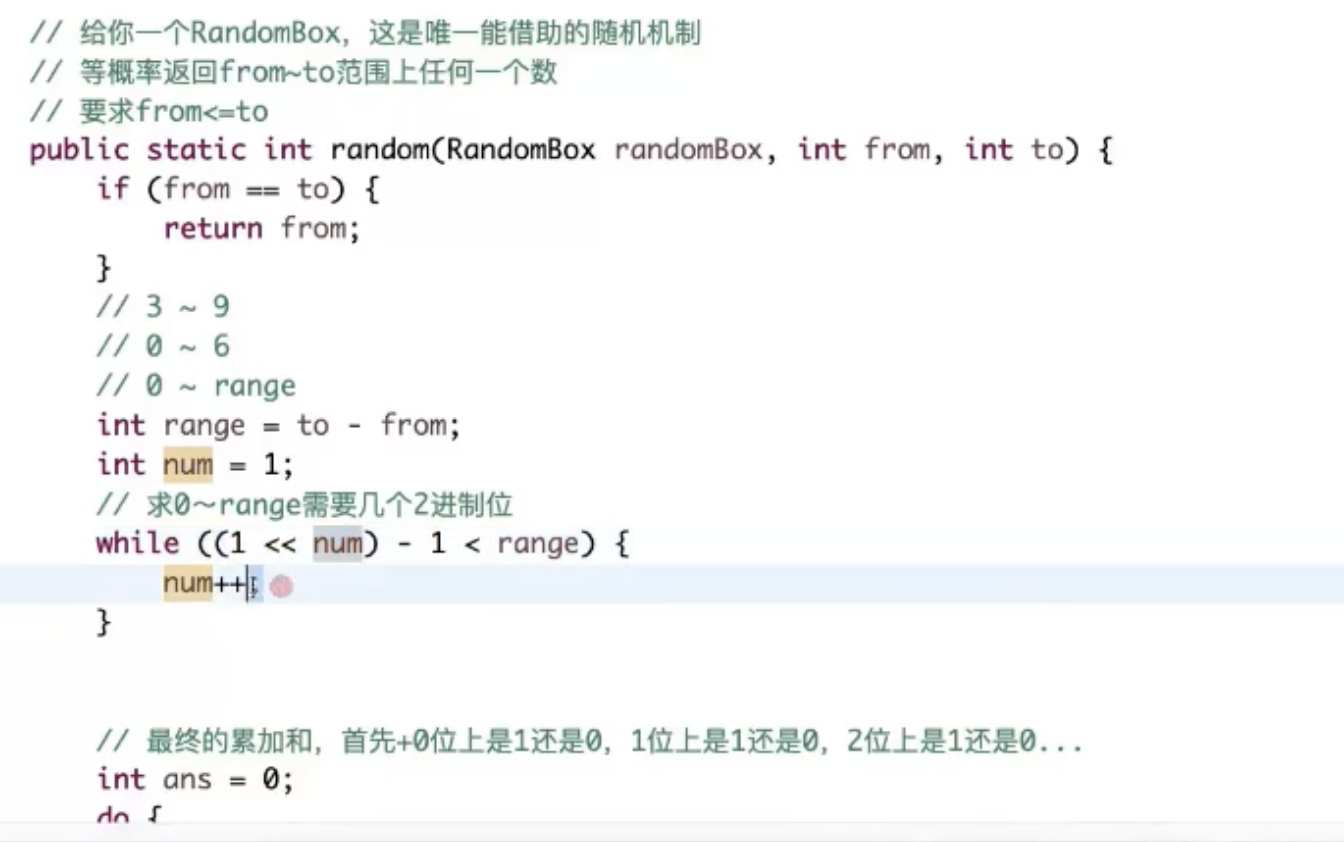
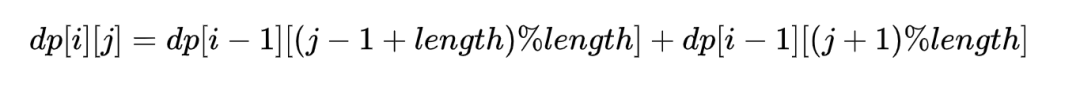1.打家劫舍3(动态规划)*
image-20210715223605747
解法一
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution {new HashMap <>();public int rob (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) return 0 ; if (map.containsKey(root)) return map.get(root);int money = root.val;if (root.left != null ) {if ( root.right != null ) {int res = Math.max(money, rob(root.left) + rob(root.right));return res;
由于在偷爷爷的时候,会计算孙子能偷到的钱,其中也会计算到儿子能偷到的钱。所以递归到儿子成为爷爷的时候,就不需要再继续计算了,而是直接从map里面拿,跟斐波那契数列的去重非常相似。
非常妙的是,下一层的money返回后会加到上一层的money上,所以返回到最终,money就是下面节点累加的值。
解法二
对每个节点都生成一个一维数组,大小为2,代表偷它能得到最大的钱和不偷它能得到最大的钱。递归的时候从叶子结点返回,依此给每个节点的数组进行赋值,最后我们只需要返回偷根节点和不偷根节点谁能获得更多即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution {public int rob (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) return 0 ;int [] res = robOrNot(root);return Math.max(res[0 ], res[1 ]);public int [] robOrNot(TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) return new int [2 ];int [] result = new int [2 ];int [] left = robOrNot(root.left);int [] right = robOrNot(root.right);0 ] = root.val + left[1 ] + right[1 ];1 ] = Math.max(left[0 ], left[1 ]) + Math.max(right[0 ], right[1 ]);return result;
小结
树形的动态规划做得非常少,线性的我们通常用数组进行存储,树形的由于不能索引,我们就使用Map来存储,其实本质都是一样,能够记录之前的结果并且复用。
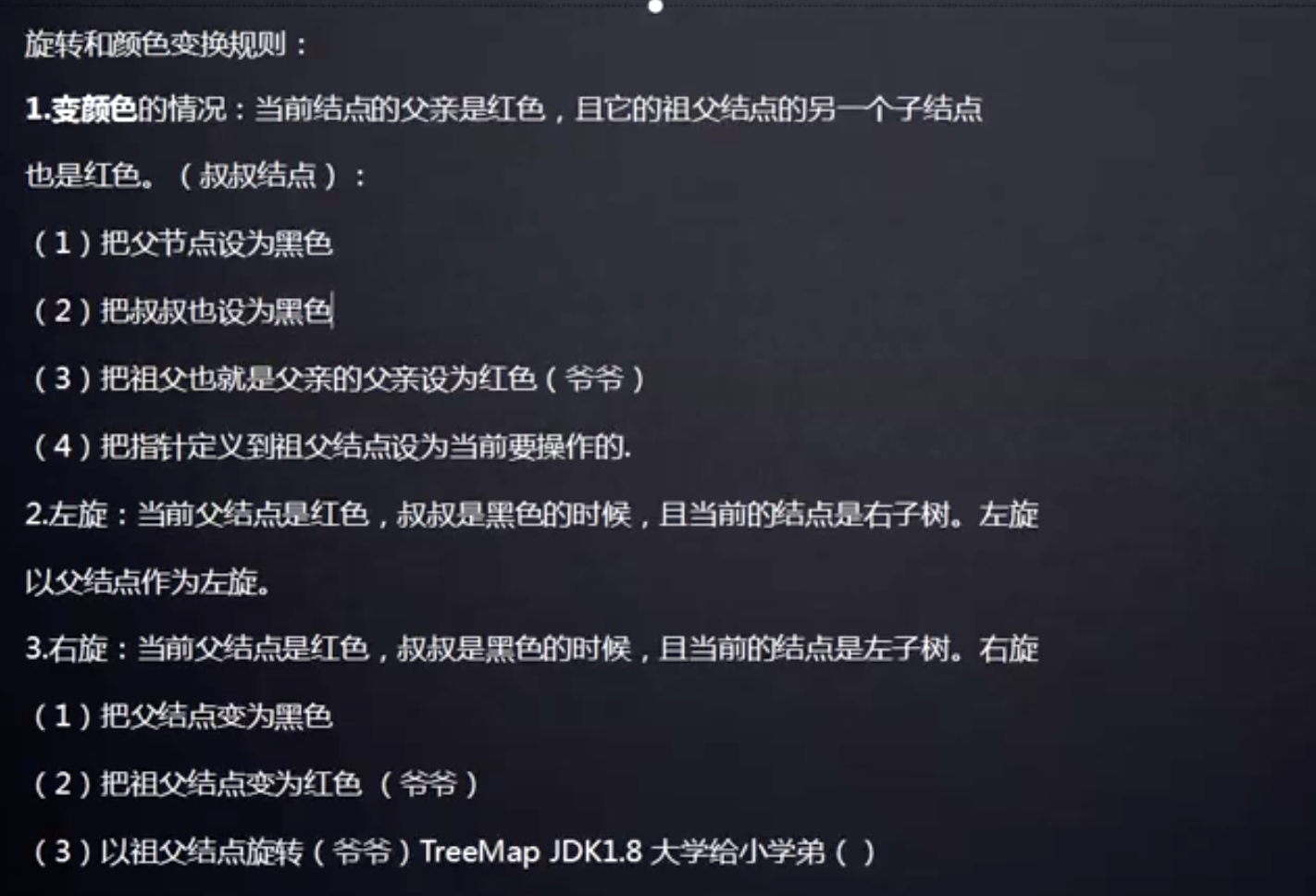
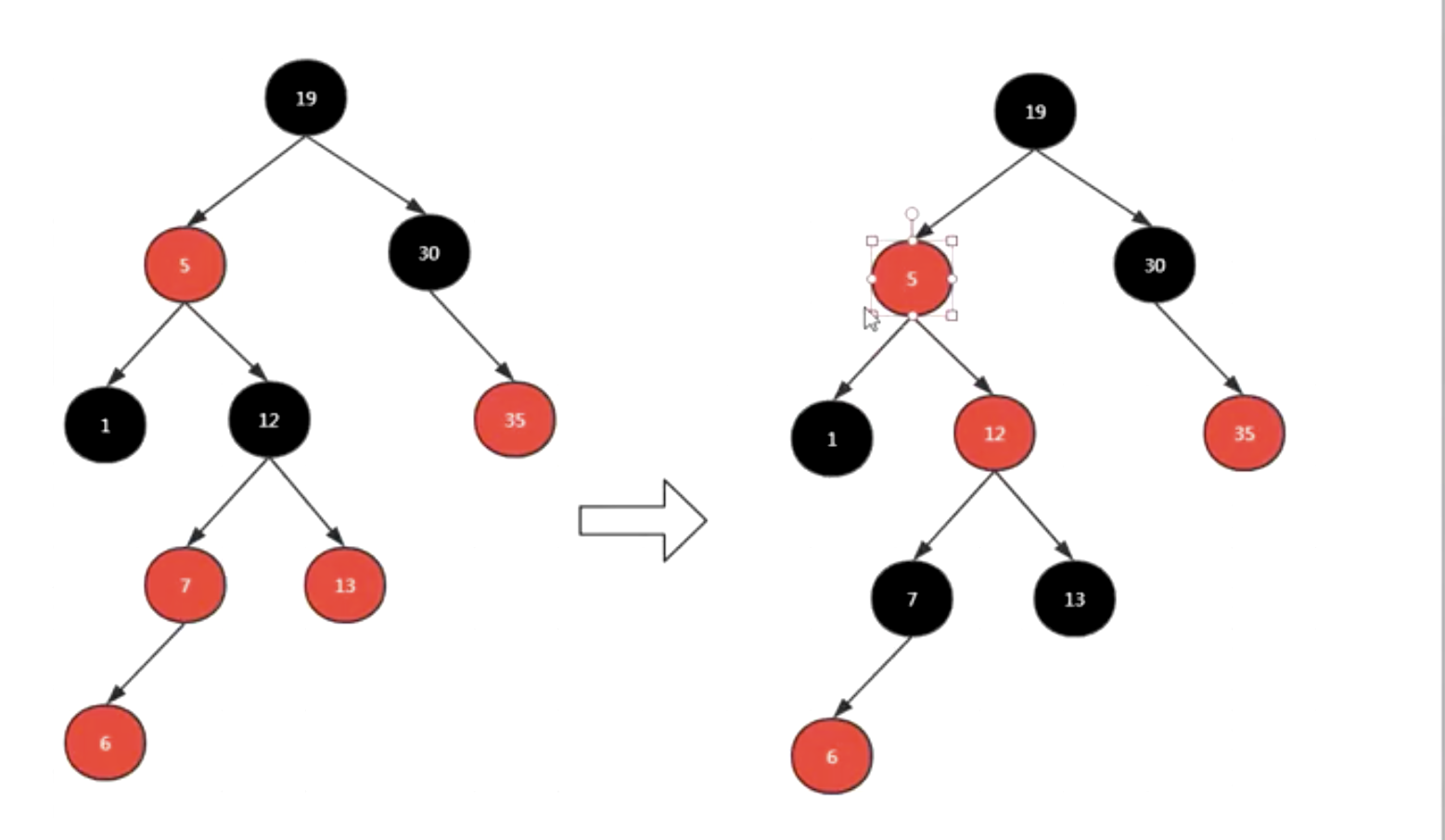
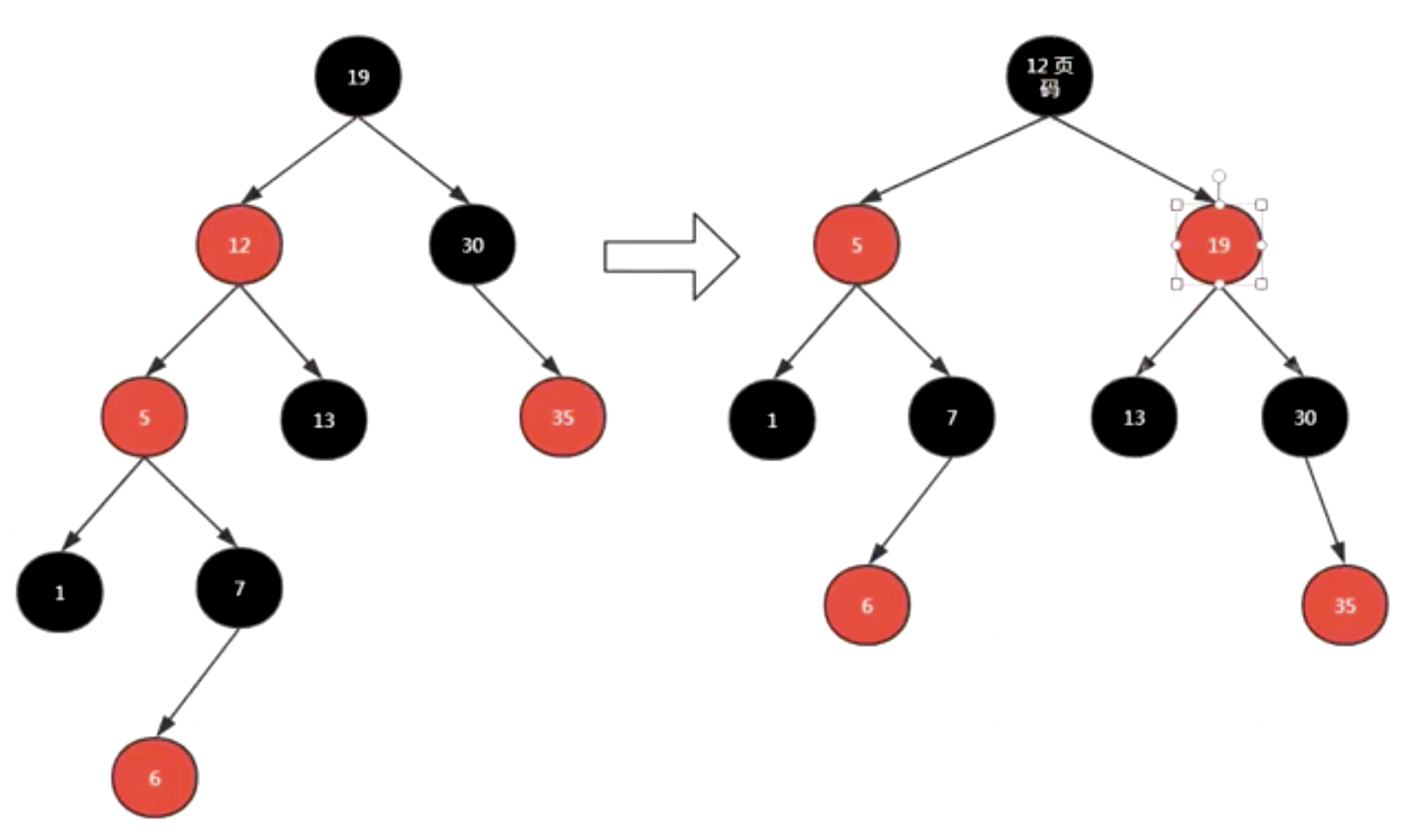
2.红黑树
所有插入的点默认为红色。
变颜色的条件:插入的红色节点的父亲节点和叔叔节点 都是红色的时候。
(父亲是红色,儿子也是红色不干,插入的儿子是红色后,父亲和叔叔都变成黑色,区分辈分,爷爷也要从黑色变成红色,区分辈分)
image-20210718215331500
image-20210718220001335
image-20210718220226766
3.零钱兑换(完全背包最值)*
image-20210718225517361
典型的01完全背包,dp[i]表示组成金额为i,最少需要多少枚硬币。括号里第一个dp[i]如果小,表示无法组成,dp[i - coins[i]] + 1表示当前金额减去当前硬币金额后所需的最少数量已经计算出来了,而且当前硬币金额小于amout,可以兑换一个,那么+1;
注意点是dp[]大小要设置成amount+1,不能是amount,会导致少算一次。
然后在初始化的时候第一次用Integer.MAX_VALUE,后面+1后就溢出了,不好判断。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution {public int coinChange (int [] coins, int amount) {int max = amount + 1 ;int [] dp = new int [amount + 1 ];0 ] = 0 ;for (int i= 1 ; i <= amount; i++) {for (int coin : coins) {if (i >= coin) {1 );return dp[amount] > amount ? -1 : dp[amount];
4.变位数组
image-20210718232550508
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams (String[] strs) {new HashMap <>();for (String s : strs) {char [] chars = s.toCharArray();String newStr = String.valueOf(chars);new ArrayList <>());new ArrayList <>();for (Map.Entry<String, List<String>> entry : map.entrySet()) {return res;
5.除自身以外数组的乘积
image-20210720172007105
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public int [] productExceptSelf(int [] nums) {int [] l = new int [nums.length];int [] r = new int [nums.length];0 ] = 1 ;for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length;i++) {1 ] * nums[i-1 ];1 ] = 1 ;for (int i = nums.length - 2 ; i >= 0 ;i--) {1 ] * nums[i + 1 ];int [] res = new int [nums.length];for (int i = 0 ; i<nums.length; i++) {return res;
用左右数组保存索引为i的左右两边的乘积。
6.LRU
缓存设计(数据结构,优先队列)*
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 import java.util.*;public class Solution {static class ListNode {int key;int value;public ListNode () {};public ListNode (int key, int value) {this .key = key;this .value = value;private Map<Integer, ListNode> map = new HashMap <>();int size = 0 ;int cap;final ListNode head = new ListNode (-1 ,-1 );final ListNode tail = new ListNode (-1 ,-1 );public Solution () {public int [] LRU (int [][] operators, int k) {this .cap = k;int m = operators.length;int n = operators[0 ].length;int len = (int )Arrays.stream(operators).filter(x -> x[0 ] == 2 ).count();int [] res = new int [len];for (int i=0 , j = 0 ;i < m ; i++) {if (operators[i][0 ] == 1 ) {1 ],operators[i][2 ]);else {1 ]);return res;public int get (int key) {ListNode node = map.get(key);if (node == null ) {return -1 ;return node.value;public void put (int key, int value) {ListNode node = map.get(key);if (node == null ) {new ListNode (key, value);if (size > cap) {else {public void moveToHead (ListNode node) {public void removeNode (ListNode node) {public void addNode (ListNode node) {
注意添加和删除的顺序,以及size++和size--的位置,把移动到队首分解为删除节点然后添加节点。
链表ListNode存储的是节点顺序,作用就是记录使用的长短,从队尾入队,队首出队。
HashMap存储的是(ListNode.key,ListNode)。
删除的时候记得链表和Map都要删除,但是size只是-1;
7.最小K个数(大根堆)
找出一组数的最小的k个数。
import java.util.*;public class Solution {public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution (int [] input, int k) {new PriorityQueue <>(k, (o1, o2) -> o2 - o1);for (int num : input) {return new ArrayList <>(maxHeap);
使用大根堆进行操作,个数满了的时候移除掉最大的元素。
使用了
PriorityQueue<Integer> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>(k, (o1, o2) -> o2 - o1);lambda表达式,匿名Comparator,o2-o1表示从大到小。
8.二叉树层序遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 import java.util.*;public class Solution {public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList ();if (root == null ) return res;new LinkedList <TreeNode>();while (!q.isEmpty()){int n = q.size();new ArrayList <>();for (int i = 0 ;i < n;i ++){TreeNode node = q.poll();if (node.left != null ) q.add(node.left);if (node.right != null ) q.add(node.right);return res;
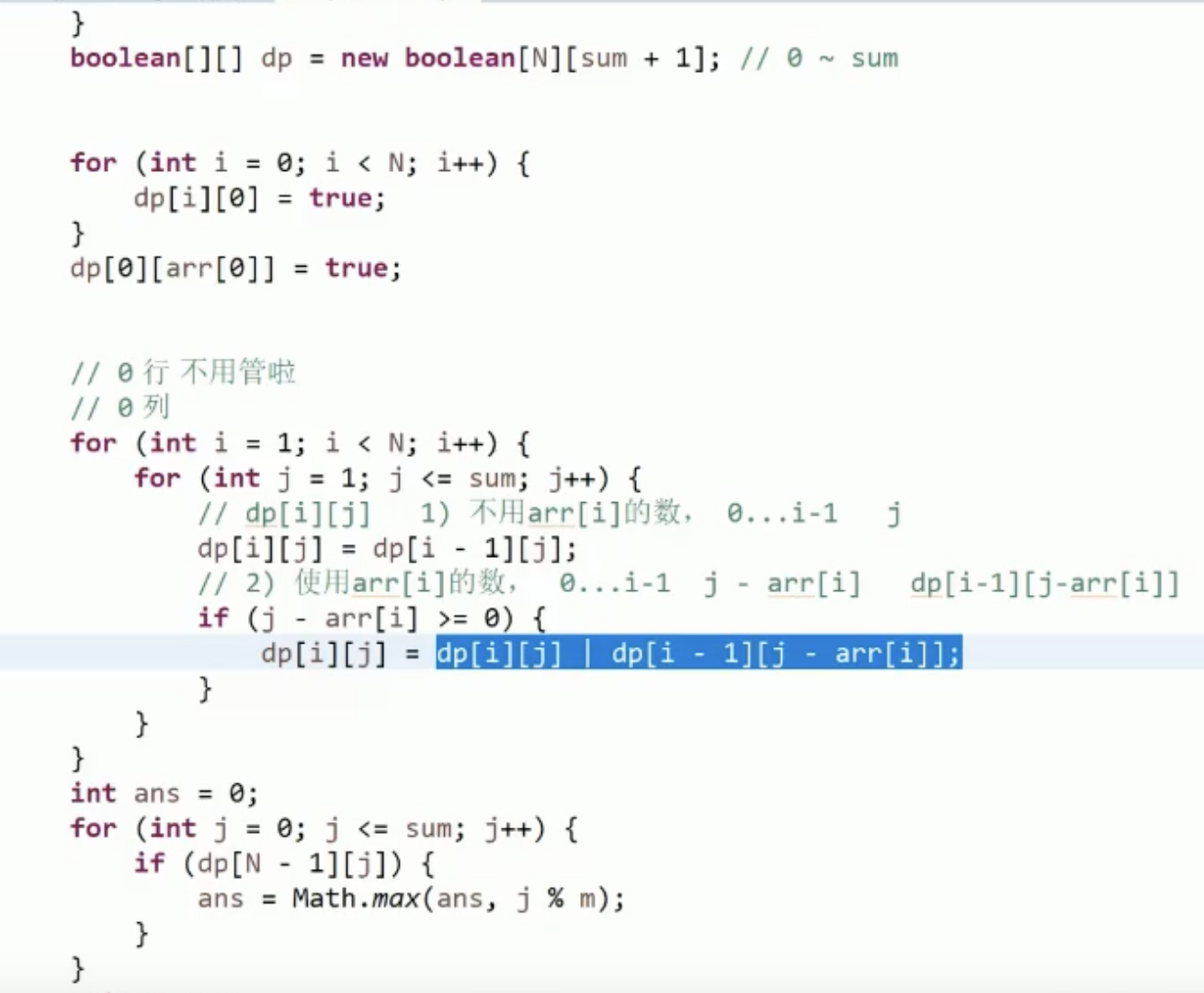
9.分割等和子集(背包问题)*
image-20210722225638064
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution {public boolean canPartition (int [] nums) {int sum = Arrays.stream(nums).sum();if (sum % 2 != 0 ) {return false ;int subSum = sum / 2 ;boolean [] dp = new boolean [sum];0 ] =true ;for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length;i++) {for (int j = subSum; j >= nums[i];j--) {return dp[subSum];
10.背包问题总结
P、NP、NPC。
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/coin-change/solution/yi-pian-wen-zhang-chi-tou-bei-bao-wen-ti-sq9n/
10.1背包问题分类
1、0/1背包问题:每个元素最多选取一次
2、完全背包问题:每个元素可以重复选择
3、组合背包问题:背包中的物品要考虑顺序
4、分组背包问题:不止一个背包,需要遍历每个背包
而每个背包问题要求的也是不同的,按照所求问题分类,又可以分为以下几种:
1、最值问题:要求最大值/最小值 2、存在问题:是否存在…………,满足…………
3、组合问题:求所有满足……的排列组合
因此把背包类型和问题类型结合起来就会出现以下细分的题目类型:
1、0/1背包最值问题 2、0/1背包存在问题 3、0/1背包组合问题
4、完全背包最值问题 5、完全背包存在问题 6、完全背包组合问题
7、分组背包最值问题 8、分组背包存在问题 9、分组背包组合问题
这九类问题我认为几乎可以涵盖力扣上所有的背包问题
10.1.1分类解题模板
背包问题大体的解题模板是两层循环,分别遍历物品nums和背包容量target,然后写转移方程,
根据背包的分类我们确定物品和容量遍历的先后顺序,根据问题的分类我们确定状态转移方程的写法
首先是背包分类的模板:
1、0/1背包:外循环nums数组,内循环target数组,target倒序且target>=nums[i];
2、完全背包:外循环nums,内循环target,target正序且target>=nums[i];
3、组合背包(考虑顺序):外循环target,内循环nums,target正序且target>=nums[i];
4、分组背包:这个比较特殊,需要三重循环:外循环背包bags,内部两层循环根据题目的要求转化为1,2,3三种背包类型的模板
然后是问题分类的模板: 1、最值问题:
dp[i] = max/min(dp[i], dp[i-nums]+1)或dp[i] = max/min(dp[i], dp[i-num]+nums);
2、存在问题(bool):dp[i]=dp[i]||dp[i-num];
3、组合问题:dp[i]+=dp[i-num];
这样遇到问题将两个模板往上一套大部分问题就可以迎刃而解
10.2 0/1背包组合问题
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/target-sum/
image-20210723163416186
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution {public int findTargetSumWays (int [] nums, int target) {if (nums == null || nums.length == 0 ) return 0 ;int sum = Arrays.stream(nums).sum();if ((sum + target) % 2 != 0 || sum < target) {return 0 ;int xSum = (target + sum) / 2 ;int [] dp = new int [xSum + 1 ];0 ] = 1 ;for (int num : nums) {for (int i = xSum; i >= num; i--) {return dp[xSum];
数组中包含正数和x,负数和y(y<0),两部分加起来等于target。我们想要忽略掉负数和,因为dp数组表示负数不好表示。那么我们得到
x+y = target
此时x,y都是未知,那么我们需要替换掉一个,而x-y=sum,sum是很好求的,那么替换掉负数和y,x+x-target=sum,即x = (target+sum)/2。我们只需要求正数和为x的组合即可。
dp[i]就表示和为i的组合数。根据01组合背包的公式:dp[i]+=dp[i - num],即可得到状态转移方程。
而01背包外层循环nums数组,内层反向循环target数组(0-x所有数字的数组)。
10.3 完全背包最值问题
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/perfect-squares/
image-20210723171730997
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution {public int numSquares (int n) {if (n < 1 ) return 0 ;int [] dp = new int [n + 1 ];for (int i = 1 ;i <= n; i++) {for (int j = 1 ;i - j * j >= 0 ; j++) {1 );return dp[n];
注意for循环内层的顺序,以及边界条件,
i - j * j >=0表示将i从j^2开始减,直到i = 0减完。
11.单源最短路径
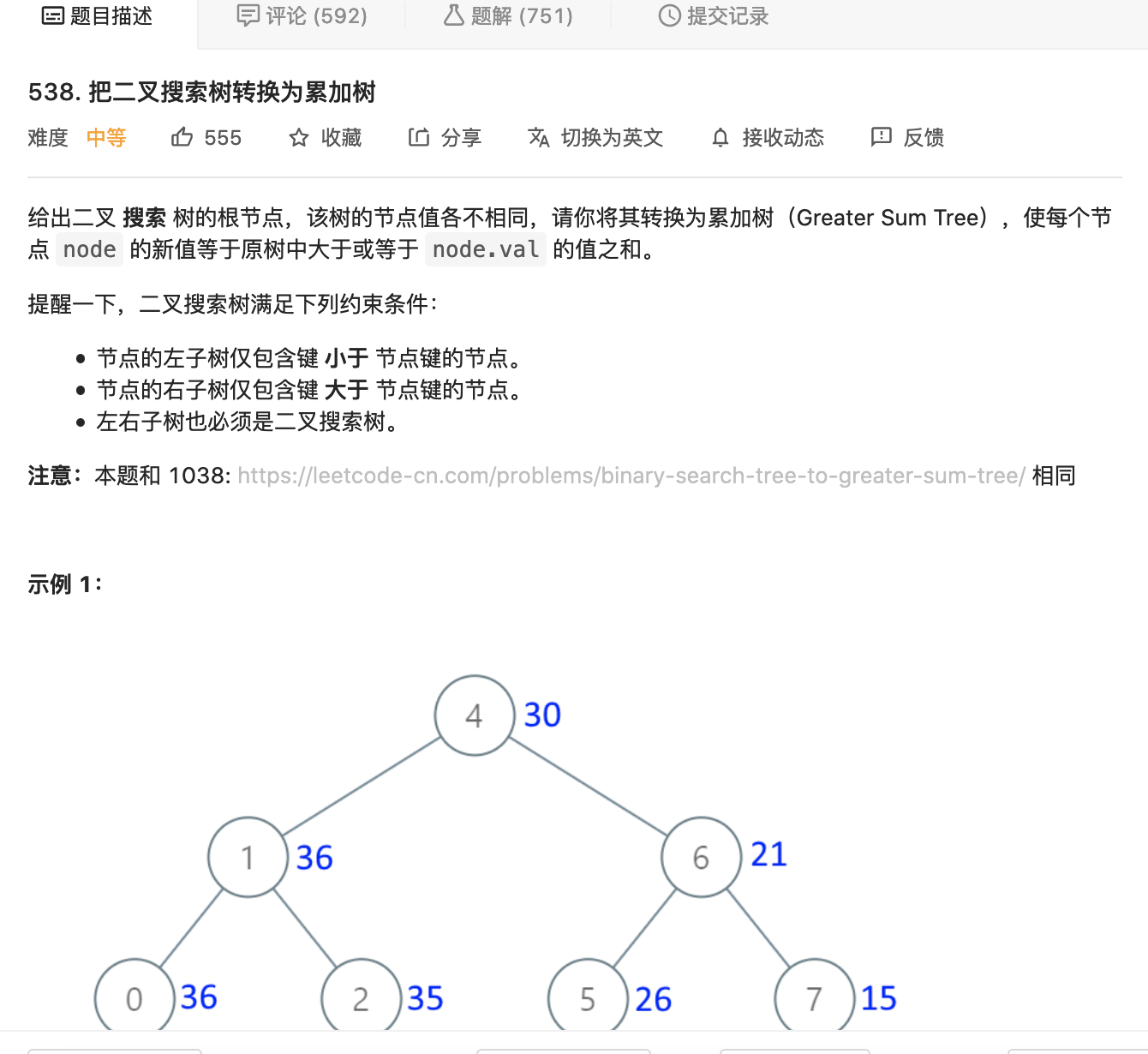
12.把二叉搜索树转换为累加树(中序遍历)
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/convert-bst-to-greater-tree/
image-20210723173453761
即当前节点的值为,所有比当前节点值大的节点值之和。
二叉排序树中序遍历从小到大,那么逆中序遍历(非后序遍历)就是从大到小。然后我们将遍历过的节点依此相加到前一个节点就可以完成。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution {int score = 0 ;public TreeNode convertBST (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) return null ;if (root.right != null ) {if (root.left != null ) {return root;
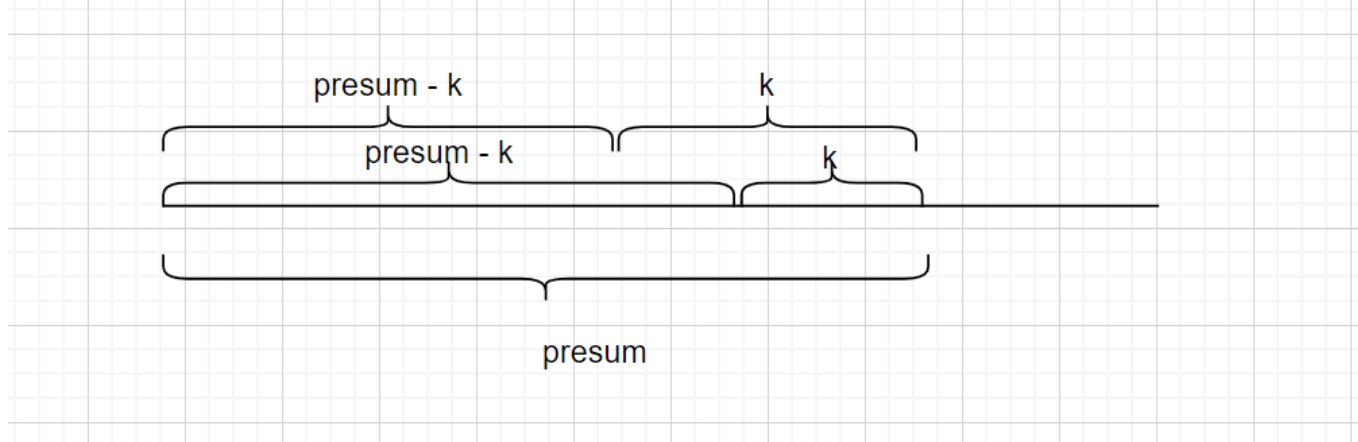
13.和为k的数组(前缀和)
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/subarray-sum-equals-k/
image-20210723183823657
知识点:前缀和
前缀和+HashMap:时间复杂度(O(n))。
跟两数之和类似,对于区间0-i,要得到k,只需要判断map是否包含0-i区间和减去k是否存在即可。 类似两数之和只需要判断是否存在和减去当前数即可。
image-20210723183648913
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution {public int subarraySum (int [] nums, int k) {if (nums == null ) return 0 ;int count = 0 ;int n = nums.length;new HashMap <>();0 , 1 );int sum = 0 ;for (int num : nums) {if (map.containsKey(sum - k)) {0 ) + 1 );return count;
暴力枚举法:时间复杂度(O(n^2))
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public int subarraySum (int [] nums, int k) {if (nums == null ) return 0 ;int count = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) {int sum = nums[i];if (sum == k) {for (int j = i+1 ; j < nums.length;j++) {if (sum == k) {return count;
14.找到字符串中所有字母异位词(滑动窗口)
image-20210724223335709
第一想法就是按照p的长度进行搜索,不过每次搜索为了判断是否一致都需要将数组排序后再转成字符串,时间复杂度O(n),但是耗时2200ms。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution {public List<Integer> findAnagrams (String s, String p) {new ArrayList <>();int m = s.length();int n = p.length();char [] pChars = p.toCharArray();String word = new String (pChars);for (int i = 0 ; i <= m - n;i++) {char [] sChars = s.substring(i, i + n).toCharArray();if (word.equals(new String (sChars))) {continue ;return res;
15.单调栈
单调栈分为单调递减栈和单调递增栈,什么场景用什么栈需要区分清楚。
判别是否需要使用单调栈,如果需要找到左边或者右边第一个比当前位置的数大或者小,则可以考虑使用单调栈;单调栈的题目如矩形米面积等等
image-20210724230857574
15.1 每日温度
image-20210725092454906
使用单调递增栈(栈顶到栈底)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution {public int [] dailyTemperatures(int [] temperatures) {int n = temperatures.length;new Stack ();int [] res = new int [n];for (int i = 0 ; i< n;i++) {int temperature = temperatures[i];while (!s.isEmpty() && temperature > temperatures[s.peek()]) {int lastBigger = s.pop();return res;
15.2 接雨水(hard)
image-20210725100710487
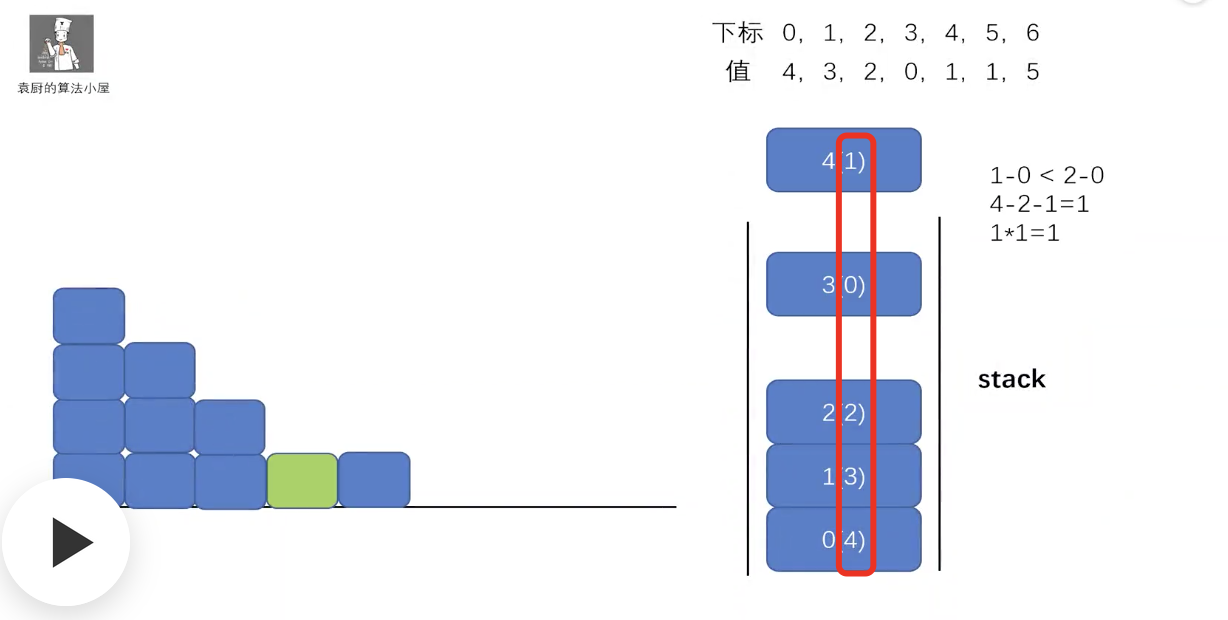
根据短板效应,使用递增栈,1、2、3、4、5;栈中存储的是索引,对应的高度由height[i]确定
image-20210725101233689
如果当前元素比栈顶小,则直接入栈。
如果当前元素比栈顶大,那么取出栈顶元素,肯定为低谷。
如当前栈元素为 2、3、4。那么取出的就是2;
然后再取出下一个栈顶元素(peek),即3;
那么当前元素、2、3 就组成了一个坑洼 .
然后就可以计算这个坑洼可以接多少水。
高度即(Math.min(当前元素高度-2), 3-2);
宽度即坑洼底端的长度。即3的索引 - 当前位置索引
-1 ,如上图绿色位置的宽度即 4 - 2 - 1 = 1.
然后保存结果。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution {public int trap (int [] height) {int n = height.length;new Stack ();int res = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ;i < n; i++) {while (!s.isEmpty() && height[i] > height[s.peek()]) {int popIdx = s.pop();while (!s.isEmpty() && height[popIdx] == height[s.peek()]) {if (!s.isEmpty()) {int temp = height[s.peek()];int resHeight = Math.min(height[i] - height[popIdx], temp - height[popIdx]);int width = i - s.peek() - 1 ;return res;
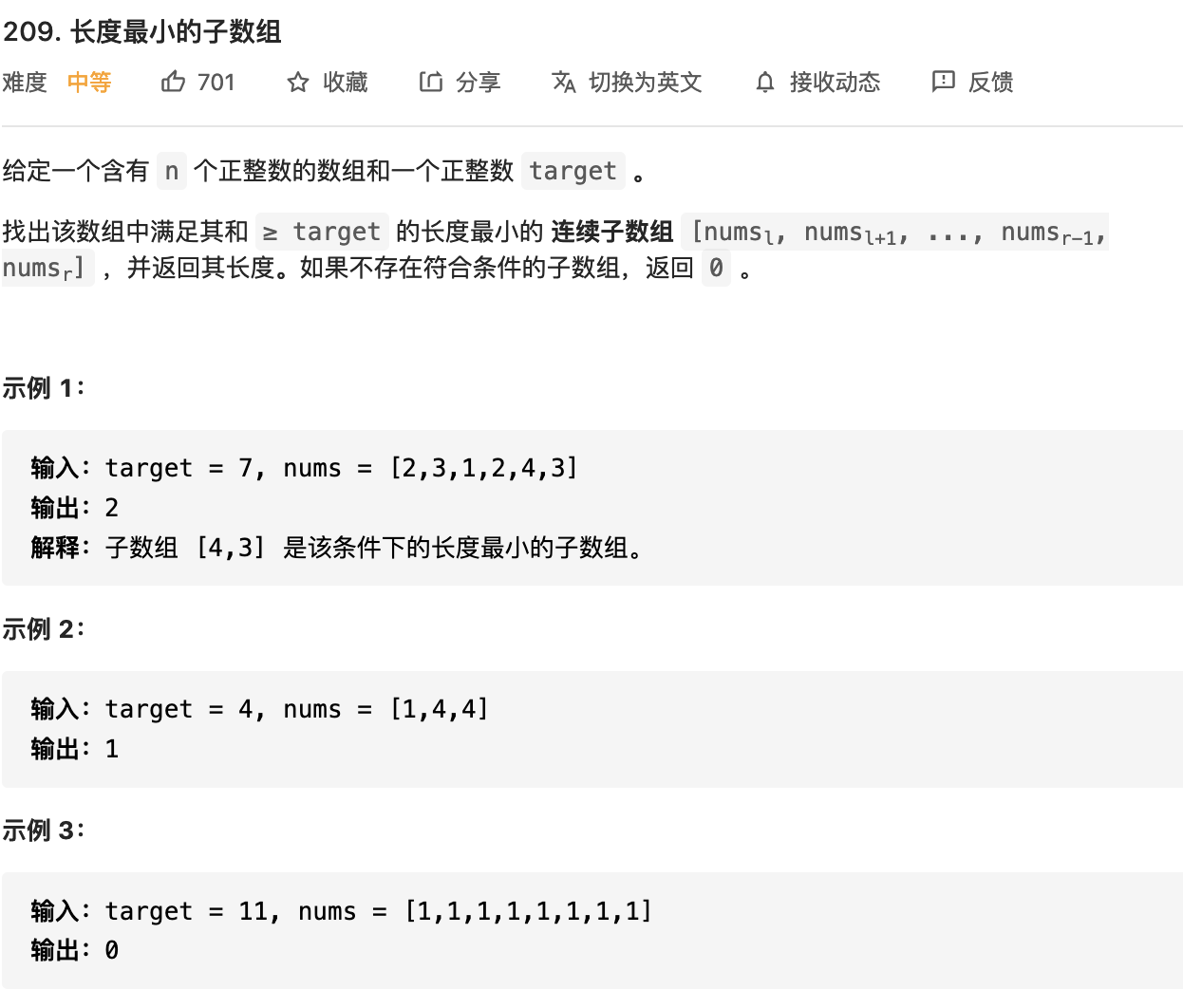
16.长度最小的子数组(滑动窗口、前缀和)
前缀和:数组前i个数的和组成新的数组。如果是正数,所以一般递增,可以考虑使用二分法。
涉及连续子数组的问题,我们通常有两种思路:一是滑动窗口、二是前缀和。
image-20210726171538696
只需要最小的长度,且子数组连续,可以使用滑动窗口,当sum <
target的时候 right++,当sum ==
target的时候,取长度最小值,不结束,然后right++。当sum >
target的时候,sum -= nums[left],left++;
注意边界值,退出的条件:right > nums.length
滑动窗口:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public int minSubArrayLen (int target, int [] nums) {if (nums.length == 0 ) return 0 ;int left = 0 ;int right = 0 ;int minLength = 0 ;int n = nums.length;int sum = 0 ;while (right < n) {while ( sum >= target) {0 ? right - left + 1 : Math.min(right - left + 1 , minLength);return minLength;
前缀和
很巧妙的一个是利用了二分法,然后查询中间子数组的时候不变nums而变target,让newTarget
= target + sums[i-1],
newTarget就是从i-1开始查找的值,相当于从第一个元素开始查找的target。
还有注意到是当未查找到时候不能直接跳过,而需要继续进行比较。
-mid-1 可以用 ~mid取反操作代替。
我们只需要找到 sums[k]-sums[j]>=s,那么 k-j
就是满足的连续子数组,但不一定是最小的,所以我们要继续找,直到找到最小的为止。怎么找呢,我们可以使用两个
for 循环来枚举,但这又和第一种暴力求解一样了,所以我们可以换种思路,求
sums[k]-sums[j]>=s 我们可以求
sums[j]+s<=sums[k],那这样就好办了,因为数组sums中的元素是递增的,也就是排序的,我们只需要求出
sum[j]+s 的值,然后使用二分法查找即可找到这个 k。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution {public int minSubArrayLen (int target, int [] nums) {int n = nums.length;int [] sums = new int [n + 1 ];int sum = 0 ;int minLength = Integer.MAX_VALUE;for (int i = 1 ;i<= n; i++) {1 ] + nums[i - 1 ];for (int i = 1 ;i <=n; i++) {int newTarget = target + sums[i - 1 ];int mid = Arrays.binarySearch(sums, newTarget);if (mid < 0 ) {1 ;if (mid <= n)1 );return minLength = = Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : minLength;
17. LIS
无重复的最长连续子数组(滑动窗口板子)
image-20210727163626121
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution {public int lengthOfLongestSubstring (String s) {if (s.length() == 0 ) {return 0 ;int left = 0 ;int right = 0 ;int max = 0 ;new HashMap <>();while (right < s.length()) {char c = s.charAt(right);if (map.containsKey(c)) {1 , left);1 );return max;
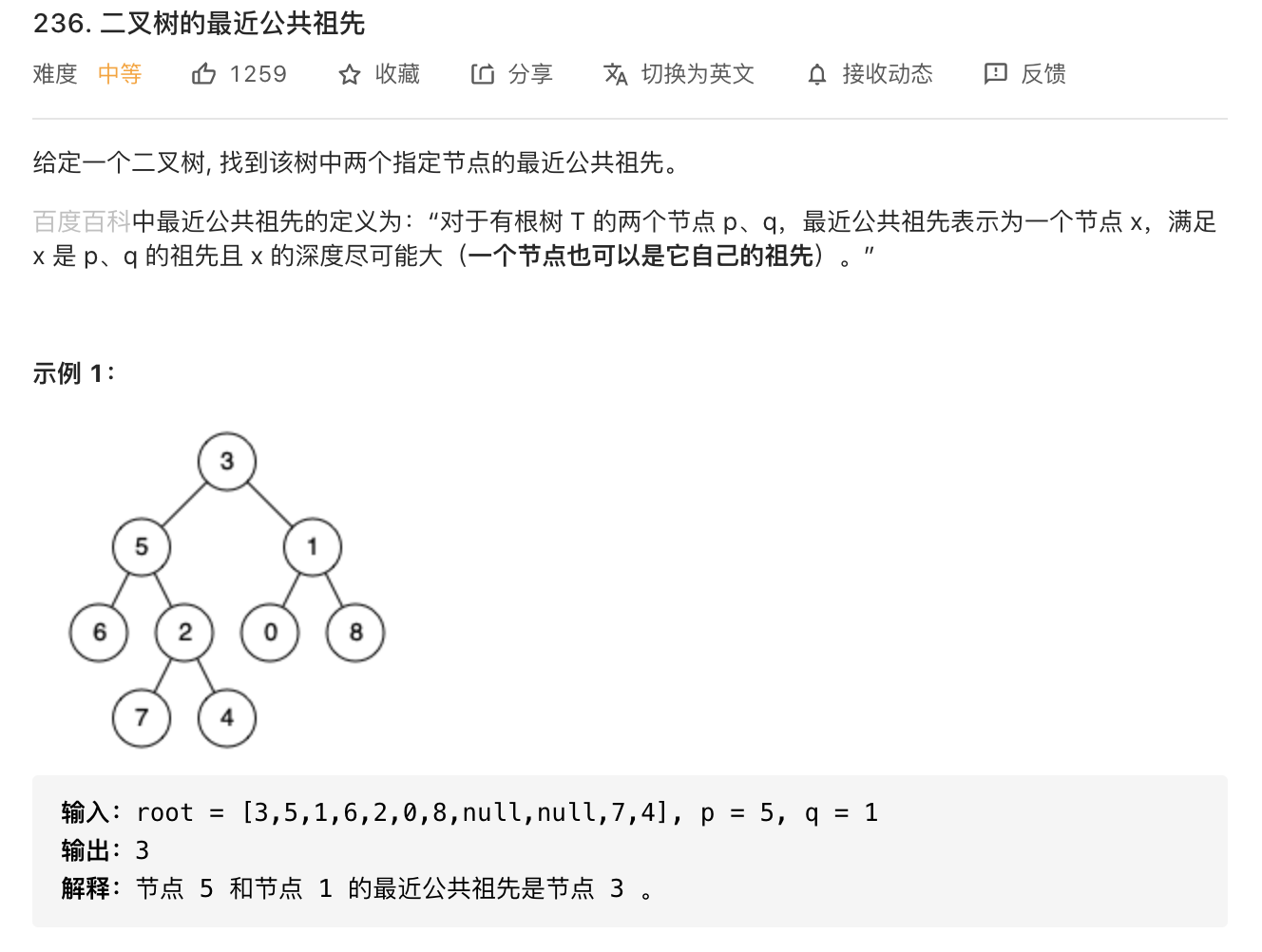
18. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution {public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (root == null || p == null || q == null ) {return null ;if (root == p || root == q) {return root;TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p , q);TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);if (left != null && right != null ) return root;if (left != null ) return left;if (right != null ) return right;return null ;
19 相交链表
public class Solution {public ListNode getIntersectionNode (ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {if (headA == null || headB == null ) return null ;ListNode pA = headA;ListNode pB = headB;while (pA != pB) {null ? headB : pA.next;null ? headA : pB.next;return pA;
左神算法笔记
1。
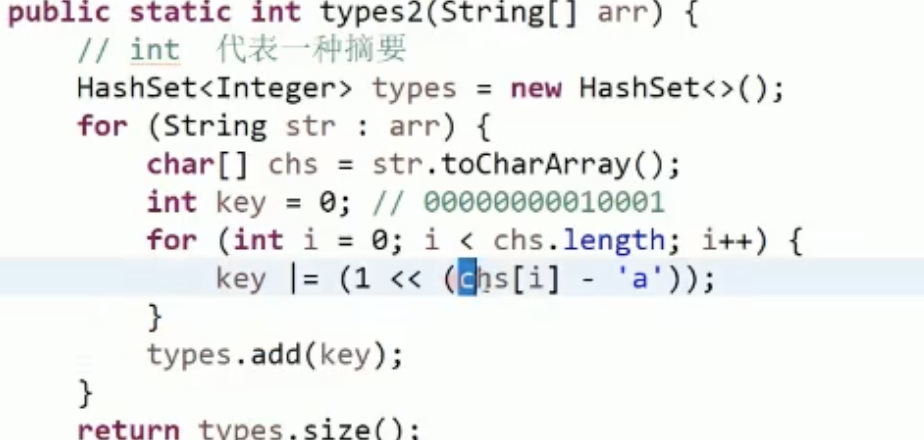
image-20210731094636587
a-z一共26个字符,所以首先可以想到用26位的boolean数组代表每个字符是否出现过。
再优化,可以将数组优化为位运算。
image-20210731094809098
key |= (1 << (chs[i] - 'a'))表示出现一个字符,那么key
进行或操作,可以将该字符的位置置为1,最后每出现的位置不一样代表一个不同的组合。相当于把数组优化成为位运算,int
32位替代boolean[]数组,0和1代表false和true。
同理如果表示小写字母a-zA-Z,可以用long类型进行代替,long类型64位,足够。
image-20210731102300531
背包存在问题:
image-20210731101612484
image-20210731150053618
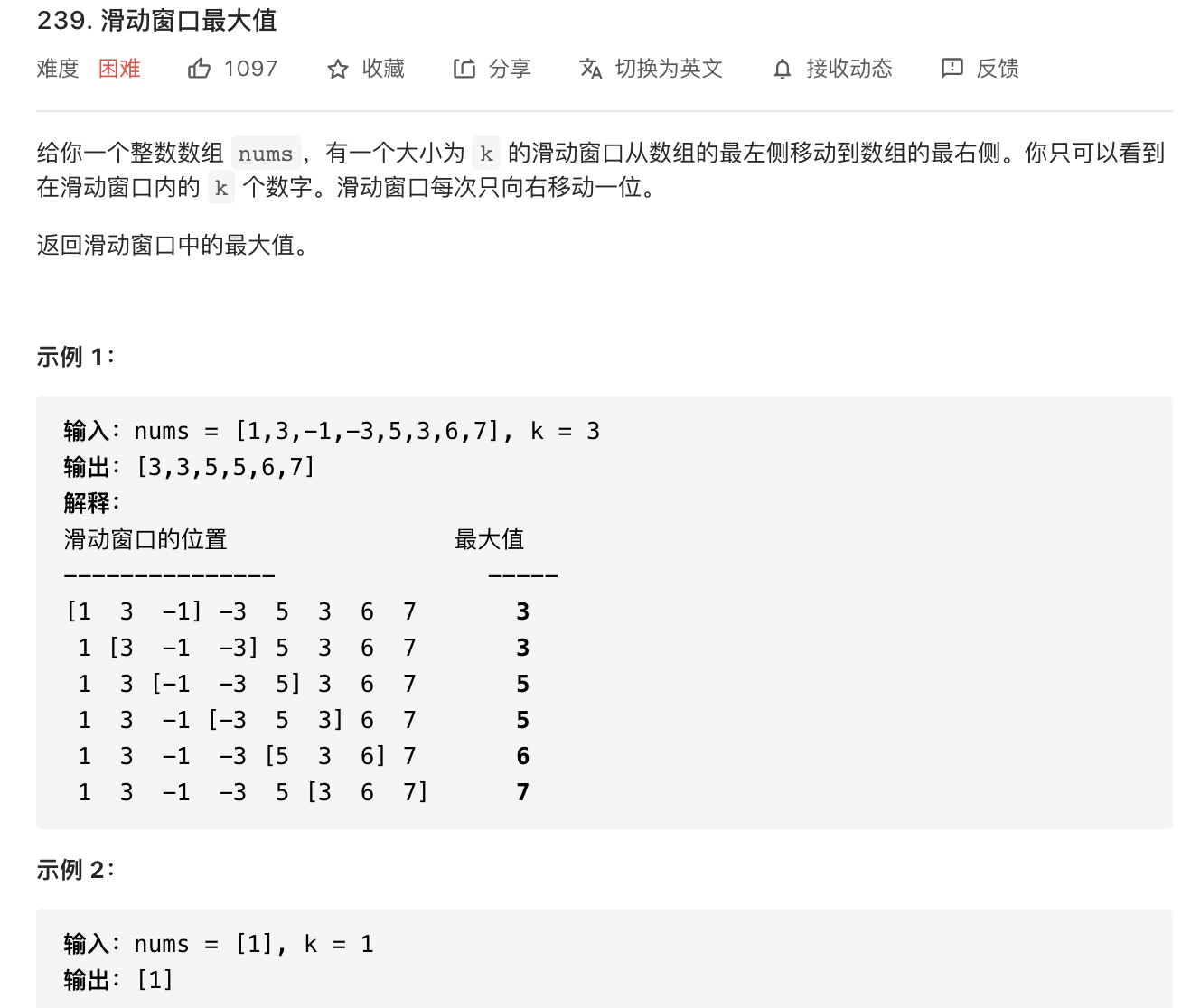
20.滑动窗口最大值(大根堆、单调队列、分块+预处理)
image-20210731160059157
一开始看错题意,求成了前i个最大的数字,使用了动态规划,有点尴尬。
暴力的话基本用例能过,但是后面会超时,时间复杂度是O(n^2);
方法一:使用大根堆,存储一个二元组(这个存储方式很方便,学习了 ),先按num降序排列,然后按照idx降序排列。滑动窗口每次移动都新加一个元素,然后查看堆顶元素的索引是否在窗口内,如果不在就抛弃掉。时间复杂度O(nlogn)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution {public int [] maxSlidingWindow(int [] nums, int k) {int n = nums.length;if (n == 1 || k == 1 ) return nums;int []> queue = new PriorityQueue <>((o1,o2) -> 0 ] != o1[0 ] ? o2[0 ] - o1[0 ] : o2[1 ] - o1[1 ]);int [] res = new int [n - k + 1 ];for (int i = 0 ; i < k; i++) {new int [] {nums[i], i});0 ] = queue.peek()[0 ];for (int i = 1 ; i < n - k + 1 ; i++) {new int [] {nums[i + k - 1 ], i + k -1 });while (!queue.isEmpty() && queue.peek()[1 ] < i) {0 ];return res;
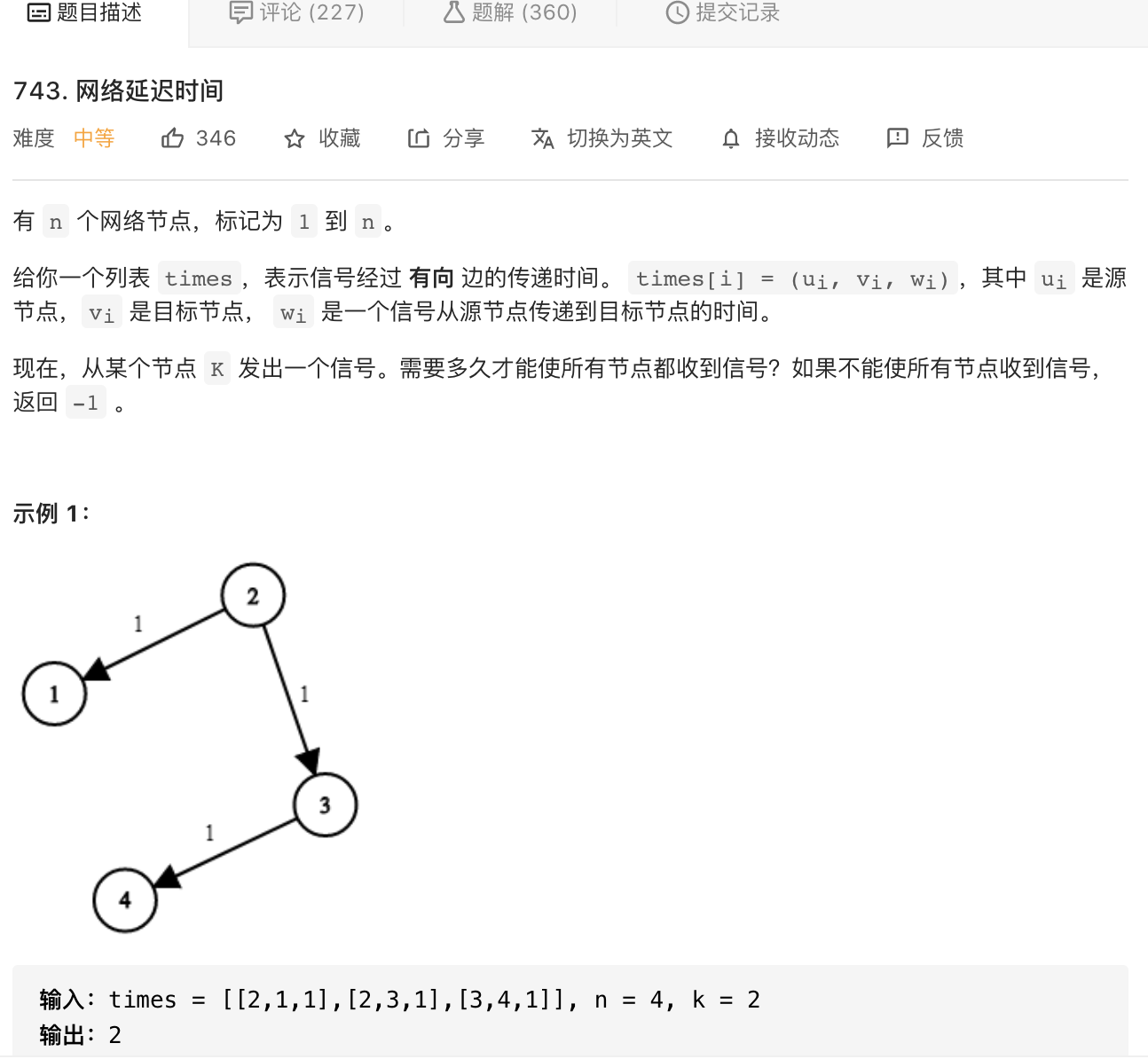
21.网络延迟时间(Dijkstra)
image-20210802160852717
主要学习Dijkstra算法,还可以使用优先队列优化,因为Dijkstra每次从未选择结点中距离最小的点开始,所以很适合使用小根堆进行存储。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 class Solution {public int networkDelayTime (int [][] times, int n, int k) {final int INF = Integer.MAX_VALUE / 2 ;int [][] g = new int [n][n];for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {for (int [] t : times) {0 ] - 1 ][t[1 ] - 1 ] = t[2 ];int dist[] = new int [n];1 ] = 0 ;boolean [] visited = new boolean [n];for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {int middle = -1 ;for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) {if (!visited[j] && (middle == -1 || dist[j] < dist[middle])) {true ;for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) {int res = Arrays.stream(dist).max().getAsInt();return res = = INF ? -1 : res;
22.分割回文串
image-20210802165349851
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();public List<List<String>> partition (String s) {int n = s.length();boolean [][] dp = new boolean [n][n];for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {true );for (int i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) {for (int j = i + 1 ; j < n; j++) {1 ][j - 1 ];0 ,n,new LinkedList <String>(),dp);return res;private void backTrack (String s, int i, int n,LinkedList<String> track, boolean [][] dp) {if (i == n) {new ArrayList <>(track));return ;for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {if (isHuiWen(dp,i,j)) {1 ));1 ,n,track,dp);public boolean isHuiWen (boolean [][] dp, int i, int j) {return dp[i][j];
23.圆环回原点问题
圆环上有10个点,编号为0~9。从0点出发,每次可以逆时针和顺时针走一步,问走n步回到0点共有多少种走法。
本题考察的是动态规划。
如果你之前做过leetcode的70题爬楼梯,则应该比较容易理解这题的思路:走n步到0的方案数=走n-1步到1的方案数+走n-1步到9的方案数。
因此,若设dp[i][j]为从0点出发走i步到j点的方案数,则递推式为:
ps: 公式之所以取余是因为j-1或j+1可能会超过圆环0~9的范围
参考代码
class Solution :def backToOrigin (self,n ):10 0 for i in range (length)] for j in range (n+1 )]0 ][0 ] = 1 for i in range (1 ,n+1 ):for j in range (length):1 ][(j-1 +length)%length] + dp[i-1 ][(j+1 )%length]return dp[n][0 ]
24.最长回文子串(动态规划)
image-20210809162416109
shopee一面,没怎么做出来,我和面试官思路不一样,导致面试官提示我修改的时候我一脸懵逼。
dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j - 1] && s[i] ==
s[j].表示从i到j的子串是不是回文串。
由于计算dp[i] 需要用到dp[i+1]. 所以选择从后往前遍历。
dp[i][j] = s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j) && (j - i + 1< 3 ||
dp[i + 1][j - 1]);
在首尾相等的时候, j-i+1 <3
表示长度为3,去掉首位后为1,必然是回文串,dp[i + 1][j - 1]
=true表示长度超过3,但是去掉首尾后也是回文串。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution {public String longestPalindrome (String s) {int n = s.length();String res = "" ;boolean [][] dp = new boolean [n][n];for (int i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) {for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {2 || dp[i + 1 ][j - 1 ]); if (dp[i][j] && j - i + 1 > res.length()) {1 );return res;
25.最长无重复子串(滑动窗口)
image-20210811210954661
快慢指针
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution {public int lengthOfLongestSubstring (String s) {if (s.length() == 0 ) return 0 ;int left = 0 ;int right = 0 ;int res = 0 ;new HashMap <>();0 ), 0 );while (right < s.length()) {char c = s.charAt(right);if (map.containsKey(c)) {1 , left);1 );return res;
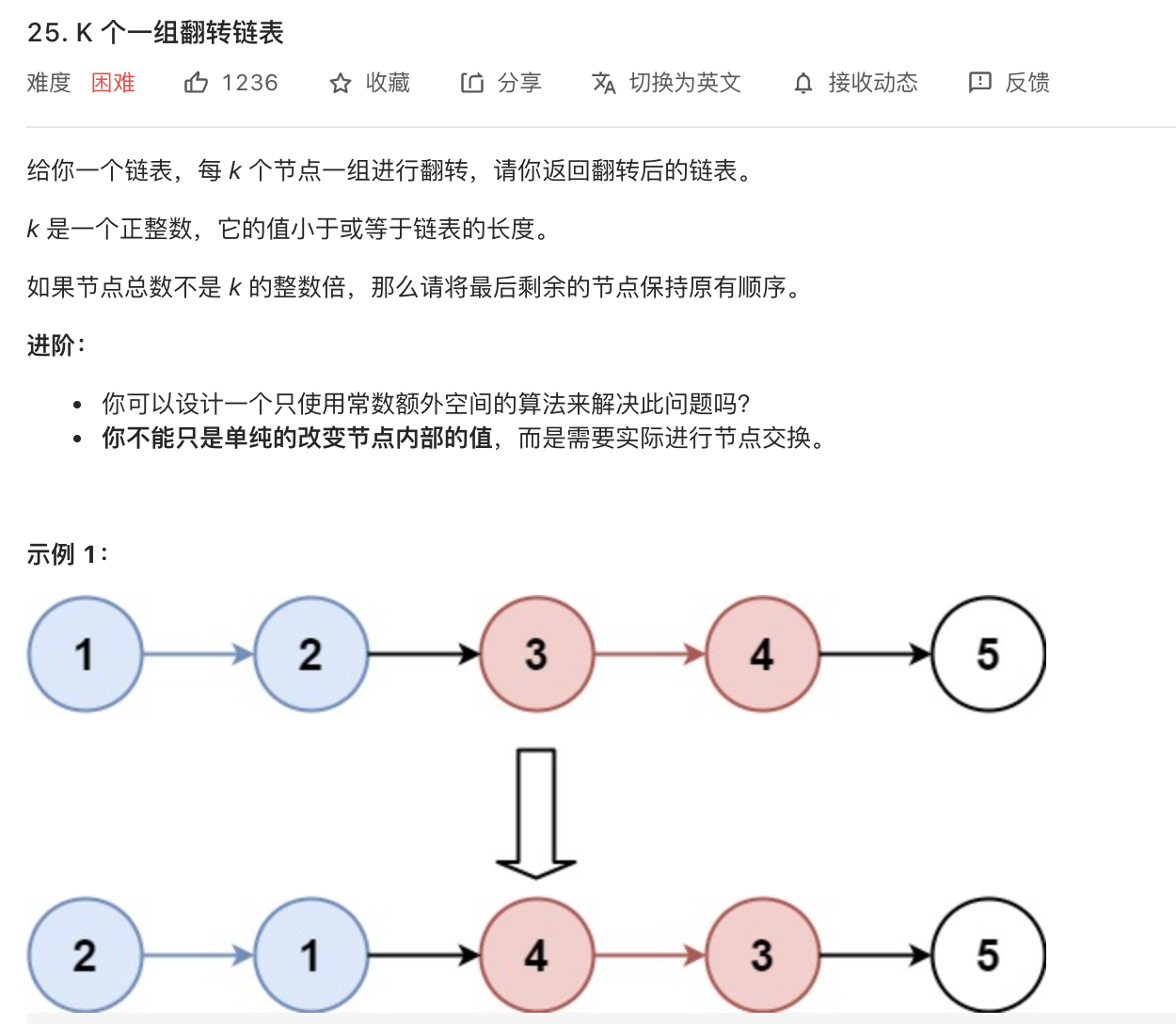
26.K个一组反转链表(迭代)
image-20210811223826336
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 **for singly-linked list.public class ListNode {int val;int x) { val = x; }class Solution {public ListNode reverseKGroup (ListNode head, int k) {if (head == null || head.next == null ){return head;new ListNode (0 );while (end.next!=null ){for (int i=0 ;i<k&&end != null ;i++){if (end==null ){break ;null ;return dummy.next;public ListNode reverse (ListNode head) {if (head == null || head.next == null ){return head;ListNode preNode = null ;ListNode curNode = head;ListNode nextNode = null ;while (curNode != null ){return preNode;
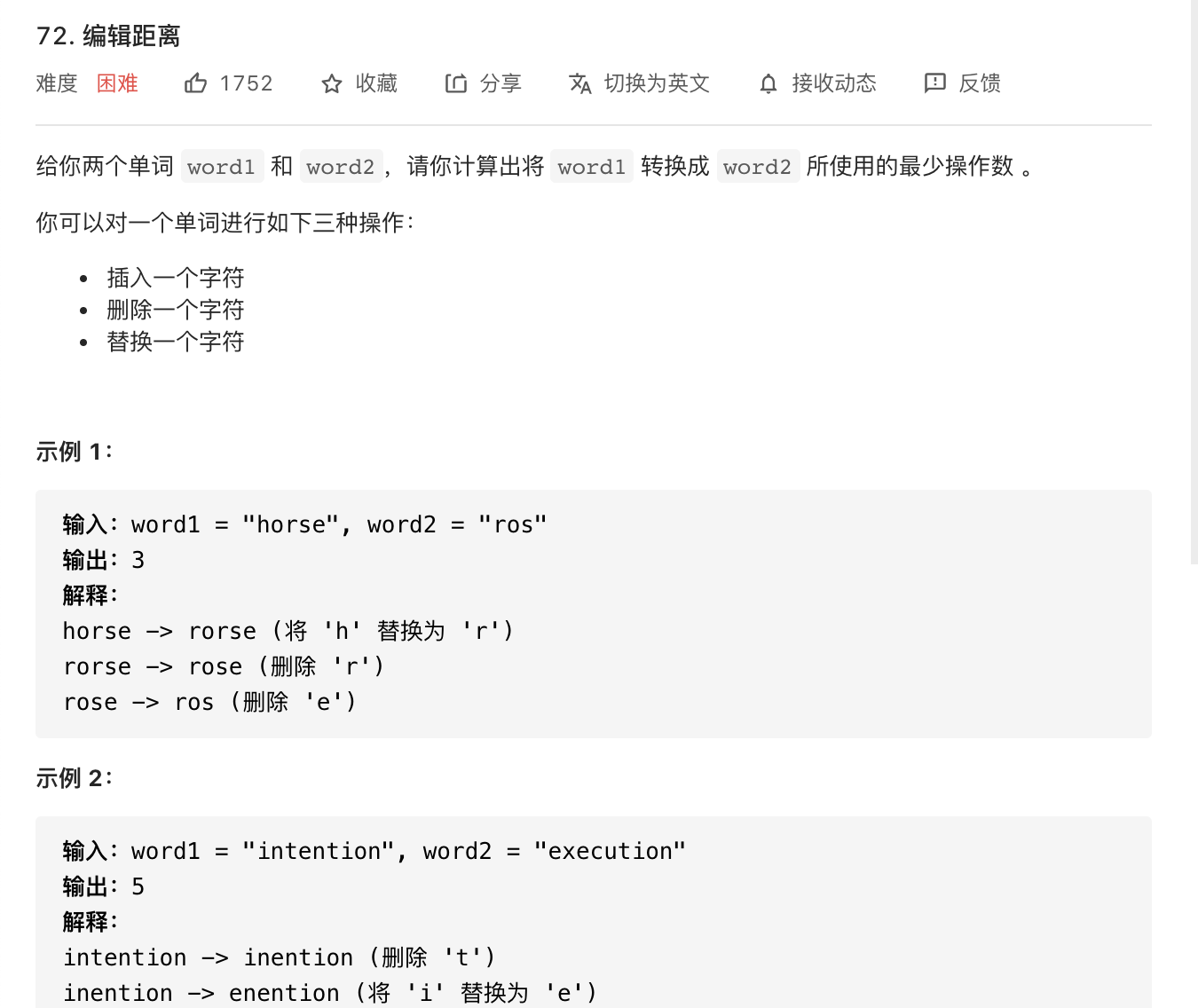
27.编辑距离*
image-20210812220723796
这道题比较难,但是是典型的动态规划。需要反复吃透。
要把一个单词变成另一个单词,先不考虑其他的,变成另一个单词前有哪几种状态?
题目提供了三种操作,那么最后也可以通过三种方式变换。
第一种,比word1少一个字符变为word2的步数+1,即只需要多删除一次。
第二种,word1变成word2少一位的步数+1,即只需要多插入一个。
第三种,word2变成和word2字符数一样的步数。分两种情况:最后一个字符相等,可以直接变换。不相等,多一次替换+1.
考虑初始化,任何空串到单词,和单词到空串,都需要删除或插入n次。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Solution {public int minDistance (String word1, String word2) {int m = word1.length();int n = word2.length();int [][] dp =new int [m + 1 ][n + 1 ];for (int i = 0 ; i <= n; i++ ) {0 ][i] = i;for (int j = 0 ; j <= m; j++) {0 ] = j;for (int i = 1 ; i <= m; i++) {for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j++) {if (word1.charAt(i - 1 ) == word2.charAt(j - 1 )) {1 ][j] + 1 , dp[i][j - 1 ] + 1 ), dp[i - 1 ][j -1 ]);else {1 ][j] + 1 , dp[i][j - 1 ] + 1 ), dp[i - 1 ][j -1 ] + 1 ); return dp[m][n];
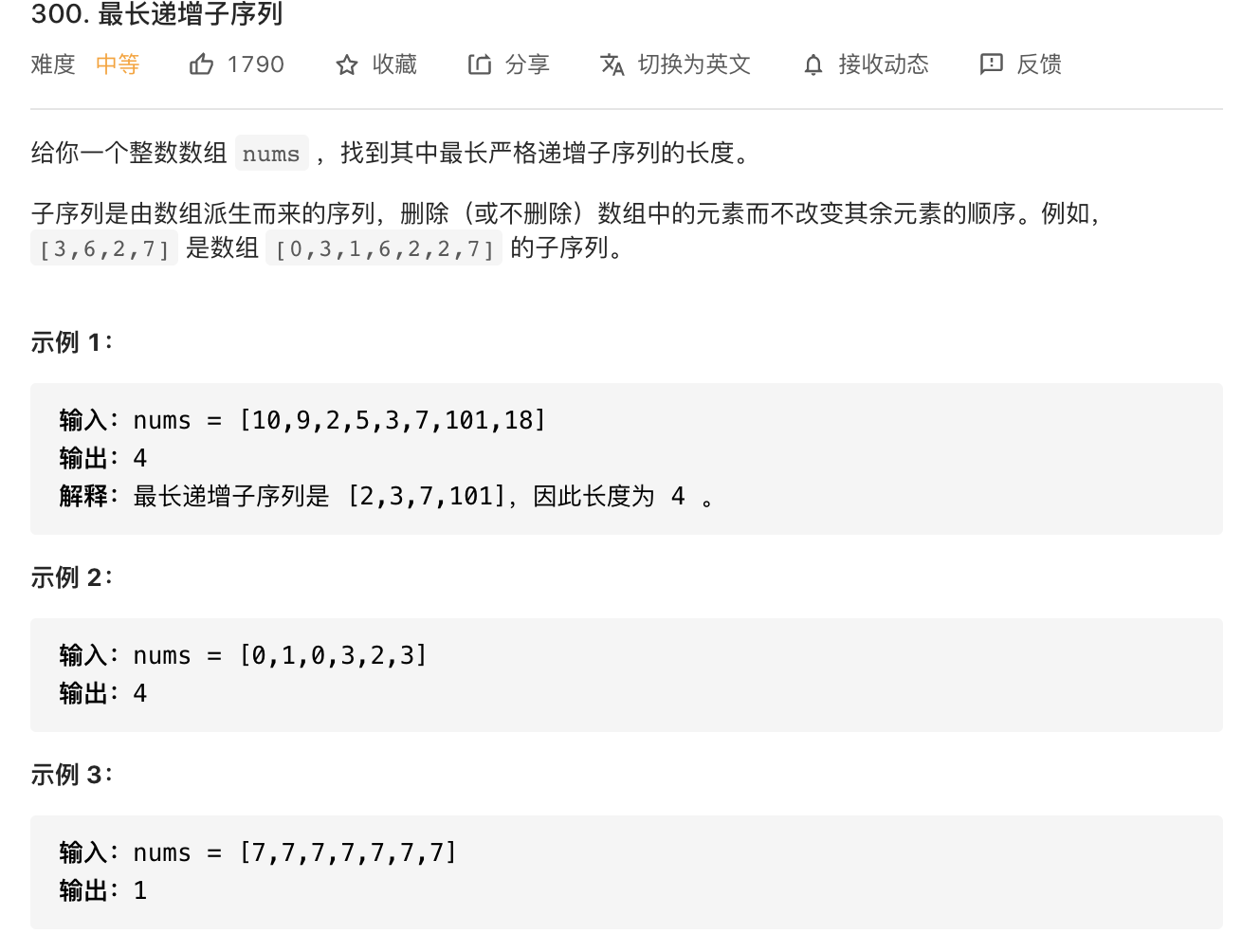
28.最长自增子序列(动态规划)
image-20210812232230313
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution {public int lengthOfLIS (int [] nums) {int n = nums.length;if (n <= 0 ) return 0 ;int [] dp = new int [n];1 );int res = 1 ;for (int i = 1 ; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0 ; j < i; j++) {if ( nums[j] < nums[i]) {1 );return res;
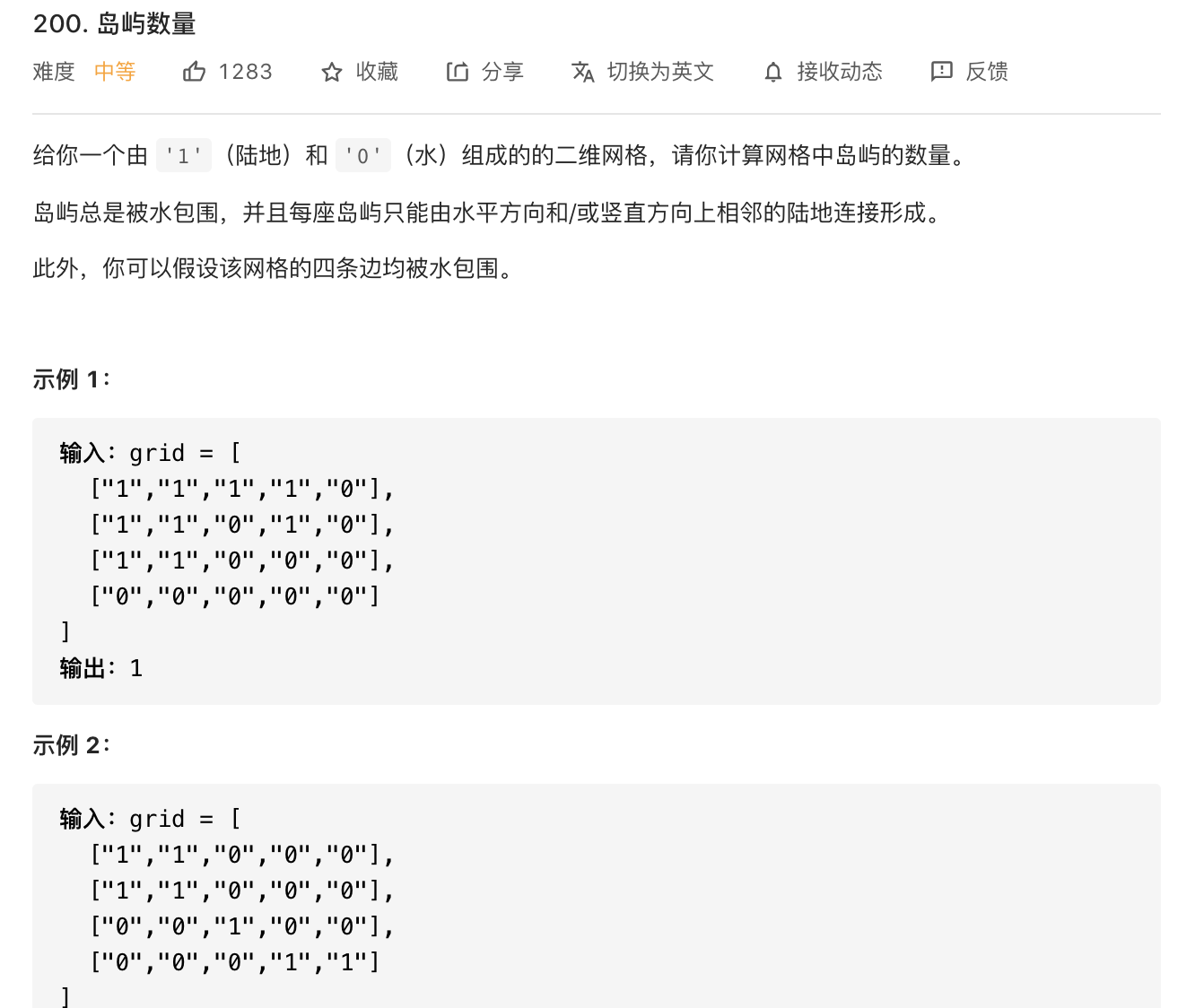
29.岛屿数量(DFS、并查集)
image-20210816225054217
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution {int m;int n;public int numIslands (char [][] grid) {0 ].length;int res = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) {for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) {if (grid[i][j] == '1' ) {return res;public void infect (char [][] grid, int i, int j) {if (i < 0 || i >= m || j < 0 || j >= n || grid[i][j] != '1' ) {return ;if (grid[i][j] == '1' ) {'2' ;1 , j);1 );1 , j);1 );
DFS的方法比较简单,主要学习并查集的方式。
并查集:并查集 是一种树型的数据结构,用于处理一些不交集(Disjoint
Sets)的合并及查询问题 。
特点:孩子节点保存父节点的指针。
无向图中(上图二维矩阵就可以看作一个无向图),如果两个元素有关联,那么将一个作为根节点,然后将其他元素指向根节点,如果两个元素连通,那么他们的最祖先的结点一定是一样的 。可以进行聚类。
在并查集中,每个集合的代表即是集合的根节点 。
“查找”根据其父节点的引用向根行进直到到底树根 。“联合”将两棵树合并到一起,这通过将一棵树的根连接到另一棵树的根 。
但是树可能不平衡,退化成链表。有两种优化方法:
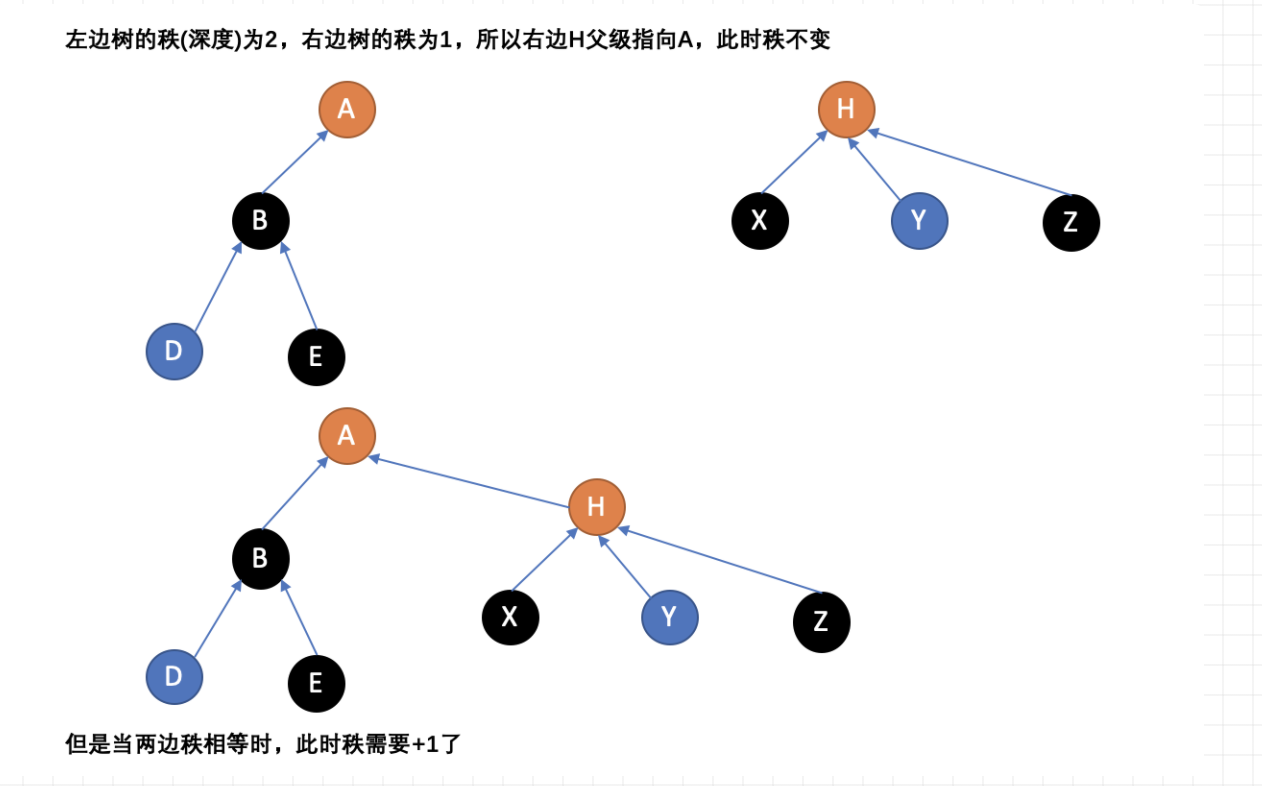
1.按秩合并(按深度合并):总是将更小的树连接至更大的树 。单元素的树的秩定义为0,当两棵秩同为r的树联合时,它们的秩r+1 。只使用这个方法将使最坏的运行时间提高至每个MakeSet、Union或Find操作
image-20210816225930951
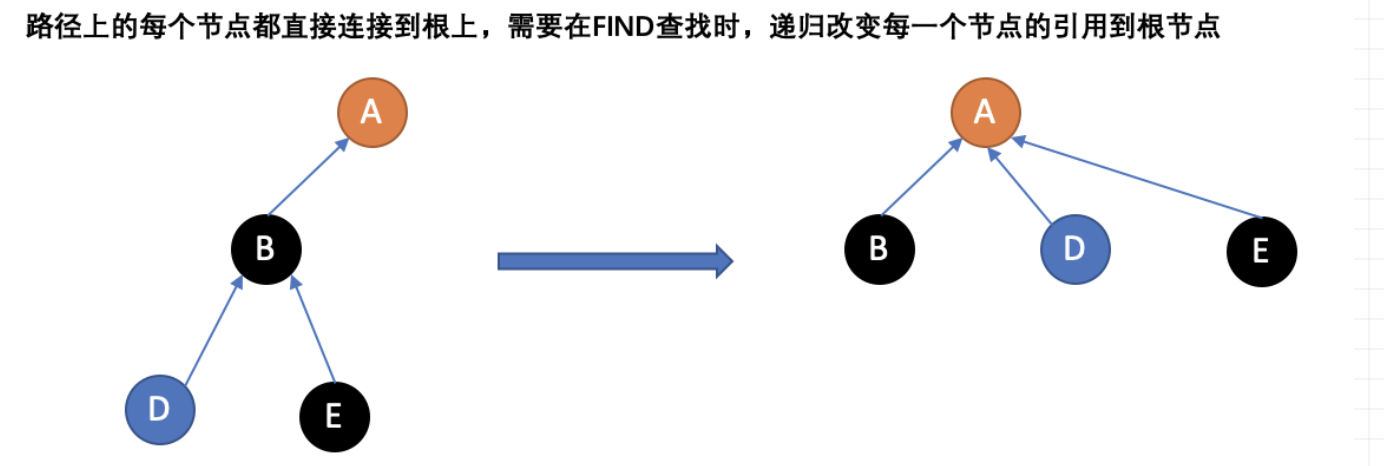
2.路径压缩。是一种在执行“查找”时扁平化树结构的方法。关键在于在路径上的每个节点都可以直接连接到根上
即把所有的孩子节点都连到最祖先节点上,树就变得很扁平化。
image-20210816230030139
30.三数之和(双指针)
image-20210818180147658
最开始想的是哈希表法,但是主要的点是去重,去重不方便。
既然寻找和为0,思路即遍历i,在i后面数组寻找和为 -nums[i]的组合。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();public List<List<Integer>> threeSum (int [] nums) {int n = nums.length;if (n <= 0 ) return new ArrayList ();for (int i = 0 ; i < n - 2 ; i++) {if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ]);if (nums[i] > 0 ) break ;int j = i + 1 ;int k = n - 1 ;int sum = nums[j] + nums[k];while (j < k) {if (sum == - nums[i]) {new ArrayList <>();while (j < k && nums[k] == nums[k - 1 ]) {while (j < k && nums[j] == nums[j + 1 ]) {else if ( sum > - nums[i]) {else {return res;
31. 计算带精度的开方(二分)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution {public int mySqrt (int x) {if (x == 1 ) return 1 ;double left = 1 ;double right = x;double newMid = 0.0 ;double mid = (left + right) / 2 ;while (left < right && Math.abs(newMid - mid) > 0.00001 ) {if (mid > x / mid) {else {2 ;return (int )mid;
32.搜索旋转排序数组
image-20210819161536022
二分法,虽然二分后一边不一定是有序数组,如 4 5 6, 7 1 2 3.但是 4 5
6是有序的,按照同样的思路再二分 7 1 2 3,得到 2 3是有序的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 class Solution {public int search (int [] nums, int target) {int n = nums.length;if (n <= 0 ) {return -1 ;if (n == 1 && nums[0 ] == target) {return 0 ;int left = 0 ;int right = n - 1 ;while (left <= right) {int mid = (left + right) / 2 ;if (nums[mid] == target) {return mid;if (nums[0 ] <= nums[mid]) {if (nums[0 ] <= target && target < nums[mid]) {1 ;else {1 ;else {if (nums[mid] < target && target <= nums[n - 1 ]) {1 ;else {1 ;return -1 ;
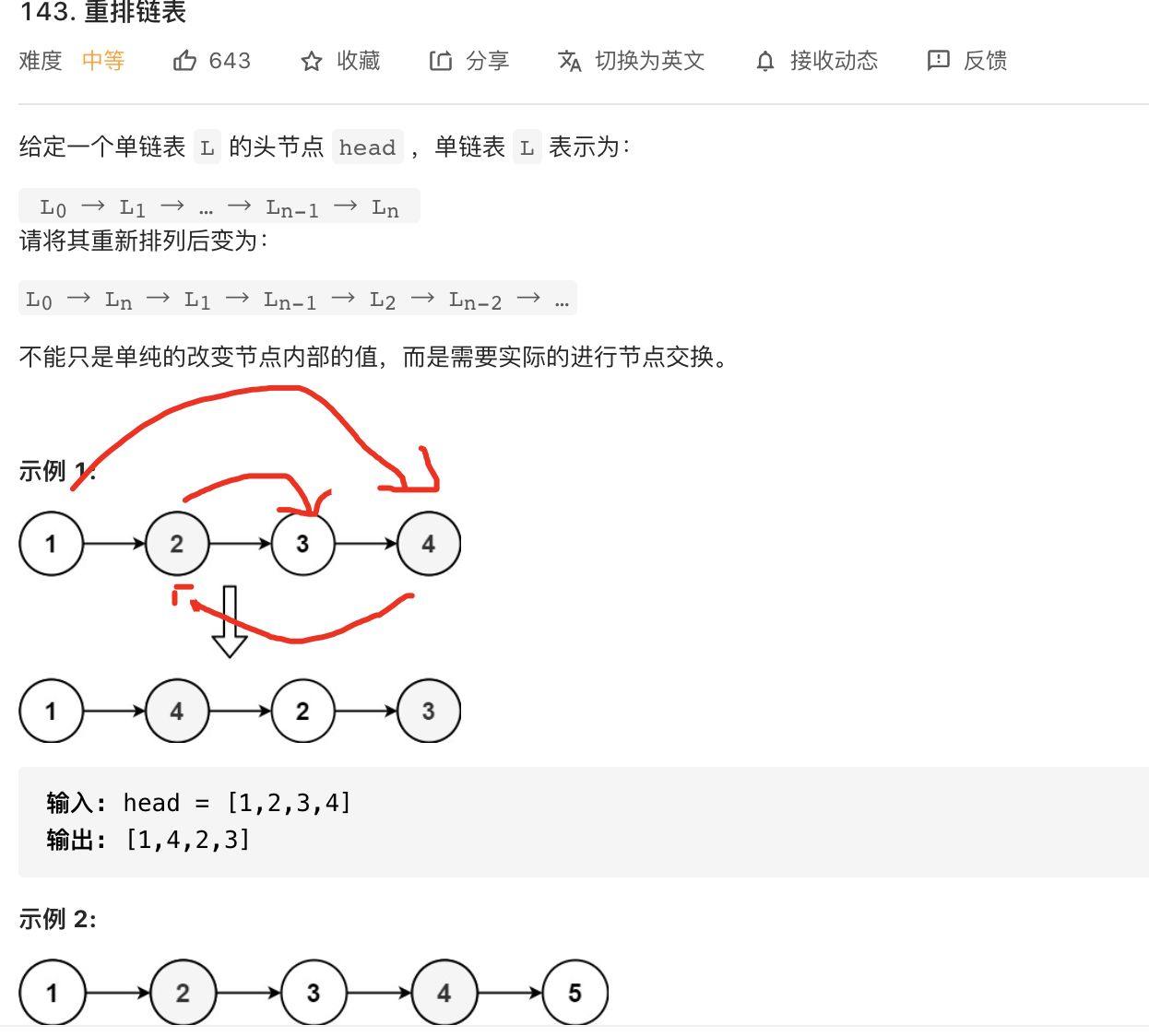
33.重排链表
image-20210819214009607
如图所示重排链表,类似一个环。
我的想法是把所有节点都存在list中,然后一次循环遍历i到 n
/2,根据索引来修改指针。
比较繁琐,而且需要消耗O(n)的空间。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 class Solution {public void reorderList (ListNode head) {new ArrayList <>();ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null ) {int n = list.size();for (int i = 1 ; i <= n / 2 ; i++) {null ;if (i != n / 2 ) {null ;if ( n % 2 != 0 ) {2 );null ;
优秀解法:不借助辅助空间。由于需要将前半段和后半段进行依次插入,所以先使用快慢指针找到链表的中点,分成两个链表,然后反转后半段链表,最后按次序合并两个链表。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 class Solution {public void reorderList (ListNode head) {ListNode midNode = getMidNode(head);ListNode l2 = midNode.next;null ;ListNode lastHead = reverse(l2);public ListNode getMidNode (ListNode head) {ListNode slow = head;ListNode fast = head;while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null ) {return slow;public ListNode reverse (ListNode head) {ListNode pre = null , cur = head;while (cur != null ){ListNode nxt = cur.next;return pre;public void merge (ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {ListNode cur1 = l1;ListNode cur2 = l2;while (cur1 != null && cur2 != null ) {
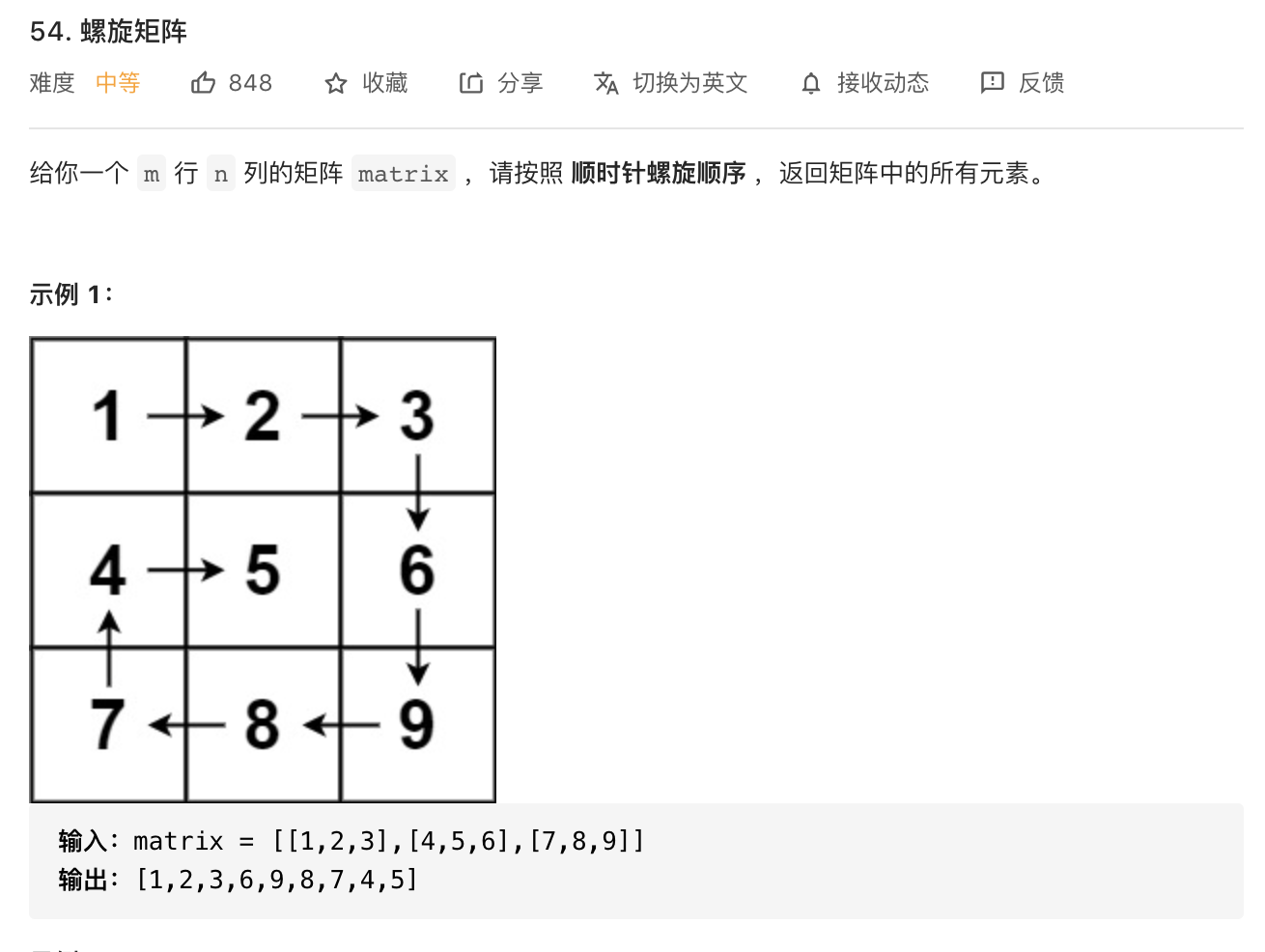
34.螺旋矩阵(技巧)
image-20210819230301483
分层地去遍历,先遍历外圈,再缩小遍历第二圈。
使用四个界限来表示上下左右
image-20210819230428531
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 class Solution {public List<Integer> spiralOrder (int [][] matrix) {int m = matrix.length;int n = matrix[0 ].length;int left = 0 , right = n - 1 ;int top = 0 , down = m - 1 ;new ArrayList <>();while (true ) {for (int i = left; i <= right; i++) {if (top > down) break ;for (int i = top; i <= down; i++) {if (left > right) break ;for (int i = right; i >= left; i--) {if (top > down) break ;for (int i = down; i >= top; i--) {if (left > right) break ;return res;
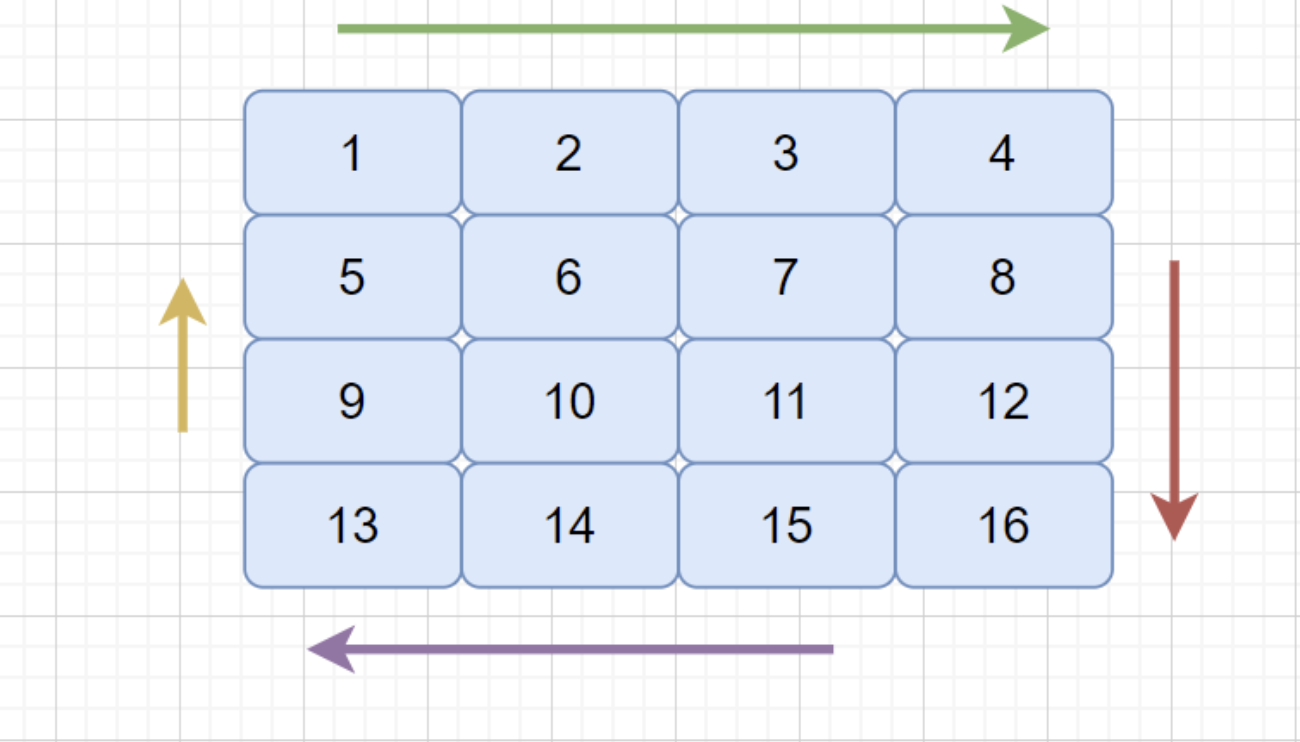
35.合并区间(排序)
image-20210821150518096
思路即按照数组第一维进行排序,然后判断当前数组第一位与前一数组最后一位的关系,如果可以合并,再看当前数组第二位和当前最大end的关系。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution {public int [][] merge(int [][] intervals) {int m = intervals.length;int n = intervals[0 ].length;if (m == 0 ) return null ;0 ] - o2[0 ]);int start = intervals[0 ][0 ];int end = intervals[0 ][1 ];int []> list = new ArrayList <>();int k = 0 ;for (int i = 1 ; i < m; i++) {if (intervals[i][0 ] <= end && intervals[i][1 ] > end) {1 ];else if (intervals[i][0 ] > end){new int []{start, end});0 ];1 ];new int []{start, end});return list.toArray(new int [list.size()][]);
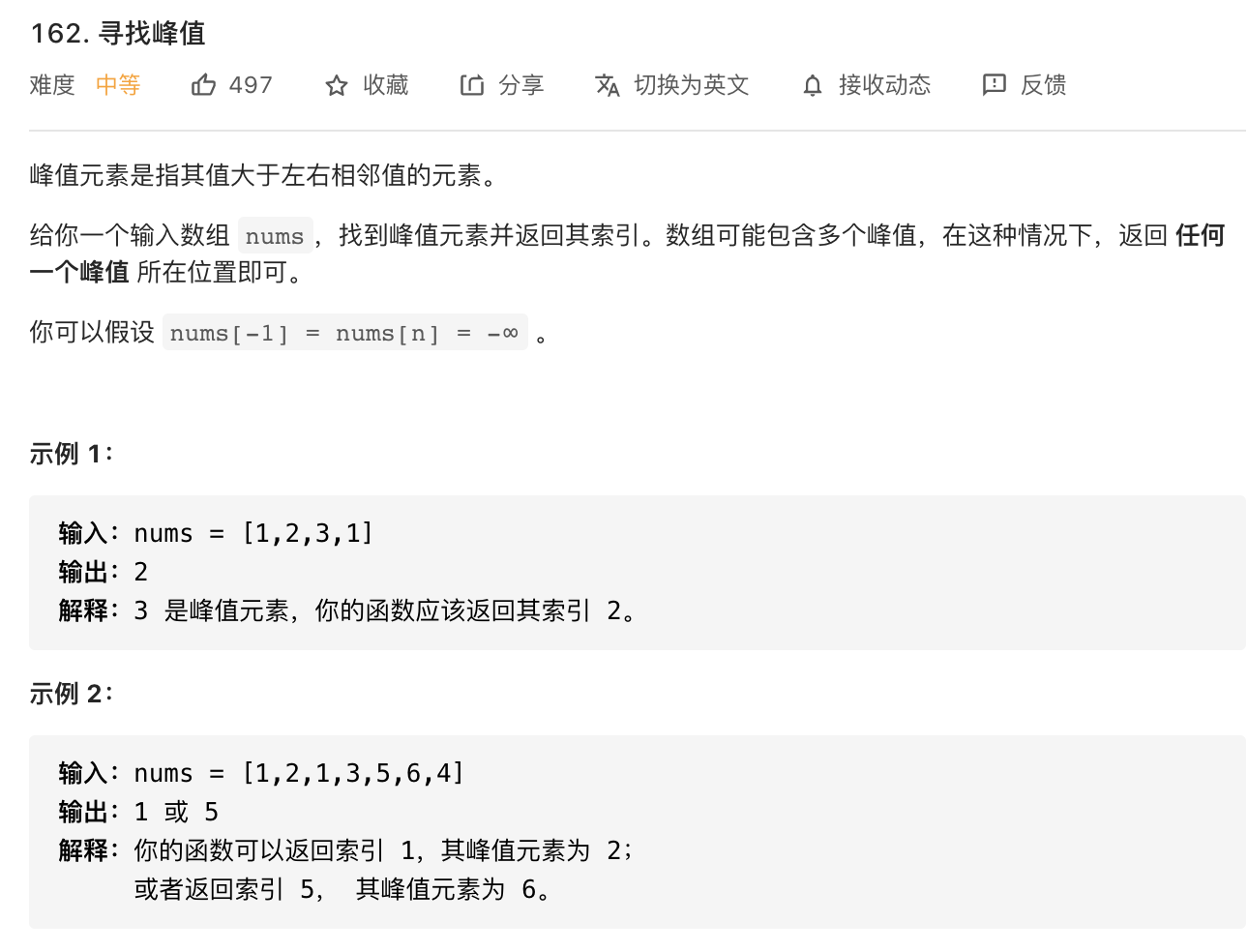
36.寻找峰值
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-peak-element/
image-20210821151156181
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution {public int findPeakElement (int [] nums) {if (nums.length==1 ) return 0 ;int l=0 ,r=nums.length-1 ; while (l<r){int mid=(l+r)/2 ; if (nums[mid]>nums[mid+1 ]){else if (nums[mid]<nums[mid+1 ]){1 ;return l;
37.二叉树最近公共祖先(递归)
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/
image-20210821152325594
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution {public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (root == null || p == null || q == null ) {return null ;if (root == p || root == q) {return root;TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p, q);TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p , q);if (left != null && right != null ) return root;if (left != null ) return left;if (right != null ) return right;return null ;
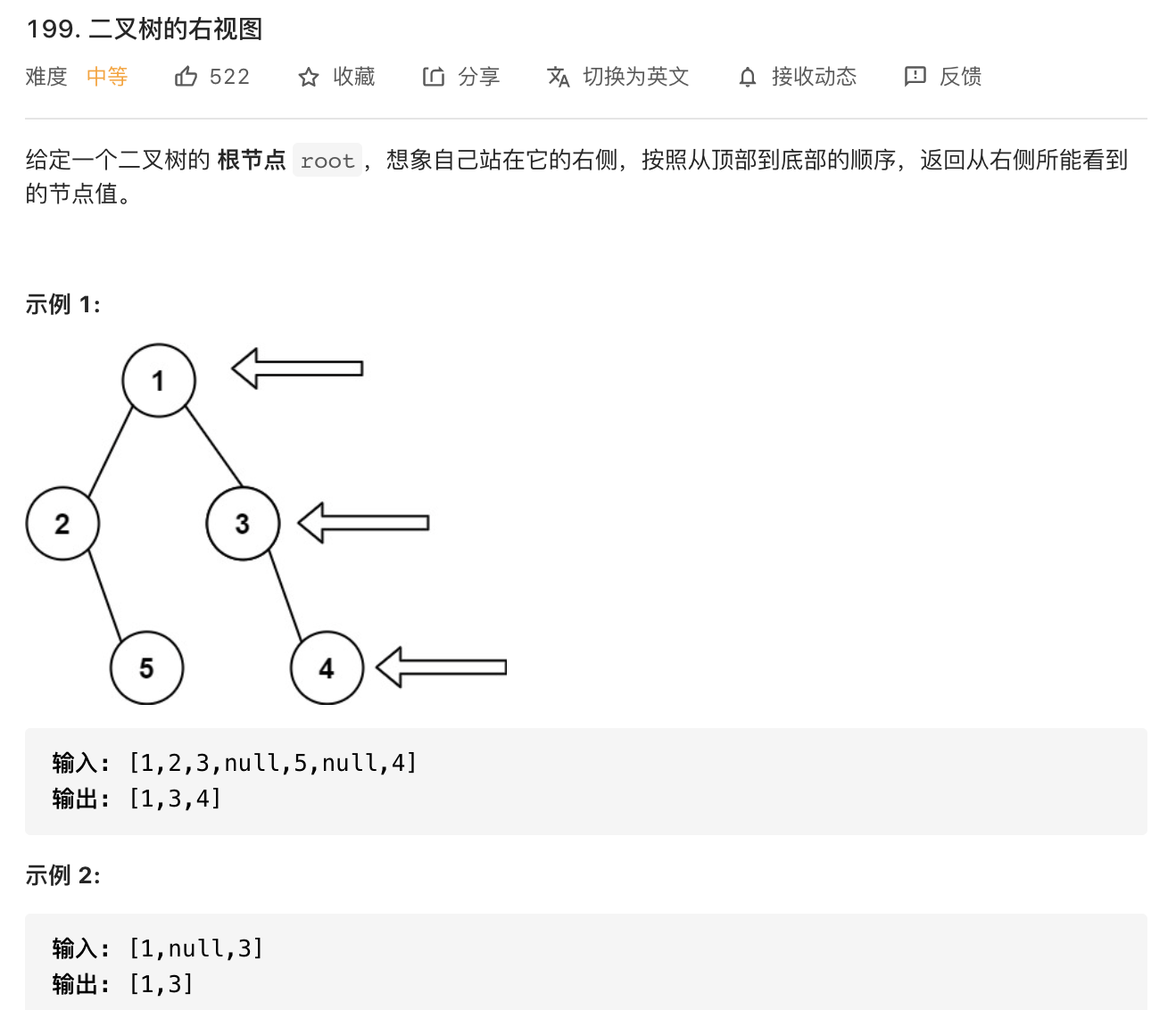
38.二叉树的右视图(层序遍历)
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-right-side-view/
image-20210822183850014
最开始是想dfs进行递归右子树,然后提交后发现如果左子树比右子树深的话,左子树下面的部分也应该看得到,就进行不下去了。
后来看到评论说层序遍历,每次把最后一个元素添加即可。看到后恍然大悟的感觉,感觉很妙,思维转化能力非常重要。顺便回顾层序遍历的代码。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();public List<Integer> rightSideView (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) {return res;return res;public void order (TreeNode root) {new LinkedList <>();while (!q.isEmpty()) {new ArrayList <>();int curSize = q.size();for (int i = 0 ; i < curSize; i++) {TreeNode temp = q.poll();if (temp.left != null ) {if (temp.right != null ) {1 ));
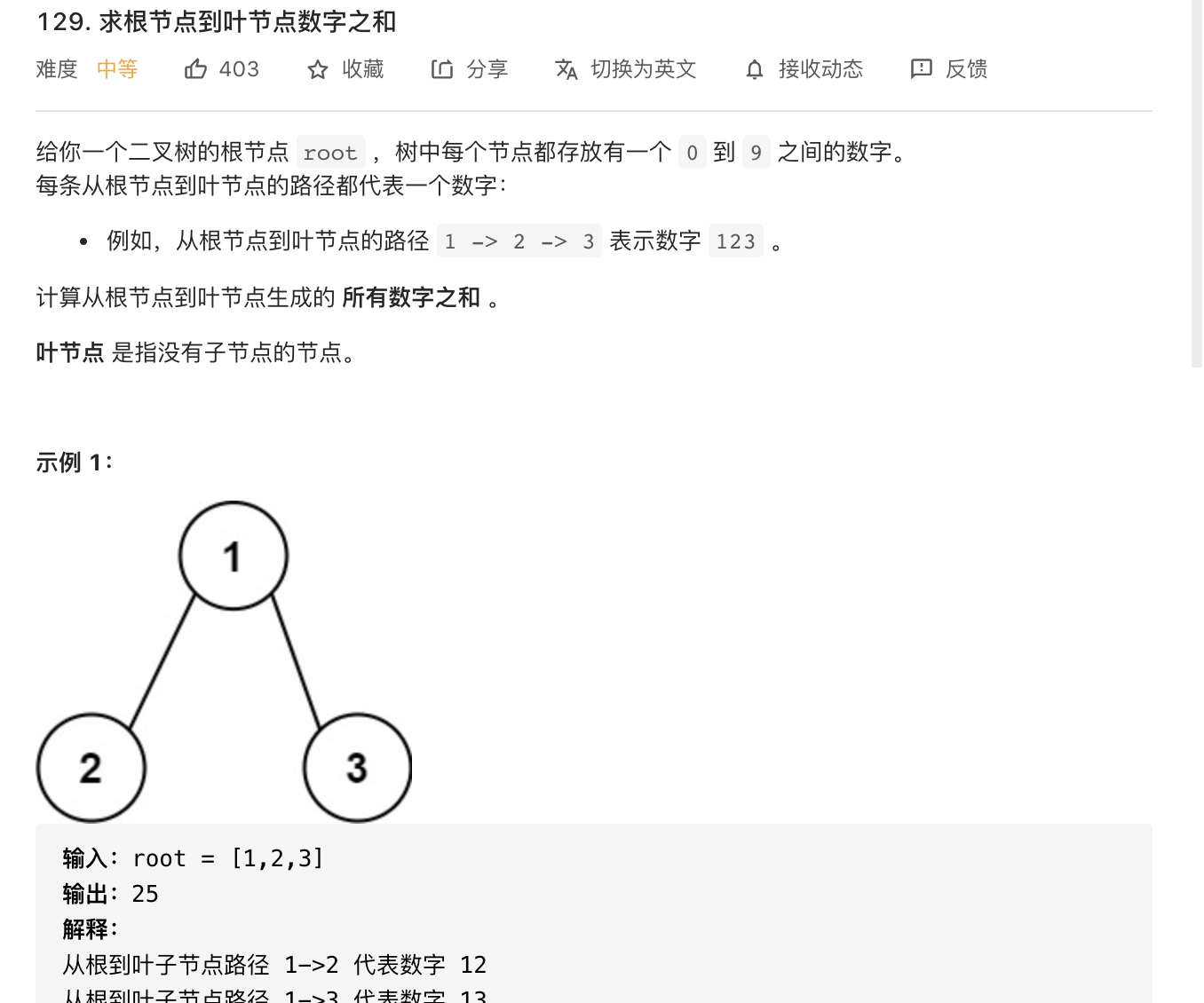
39.求根节点到叶子结点数字之和(递归)
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sum-root-to-leaf-numbers/
image-20210822213022299
dfs递归,判断当为叶子结点的时候加到sum上。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution {int sum = 0 ;public int sumNumbers (TreeNode root) {0 );return sum;public void dfs (TreeNode root, int curNum) {if (root == null ) {return ;if (root.left == null && root.right == null ) {10 + root.val;10 + root.val);10 + root.val);
40.对角线遍历(规律技巧)
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/diagonal-traverse/
image-20210822221741586
方法比较笨拙,即进行循环,先右走一步,再一直往坐下走,再下走一步,再一直往右上走,如果遇到右边界则往下走一步,遇到下边界则往右走一步。提交后只击败了9%
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 class Solution {public int [] findDiagonalOrder(int [][] mat) {int m = mat.length;int n = mat[0 ].length;if (m == 0 || n == 0 ) {return new int [0 ];int [] res= new int [m * n];int idx = 0 ;int i = 0 , j = 0 ;while (true ) {if (i == m -1 && j == n -1 ) {break ;if (i < m -1 && j == n - 1 ) {" " + j);if (j < n - 1 ) {while (i < m - 1 && j > 0 ) {if (j < n -1 && i == m - 1 ) {if (i < m - 1 ) {while (i > 0 && j < n - 1 ) {" " + j);return res;
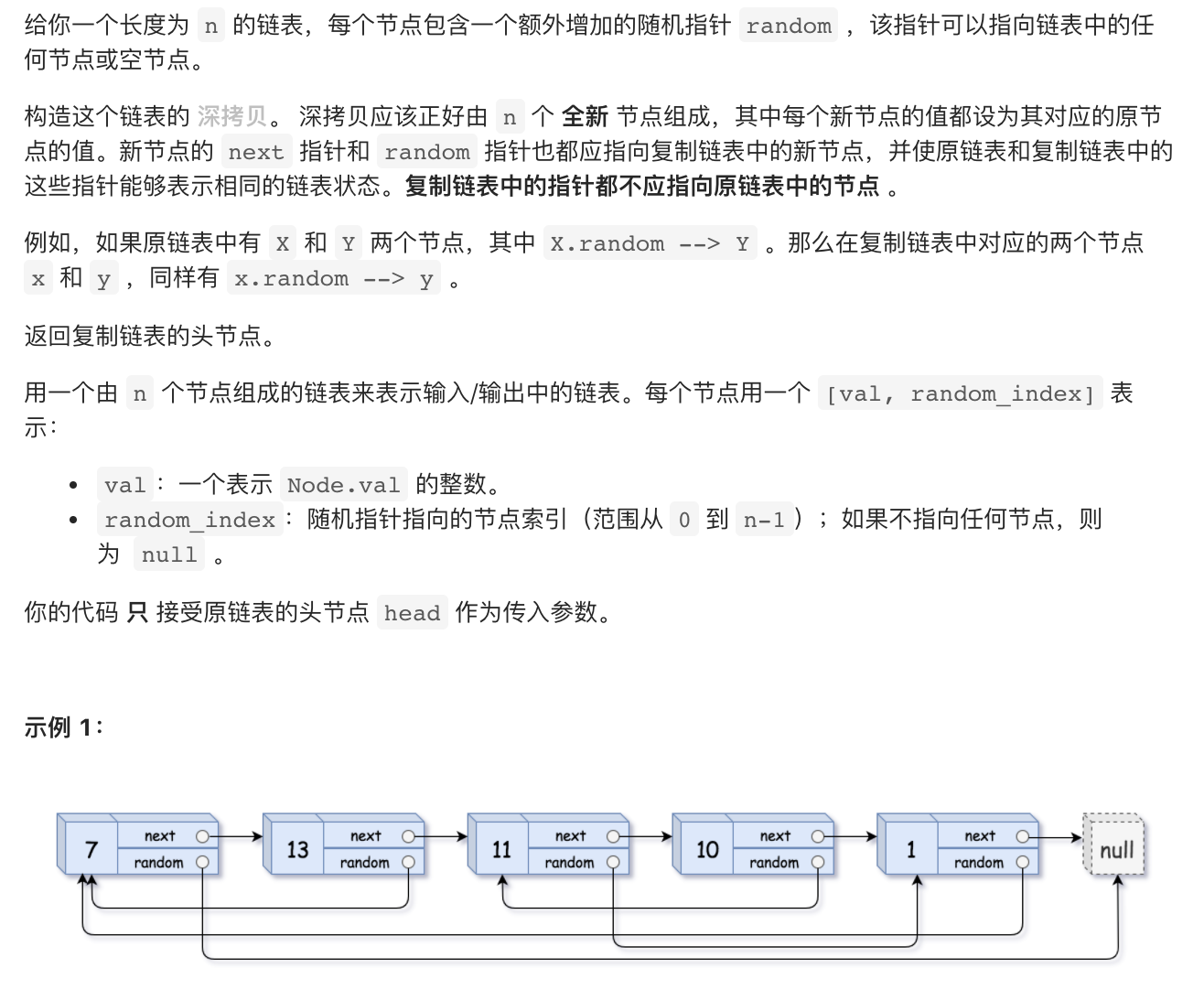
41.复制带随机指针的链表(哈希表)
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/
image-20210822231643557
题目意思即给一个单向链表,但是多了一个random指针,我们需要重新创建一个相同的单链表,每个节点都是新的节点,并且指向和原来保持一致。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 class Solution {public Node copyRandomList (Node head) {new HashMap <>();Node dummy = new Node (0 );Node oldCur = head;Node newCur = dummy;while (oldCur != null ) {Node temp = new Node (oldCur.val);while (oldCur != null ) {Node node = map.get(oldCur.random);if (node != null ) {else {null ;return dummy.next;
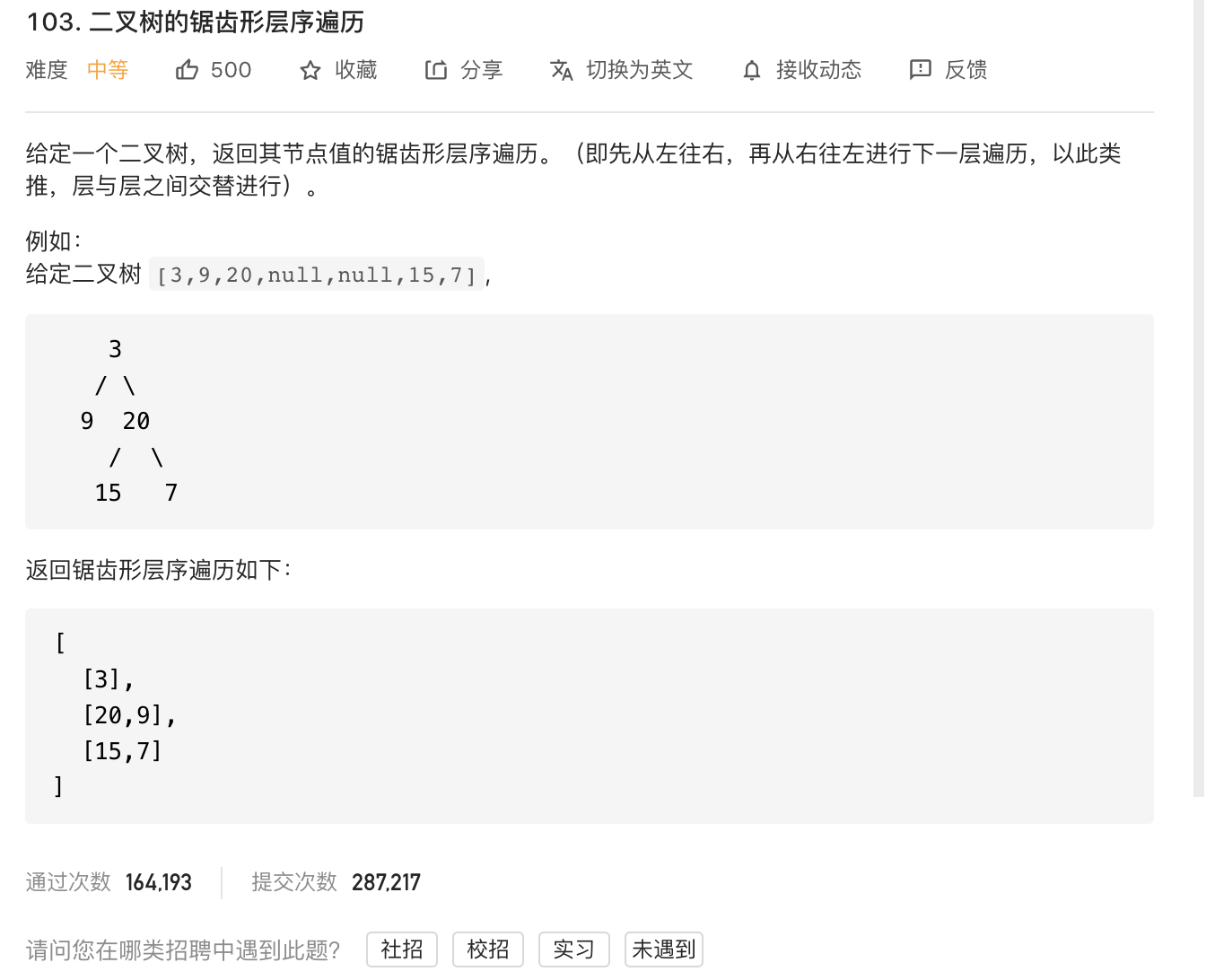
42. 二叉树锯齿层序遍历
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-zigzag-level-order-traversal/
image-20210823155318167
isOrderLeft控制加到双端队列的头部还是尾部。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder (TreeNode root) {new LinkedList <List<Integer>>();if (root == null ) {return ans;new LinkedList <TreeNode>();boolean isOrderLeft = true ;while (!q.isEmpty()) {new LinkedList <Integer>();int size = q.size();for (int i = 0 ; i < size; ++i) {TreeNode curNode = q.poll();if (isOrderLeft) {else {if (curNode.left != null ) {if (curNode.right != null ) {new LinkedList <Integer>(list));return ans;
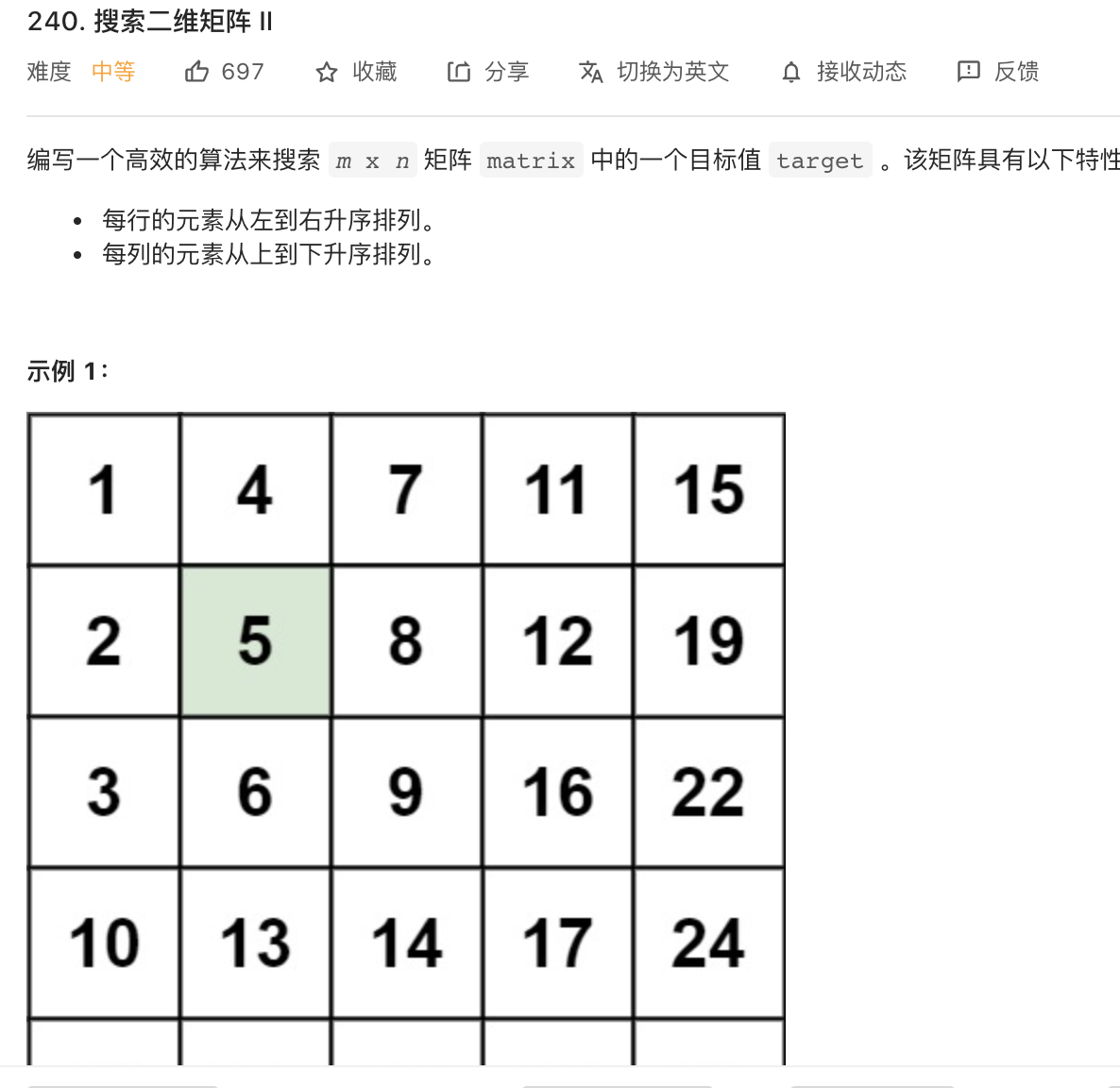
43. 搜索二维矩阵|| (技巧)
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/search-a-2d-matrix-ii/
image-20210823163054226
发现到左下角的元素比上面所有元素大,比右边所有元素小,所以以左下角为标准来不断缩小矩阵。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution {public boolean searchMatrix (int [][] matrix, int target) {int m = matrix.length;int n = matrix[0 ].length;if (m <= 0 || n <= 0 ) {return false ;int i = m - 1 ;int j = 0 ;while (i >= 0 && j < n) {if (matrix[i][j] == target) {return true ;if (matrix[i][j] < target) {else {return false ;
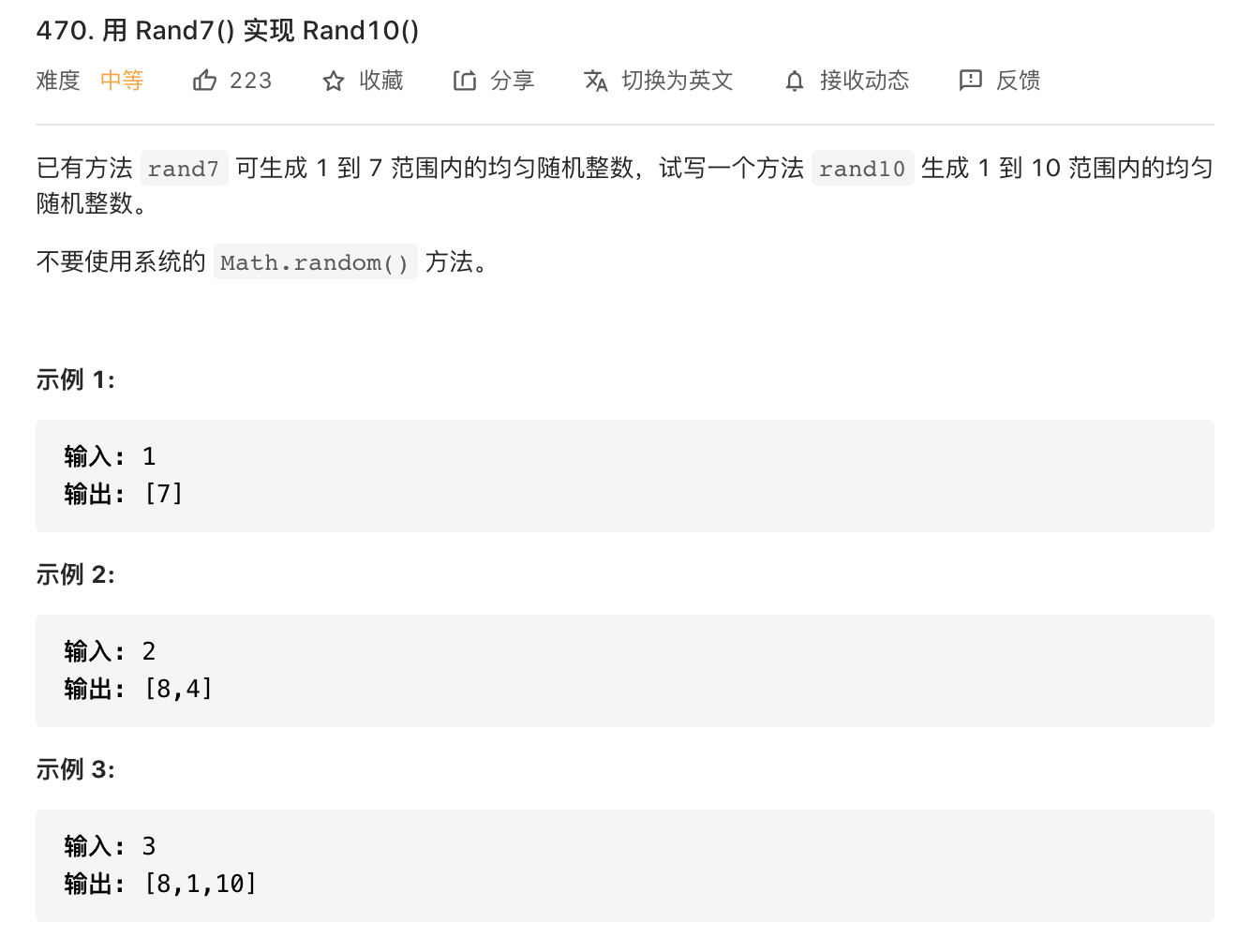
44.用rand7()实现rand10()
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/implement-rand10-using-rand7/
image-20210823212951396
第一种方法:十分之一 = 二分之一 * 五分之一。
二分之一:当a为奇或者为偶,那么rand7怎么实现?当ran7 =
7的时候,重新rand即可保证落在1-6之间,那么奇偶都为1/2.
五分之一:当b大于5的时候,重新rand即可保证落在1-5之间。
概率相乘:奇数的时候返回1-5,偶数的时候返回6-10,这样保证每个数概率都是1/10.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution extends SolBase {public int rand10 () {int a = rand7();int b = rand7();while (a == 7 ) {while (b > 5 ) {return ((a & 1 ) == 0 ? 0 : 5 ) + b;
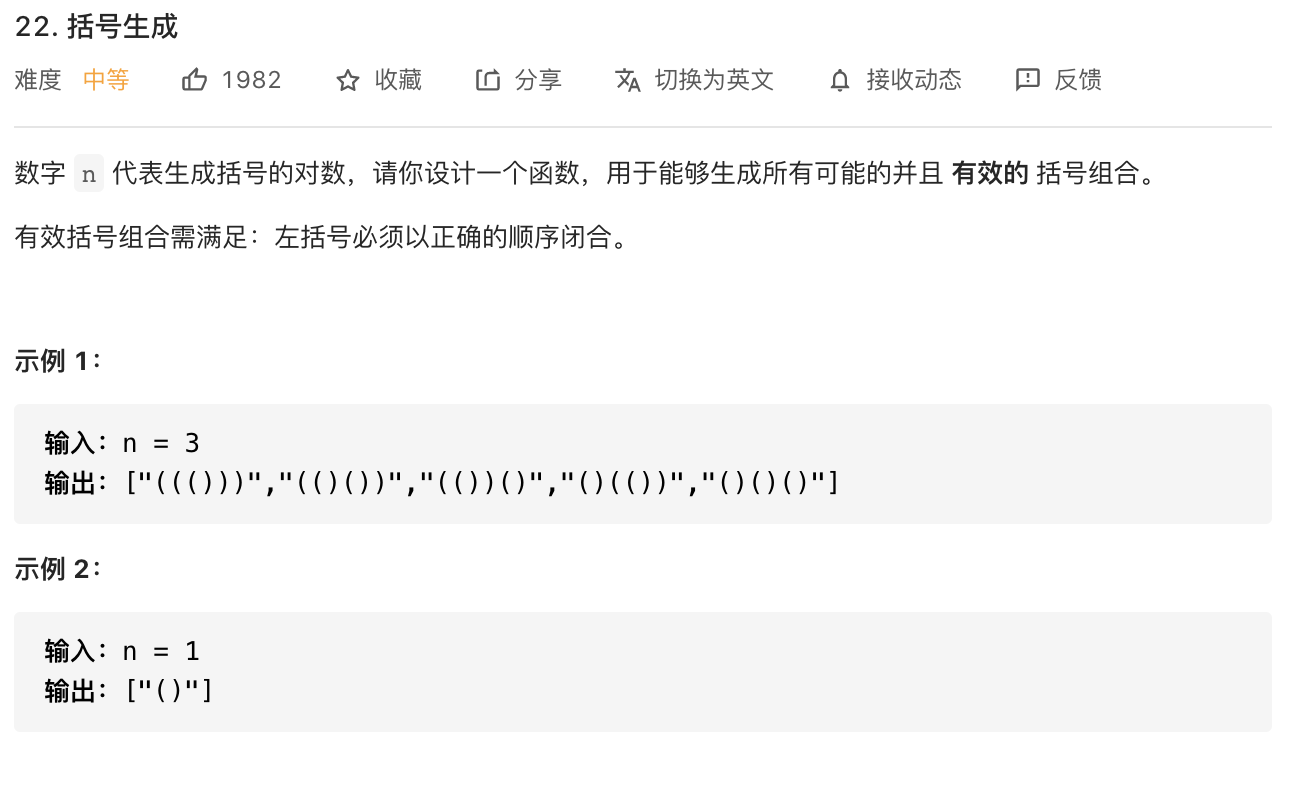
45.括号生成(DFS)
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/generate-parentheses/
image-20210824171053663
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();public List<String> generateParenthesis (int n) {"" );return list;public void dfs (int left, int right, String res ) {if (left == 0 && right == 0 ) {return ;if (left > 0 ) {1 , right, res + "(" );if (right > left) {1 , res + ")" );
46.路径总和||(DFS)
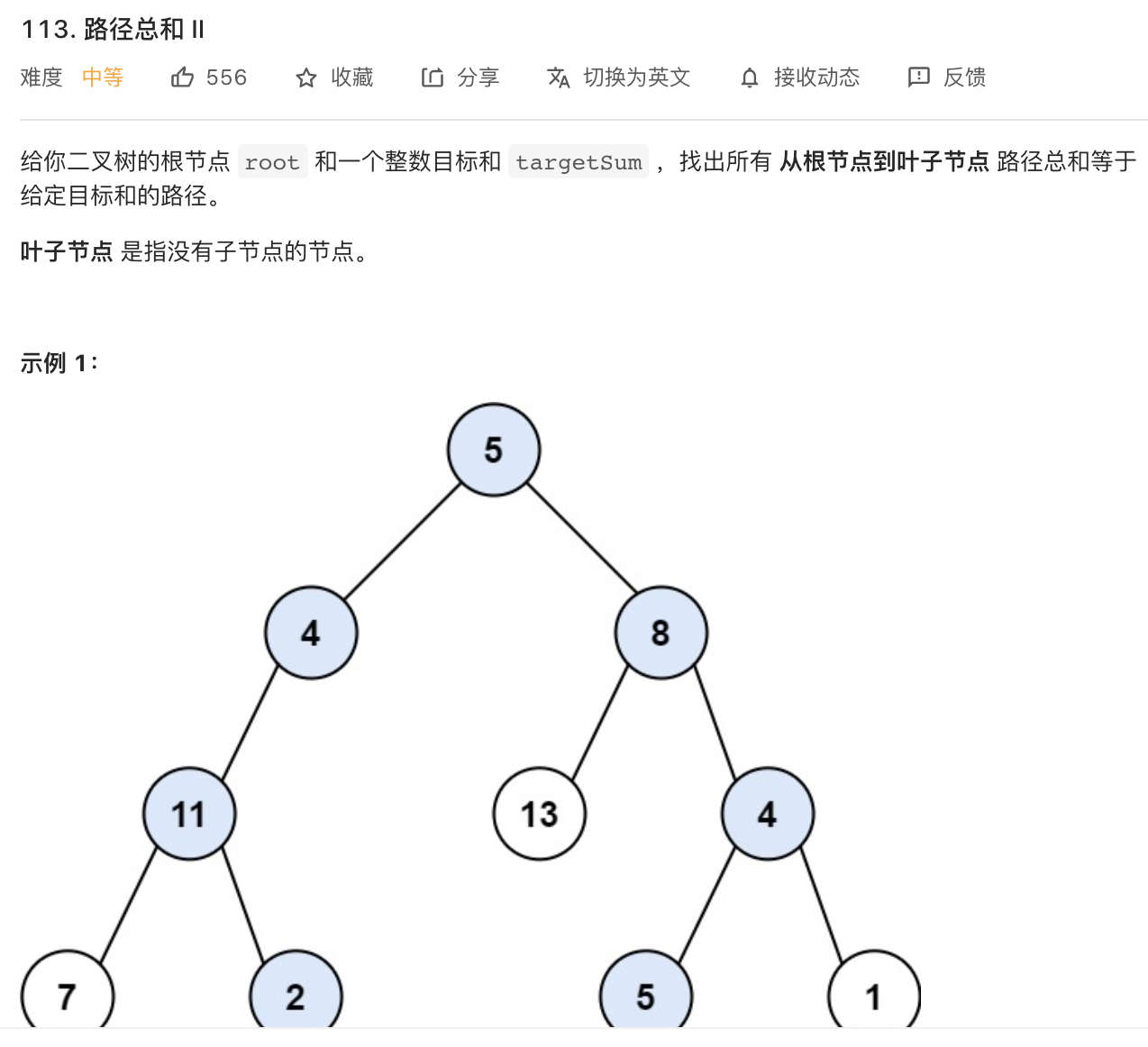
image-20210824174958415
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();public List<List<Integer>> pathSum (TreeNode root, int targetSum) {0 , new LinkedList <Integer>());return res;public void dfs (TreeNode root, int targetSum, int curSum, LinkedList<Integer> track) {if (root == null ) return ;if (root.left == null && root.right == null && targetSum == curSum + root.val) {new LinkedList (track));return ;
47.快排与归并排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 public void quickSort (int [] nums, int left, int right) {if (left >= right) return ;int i = left;int j = right;int base = nums[left];while (i < j) {while (i < j && nums[j] >= base) {while (i < j && nums[i] <= base) {1 );1 , right);public void mergeSort (int [] nums, int left, int right) {int mid = (left + right) / 2 ;if (left < right) {1 , right);public void merge (int [] nums, int left, int mid, int right) {int [] temp = new int [right - left + 1 ];int i = left;int j = mid + 1 ;int k = 0 ;while (i <= mid && j <= right) {if (nums[i] < nums[j]) {else {while (i <= mid) {while (j <= right) {for (int m = 0 ; m < temp.length; m++) {
48.零钱兑换||(动态规划)
image-20210825174408582
完全背包的组合问题。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution {public int change (int amount, int [] coins) {int n = coins.length;if (n == 0 ) return 0 ;int [] dp = new int [amount + 1 ];0 ] = 1 ;for (int coin : coins) {for (int i = 0 ; i+coin <= amount; i++) {return dp[amount];
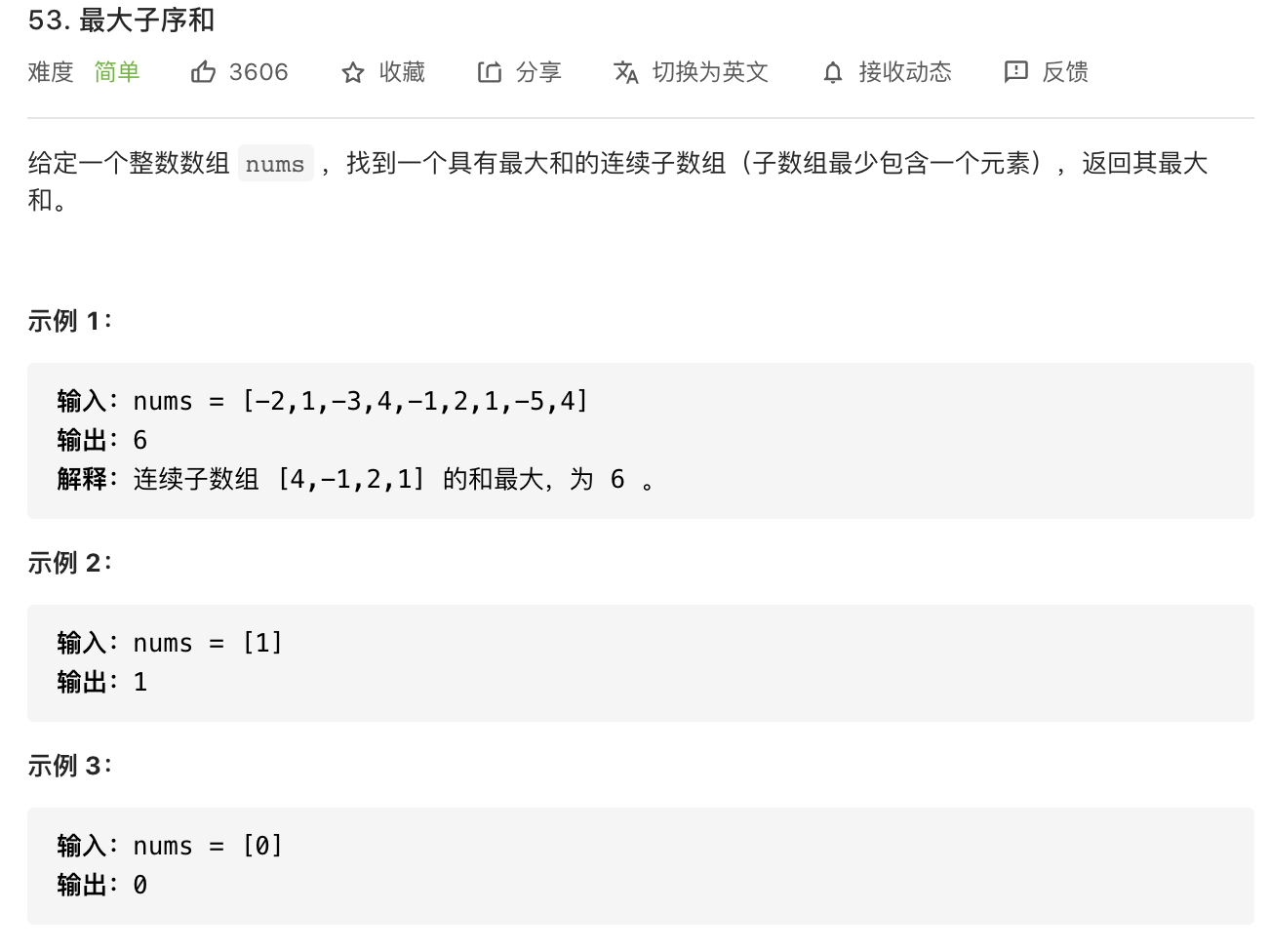
49. 最大子序和(动态规划)
image-20210825223733118
class Solution {public int maxSubArray (int [] nums) {if (nums.length == 0 ) return 0 ;int [] dp = new int [nums.length];int res = nums[0 ];0 ] = nums[0 ];for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length; i++) {1 ] + nums[i], nums[i]);return res;
50.组合总数(DFS)
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum/
image-20210825225633075
回溯法,首先先对数组进行排序,便于之后进行剪枝(大于target直接break)。
对于非重复,之前是对track进行排序然后看是否存在,存在就不添加,非常消耗性能,且慢。
可以使用begin来表示下一次递归从哪里开始,由于可以重复使用,所以begin
= i。同理如果每个元素只能使用一次,那么begin就 = i+1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum (int [] candidates, int target) {new LinkedList <>();0 , track,0 );return res;public void backTrack (int [] candidates, int target,int curSum,LinkedList<Integer> track, int begin) {if (curSum > target) {return ;if (target == curSum) {new LinkedList (track));return ;for (int i = begin; i < candidates.length; i++) {if (candidates[i] > target) break ;
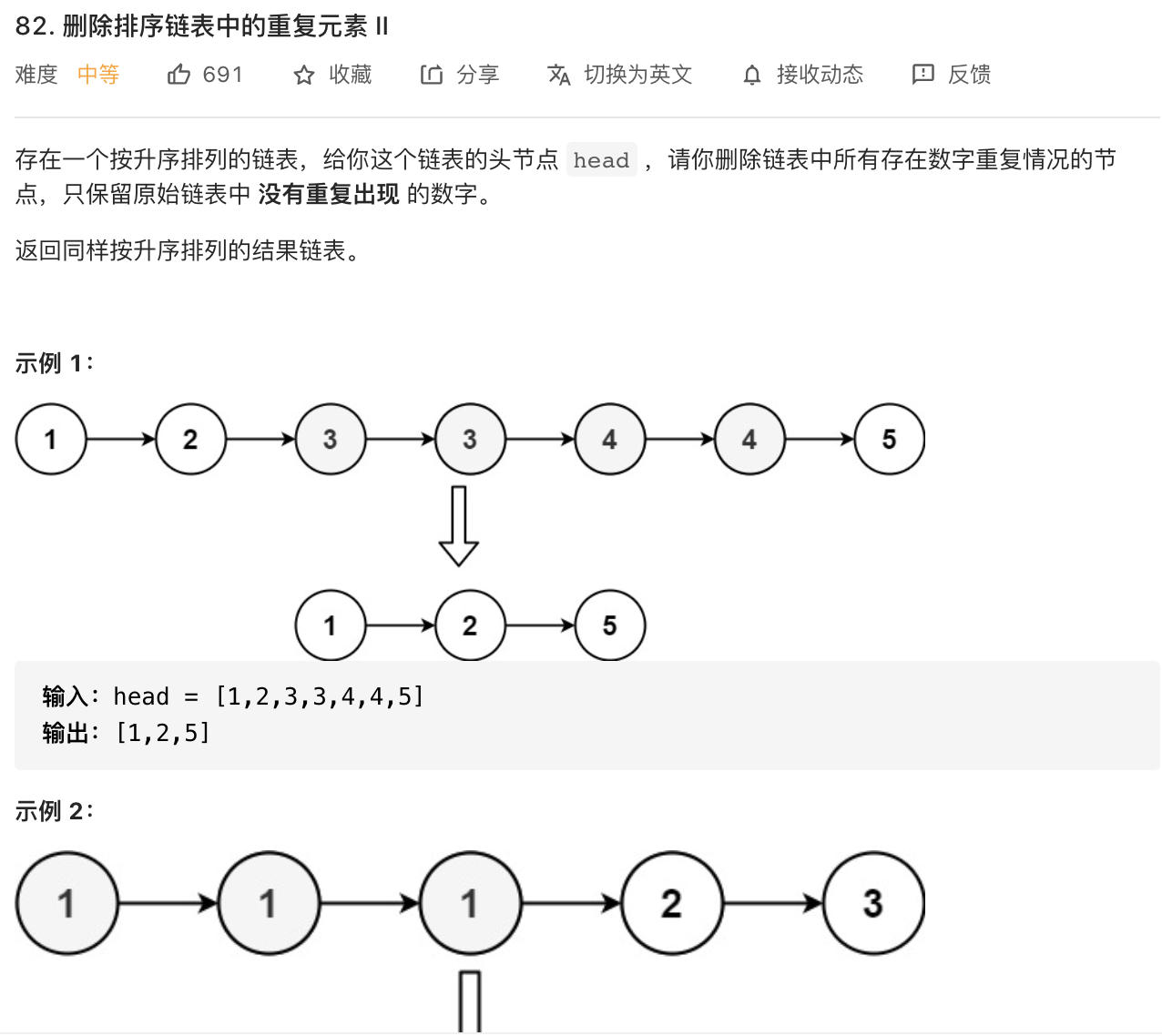
51.删除排序链表中重复的元素||(双指针)
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list-ii/
image-20210827155609093
思路即用三个变量pre、cur、next进行遍历。
当cur.val == next.val的时候,next = next.next;
然后把pre.next = next;
如果不重复,则都往后走
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution {public ListNode deleteDuplicates (ListNode head) {if (head == null ) return null ;ListNode dummy = new ListNode (0 );ListNode pre = dummy;ListNode cur = head;ListNode next = cur.next;while (cur != null && next != null ) {if (next != null && cur.val != next.val) {continue ;while (next != null && cur.val == next.val){if (cur == null ) break ;return dummy.next;
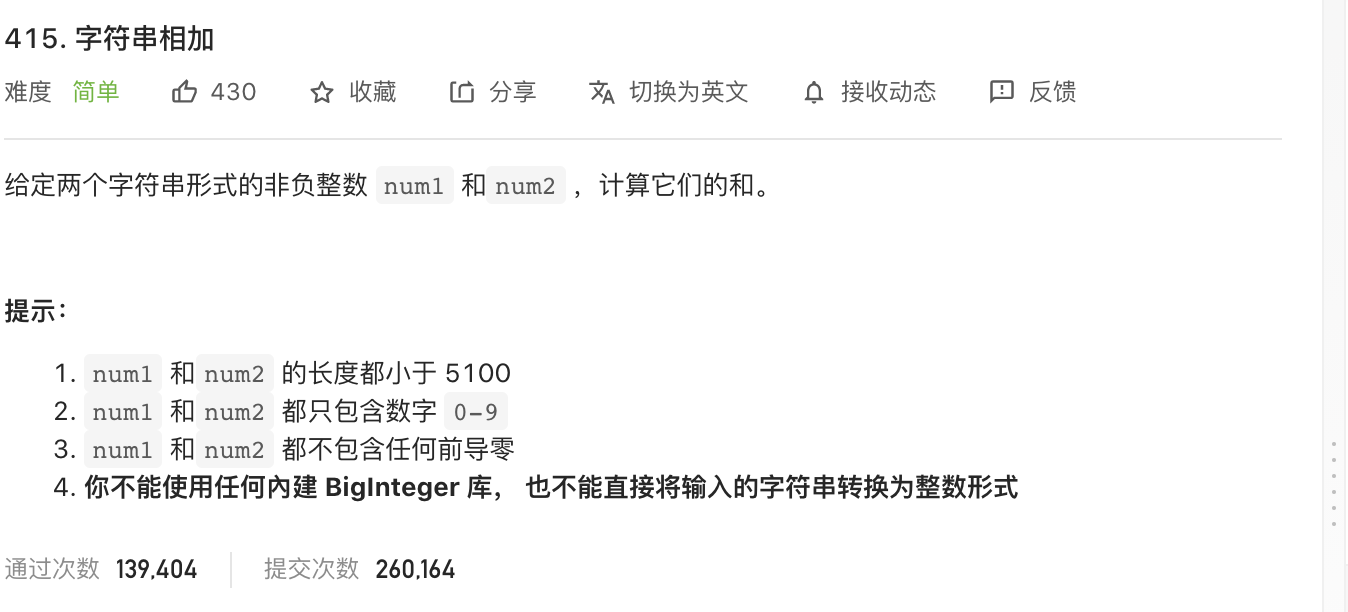
52.字符串相加(大数加法)
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/add-strings/
image-20210827163023769
大数加法,不能将字符串转成数字然后相加,会导致溢出。
所以根据小学学的竖式加法,从后往前一位一位地相加,所以重点考虑进位。
如果两个数相加 >10,进位
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution {public String addStrings (String num1, String num2) {StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder ("" );int i = num1.length() - 1 , j = num2.length() - 1 , carry = 0 ;while (i >= 0 || j >= 0 ){int n1 = i >= 0 ? num1.charAt(i) - '0' : 0 ;int n2 = j >= 0 ? num2.charAt(j) - '0' : 0 ;int tmp = n1 + n2 + carry;10 ;10 );if (carry == 1 ) res.append(1 );return res.reverse().toString();
53.二叉树的完全性校验
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/check-completeness-of-a-binary-tree/
image-20210827172954082
使用BFS,一层一层地加入到队列中,如果遇到null节点,继续遍历后面节点看是否有非空节点,如果有的话就不是完全二叉树。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution {public boolean isCompleteTree (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) {return false ;new LinkedList <>();while (!q.isEmpty()) {int size = q.size();TreeNode res = q.poll();if (res != null ) {else {while (!q.isEmpty()) {if (res != null ) {return false ;return true ;
54.买卖股票的最佳时机||(贪心、DP)
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-ii/
image-20210827175233102
题目意思即给定数组,卖出后又可以买入,找到可以获得的利润最大值。
常规思维即对于【1,2,3,4,5】,在第一天买入,最后一天卖出。
但是需要判断在什么时候卖出,就会变得复杂。
使用贪心思想,只要今天比昨天大就卖出,然后今天又买入。
依次循环,使用贪心思想就得到了最大的利润。
class Solution {public int maxProfit (int [] prices) {int res = 0 ;for (int i = 1 ; i < prices.length; i++) {if (prices[i] > prices[i - 1 ]) {1 ];return res;
55.最长连续序列
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-consecutive-sequence/
image-20210829214115973
题目要求O(n)复杂度,所以不能进行排序,通常我们用空间去换时间,或者时间去换空间。
这道题我们用哈希表来解决。
解决思路即:1、将每个元素加入到哈希Set中。
2、遍历每个元素,遍历一个删除一个。
3、如果删除成功,那么继续删除比大依次大1的元素,记录删除的个数,然后删除比他依次小1的个数,记录删除个数。如第一个示例,遍历到4的时候,删除4,然后依次删除掉3,2,1,由于没有5,所以与4相临的都删除完了,再记录删除的长度即相临的个数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution {public int longestConsecutive (int [] nums) {if (nums.length <= 0 ) {return 0 ;new HashSet <>();for (int num : nums) {int longest = 0 ;for (int num : nums) {if (set.remove(num)) {int left = 0 ;int right = 0 ;int leftNum = num;int rightNum = num;while (set.remove(leftNum - 1 )) {while (set.remove(rightNum + 1 )) {1 );return longest;
56.航班预订统计(差分数组)
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/corporate-flight-bookings/
image-20210831231401000
差分数组:第i项是第i-1项-第i项得到,反之依次累加就可以得到原数组。
对第一个示例:
[10,0 , -10, 0, 0]
[10, 20, -10, -20, 0]
[10, 45, -10, -20, 0]
即差分数组。
前缀和累加起来
[10, 55, 45, 25, 25],得到最终结果。
class Solution {public int [] corpFlightBookings(int [][] bookings, int n) {int [] nums = new int [n];for (int [] booking : bookings) {0 ] - 1 ] += booking[2 ];if (booking[1 ] < n) {1 ]] -= booking[2 ];for (int i = 1 ; i < n; i++) {1 ];return nums;
57.前序中序建立二叉树(递归,字节二面)
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-preorder-and-inorder-traversal/
image-20210909105705751
字节二面的算法题,之前试着做过这个题,但是当时有些烦躁就没做完,心里赌他不会考,结果考到了,赌狗biss。
正常思维还是很容易:前序序列第一个是root,然后去中序序列找root的索引,左边的都是左子树,右边的都是右子树。
然后依次递归,先构建左子树,前序序列第二个是根节点,然后去中序序列左边区域找root索引。
对于任意一颗树而言,前序遍历的形式总是
[ 根节点, [左子树的前序遍历结果], [右子树的前序遍历结果] ]
即根节点总是前序遍历中的第一个节点。而中序遍历的形式总是
[ [左子树的中序遍历结果], 根节点, [右子树的中序遍历结果] ]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 class Solution {new HashMap <>();public TreeNode buildTree (int [] preorder, int [] inorder) {for (int i = 0 ; i < inorder.length; i++) {int n = preorder.length;return build(preorder, inorder, 0 , n - 1 , 0 , n - 1 );public TreeNode build (int [] preorder, int [] inorder, int preLeft, int preRight, int inLeft, int inRight) {if (preLeft > preRight) {return null ;int preOrderRootIdx = preLeft;int inOrderRootIdx = map.get(preorder[preOrderRootIdx]);TreeNode root = new TreeNode (preorder[preOrderRootIdx]);int leftSize = inOrderRootIdx - inLeft;1 , preLeft + leftSize, inLeft, inOrderRootIdx - 1 );1 , preRight, inOrderRootIdx + 1 , inRight);return root;
58.二叉树的最大宽度(BFS)
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-width-of-binary-tree/
image-20210909150732610
首先想到的是层序遍历,如果为null也存入进去,最后从后往前和从前往后第一个遍历到的非null节点的索引相减即该层的宽度。
但是实施的时候出现了问题:1、null节点也添加,每层null的左右孩子节点也添加null,怎么判断是否结束?只有遍历每层都是null的时候说明树到底了,时间复杂度高,且如果树缺的很多,那么会添加很多null节点。
2、计算宽度的时候需要从后往前和从前往后,节点数只有一个的时候这个边界需要额外判断,且空间复杂度比较高,时间复杂度也比较高。
联想二叉树排列的性质,如果根节点在该层第i个,那么他左孩子节点在下一层的第2*i个,
右孩子节点在下一层的第2*i +
1个。这样遍历每个节点的时候给左右孩子节点标记一个pos,该层遍历完后用最后一个节点的pos-第一个节点的pos即可得到最大宽度。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 class Solution {public int widthOfBinaryTree (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) return 0 ;return bfs(root);public int bfs (TreeNode root) {int max = 1 ;new LinkedList <>();new TempNode (root,0 , 0 ));int curDepth = 0 , left = 0 , res = 0 ;while (!q.isEmpty()) {TempNode a = q.poll();if (a.node != null ) {new TempNode (a.node.left,a.depth + 1 , a.pos * 2 ));new TempNode (a.node.right,a.depth + 1 , a.pos * 2 + 1 ));if (curDepth != a.depth) {1 );return res;class TempNode {int depth;int pos;public TempNode (TreeNode node, int depth, int pos) {this .node = node;this .depth = depth;this .pos = pos;
59.二叉树展开为链表(递归)
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/flatten-binary-tree-to-linked-list/
image-20210909152627066
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution {public void flatten (TreeNode root) {TreeNode pre = null ;public void dfs (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) {return ;null ;
59.平衡二叉树(递归)
image-20210909174543593
对于root,递归函数返回子树最大高度,如果最大高度之差超过1就将res置为false,最后直接返回res
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution {boolean res = true ;public boolean isBalanced (TreeNode root) {0 );return res;public int dfs (TreeNode root, int level) {if (!res) {return 0 ;if (root == null ) {return level;int left = dfs(root.left, level + 1 );int right = dfs(root.right, level + 1 );if (Math.abs(right - left) > 1 ) {false ;return Math.max(left, right);
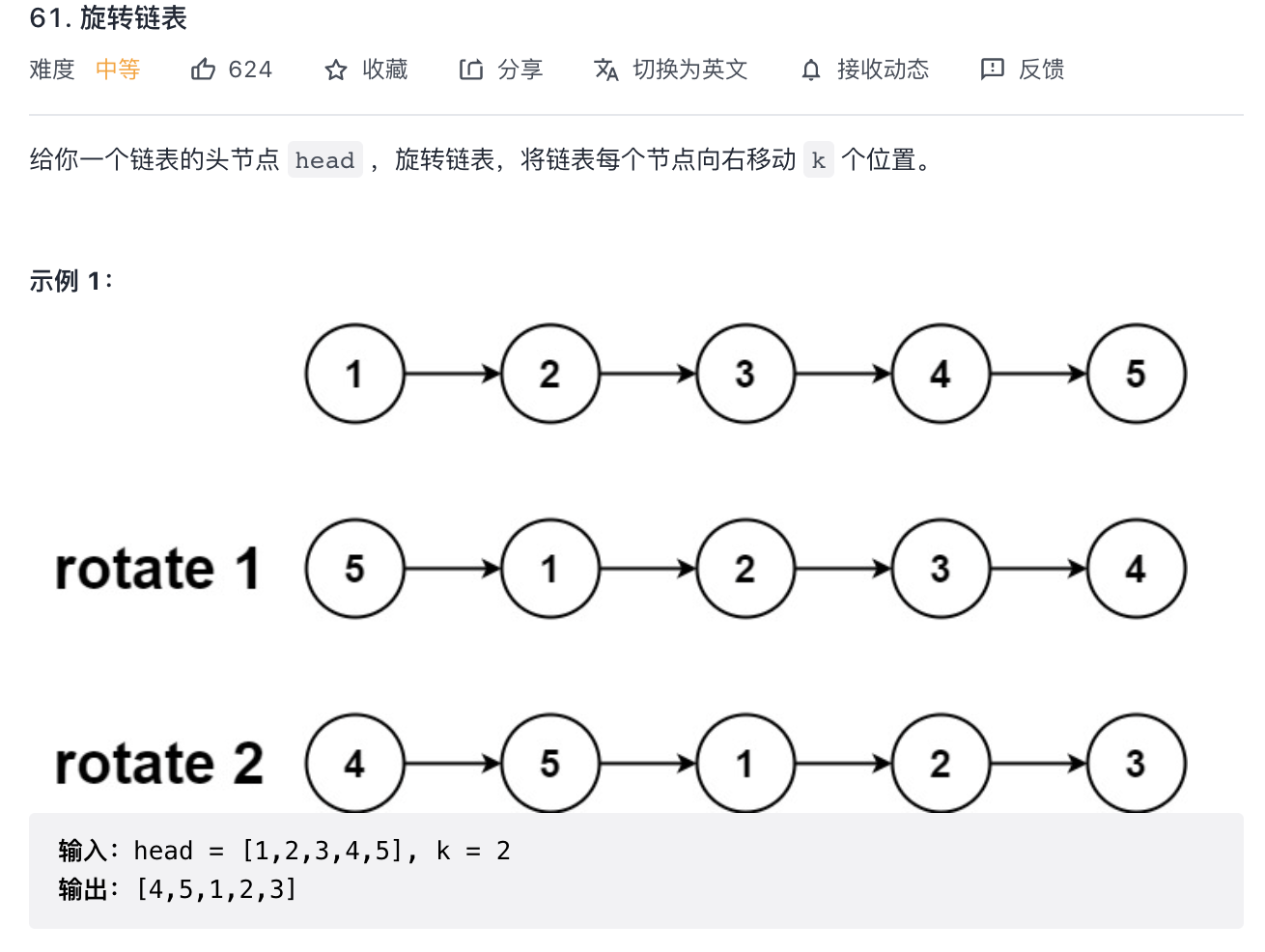
60.旋转链表(链表)
image-20210910151236993
向右移动k个位置,即将后k个节点接到head前面
如1 2 3 4 5, k=2
即将后两个节点4 5 接到1前面即可。
对于k > 链表长度,进行取模。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 class Solution {public ListNode rotateRight (ListNode head, int k) {if (head == null || head.next == null ) return head;int count = getCount(head);if (k == 0 ) return head;return getApartNode(head,k);public ListNode getApartNode (ListNode head, int k) {ListNode pre = head;ListNode left = head;ListNode right = head;for (int i = 0 ; i < k - 1 && right.next != null ; i++) {while (right.next != null ) {null ;return left;public int getCount (ListNode head) {int count = 1 ;ListNode cur = head;while (cur.next != null ) {return count;