleCacheConfiguration生效type (CacheCondition) @ConditionalOnMissingBean (types: org.springframework.cache.CacheManager; SearchStrategy: all) did not find any beans (OnBeanCondition)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 @Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) @ConditionalOnMissingBean(CacheManager.class) @Conditional(CacheCondition.class) class SimpleCacheConfiguration {@Bean cacheManager (CacheProperties cacheProperties, CacheManagerCustomizers cacheManagerCustomizers) {ConcurrentMapCacheManager cacheManager = new ConcurrentMapCacheManager ();if (!cacheNames.isEmpty()) {return cacheManagerCustomizers.customize(cacheManager);public class ConcurrentMapCacheManager implements CacheManager , BeanClassLoaderAware {@Override @Nullable public Cache getCache (String name) { Cache cache = this .cacheMap.get(name);if (cache == null && this .dynamic) {synchronized (this .cacheMap) {this .cacheMap.get(name);if (cache == null ) {this .cacheMap.put(name, cache);return cache;
运行流程
@Cacheable
方法运行之前,先调用getCache(String
name)按照cacheNames指定的名字==查询缓存==,第一次获取如果==没有缓存组件会自动创建出来==(emp缓存)
去Cache中查找缓存的==内容==,使用一个key,默认就是方法的参数(key是按照某种策略生成出来的:默认使用SimplekeyGenerator生成key)
没有查到缓存==内容==就调用目标方法(get方法)
将目标方法返回结果调用==put方法==,key是生成的key,value是返回结果,==放入缓存中==。
key生成策略
没有参数:key=new SimpleKey();
一个参数:key = 参数的值;
多个参数:key=new SimpleKey(Params);
核心
使用CacheManager(ConcurrentCacheManager)按照名字得到Cache(ConcurrentMapCache)组件
key是使用keyGenerator生成的,默认为SimpleKeyGenerator
@Cacheable其他属性 @Cacheable(cacheNames = {"emp"},key = "#root.methodName"+'['+"#id"+']') public Employee getEmp (Integer id) {"查询" +id+"号员工" );Employee empById = employeeMapper.getEmpById(id);return empById;
使用自定义的keyGenerator
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 @Configuration public class MyCacheConfig {@Bean("myKeyGenerator") public KeyGenerator keyGenerator () {return new KeyGenerator () {@Override public Object generate (Object target, Method method, Object... params) {return method.getName()+"[" + Arrays.asList(params).toString() +"]" ;@Cacheable(cacheNames = {"emp"},keyGenerator = "myKeyGenerator") @Cacheable(cacheNames = {"emp"},condition = "#a0>1")
@CachePut
既调用方法==修改数据库的值,同时又更新缓存==,从而更新数据后再查询也不用从数据库中查询
运行时机:先调用方法,再将目标方法的结果放入缓存
@CachePut(value=“emp”,key=“#result.id”)
@CacheEvict
缓存清除
@CacheEvict(value="emp",key="#id") @CacheEvict(value="emp",allEntries=true) @CacheEvict(value="emp",beforeInvocation=true,key="#id")
@Caching
与@CacheConfig
@Caching :组合复杂的cache规则
只要又cacheput那么方法一定会执行
@Caching( cacheable = { @Cacheable(value = "emp",key = "#id") //按照id查询 }, put = { @CachePut(value = "emp",key = "#result.id"), //按照id查询 @CachePut(value = "emp",key = "#result.email") //按照邮箱查询 } ) public Employee getEmp (Integer id) {"查询" +id+"号员工" );Employee empById = employeeMapper.getEmpById(id);return empById;
@CacheConfig :抽取缓存的公共配置
@Service @CacheConfig(cacheNames = "emp") public class EmployeeService {